|
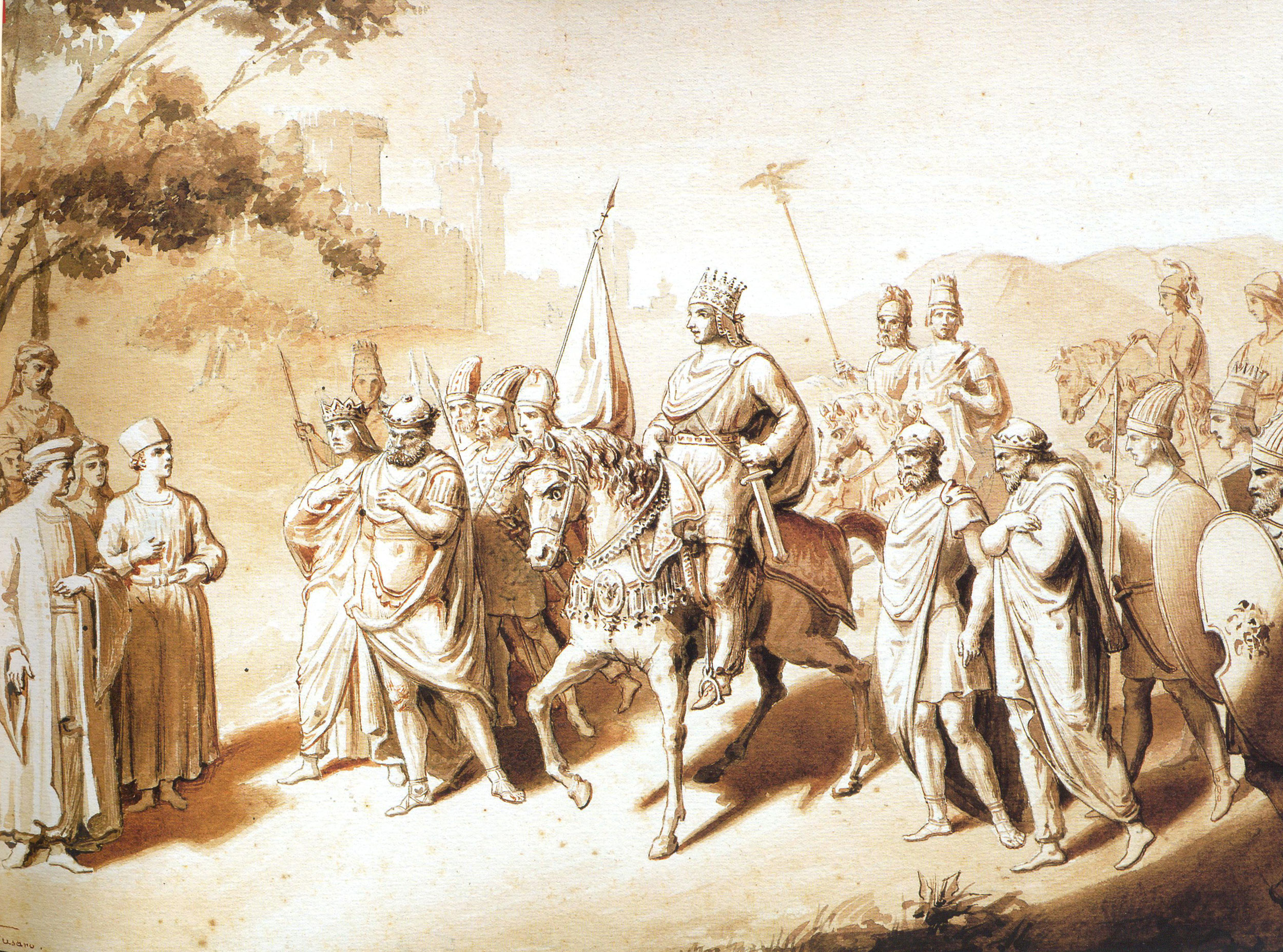
Artsruni Dynasty
The House of Artsruni (; also Ardzruni or Artsrunid) was an ancient princely and, later, royal dynasty of Armenia. Name The name ''Artsruni'' contains the ending , which is widespread in old Armenian family names. The early Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi derives the name from (, ). He implies that the Artsrunis carried standards with eagles on them and makes reference to a legend from Hadamakert (the center of the Artsrunis' home district of Aghbak) in which a bird protects a sleeping boy from the rain and sun; this is presumed to be a legend about the Artsrunis' ancestor (Sanasar, according to Manuk Abeghian) involving an eagle. James Russell notes that the eagle was a totemic animal for the Artsrunis and connects the dynasty's name with Urartian , which is attested as the name of an Urartian king's horse and may derive from Armenian . On this basis, Russell suggests that the Artsrunis may have had Urartian ancestors. Hrach Martirosyan writes that this connection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontid Dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after the collapse of the Achaemenid Empire established an independent kingdom. Later, a branch of the Orontids ruled as kings of Kingdom of Sophene, Sophene and Commagene. They are the first of the three royal dynasties that successively ruled the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (321 BC–428 AD). Although the overthrow of Orontes IV and the accession of Artaxias I to the throne of Armenia in the early 2nd century BC is traditionally treated as the start of a Artaxiad dynasty, new dynasty, Artaxias probably belonged to a branch of the Orontid dynasty. His descendants ruled Armenia until the 1st century AD. Historical background Some historians state that the Orontids were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, and sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithrobouzanes Of Sophene
Mithrobouzanes was the Orontid king of Sophene in the second half of the 2nd-century BC. His name () is the Greek transliteration of the Iranian name ''*MiΘra-bauǰ-ana-'', meaning "Delighting Mithra." The Armenian equivalent to the name would be Me(h)ruzhan (Մեհրուժան). He was the son and successor of Zariadres. Reign His reigning period is uncertain; he is attested between 188 and 163 BC. Following Mithrobouzanes' succession, his rule was contested by his brother Artaxias I, who claimed the right to rule over Sophene based on his succession rights (primogeniture). However, Mithrobouzanes managed to preserve the independence of their kingdom, due to their diplomatic (and possibly dynastic) link with Cappadocia Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir .... The next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophene
Sophene ( or , ; ) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Roman Empire. The region lies in what is now southeastern Turkey. History The region that was to become Sophene was part of the kingdom of Ararat (Urartu) in the 8th and 7th centuries BC. After unifying the region with his kingdom in the early 8th century BC, king Argishtis I of Urartu resettled many of its inhabitants in his newly built city of Erebuni (modern day Armenian capital Yerevan). Around 600 BC, Sophene became part of the newly emerged ancient Armenian Kingdom of the Orontids. This dynasty acted as satraps of Persia first under the Median Empire, later under the Achaemenid Empire. After Alexander the Great's campaigns in the 330s BC and the subsequent collapse of the Achaemenid Empire, Sophene remained part of the newly independent kingdom of Greater Armenia. In the early 3rd century BC, at the instigation of the Seleucid Empire, which was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigranes The Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great (''Tigran Mets'' in Armenian language, Armenian; 140–55 BC), was a king of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia. A member of the Artaxiad dynasty, he ruled from 95 BC to 55 BC. Under his reign, the Armenian kingdom expanded beyond its traditional boundaries and reached its peak, allowing Tigranes to claim the title Great King or King of Kings. His empire for a short time was the most powerful state to the east of the Roman Republic. Either the son or nephew of Artavasdes I of Armenia, Artavasdes I, Tigranes was given as a hostage to Mithridates II of Parthia after Armenia came under Parthian suzerainty. After ascending to the Armenian throne, he rapidly expanded his kingdom by Military Campaigns of Tigranes the Great, invading or annexing Roman and Parthian client-kingdoms. Tigran decided to ally with Mithridates VI Eupator, Mithridates VI of Pontus by marrying his daughter Cleopatra of Pontus, Cleopatra. At its height, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Markwart
Josef Markwart (originally spelled Josef Marquart: December 9, 1864 in Reichenbach am Heuberg – February 4, 1930 in Berlin) was a German historian and orientalist. He specialized in Turkish and Iranian Studies and the history of the Middle East. The ''Encyclopædia Iranica'' wrote that "His books are full of profound and nearly inexhaustible erudition, revealing that their author was a learned historian, philologist, geographer, and ethnologist." The encyclopedia cited his 1901 book ''Ērānšahr'' as "still an authoritative work and probably his most important." Biography He attended Tübingen University in Germany, where he studied Catholic theology, and then later switched his studies to classical philology and history. In 1889 he worked as an assistant to Eugen Prym, an orientalist author. His doctoral thesis ''Assyriaka des Ktesias'' was accepted and he graduated in 1892. In 1897 he began as a lecturer in ancient history. In 1900 he moved to Leiden, The Netherland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Adontz
Nicholas Adontz (; ; January 10, 1871 – January 27, 1942) was an Armenians, Armenian historian, specialising in Byzantine studies, Byzantine and Armenian studies, and a philologist. Karen Yuzbashyan, Yuzbashyan, Karen. s.v. Adonts', Nikoghayos Gevorki. Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1974, vol. 1, p. 77. Adontz was the author of ''Armenia in the Period of Justinian'', a highly influential work and landmark study on the social and political structures of Medieval Armenia, early Medieval Armenia. Biography Early life Adontz was born Nikoghayos Ter-Avetikian () in the village of Brnakot in Sisian, which was then part of the Zangezur uezd of the Elizavetpol Governorate (present-day Syunik Province, Syunik). His family traced its roots to an eighteenth-century Armenian military figure and close ally of David Bek named Ter-Avetik. Yuzbashyan, Karen. "Nikoghayos Adonts'i gitakan zharangut'yune" [The intellectual legacy of Nikoghayos Adonts], ''Patma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontids
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after the collapse of the Achaemenid Empire established an independent kingdom. Later, a branch of the Orontids ruled as kings of Sophene and Commagene. They are the first of the three royal dynasties that successively ruled the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (321 BC–428 AD). Although the overthrow of Orontes IV and the accession of Artaxias I to the throne of Armenia in the early 2nd century BC is traditionally treated as the start of a new dynasty, Artaxias probably belonged to a branch of the Orontid dynasty. His descendants ruled Armenia until the 1st century AD. Historical background Some historians state that the Orontids were of Iranian origin, and suggest that it held dynastic familial linkages to the ruling Achaemenid dynasty. Throughou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Toumanoff
Cyril Leo Toumanoff ( ka, კირილ თუმანოვი; ; 10 October 1913 – 4 February 1997) was a Georgian-American historian, and academic genealogist who mostly specialized in the history and genealogies of medieval Georgia, Armenia, Iran, and the Byzantine Empire. Born in the Russian Empire into a princely family, Toumanoff escaped to the United States after the Russian Revolution. His works have significantly influenced the Western scholarship of the medieval Caucasus. Robert H. Hewsen. "In Memoriam: Cyril Toumanoff." ''Journal of the Society for Armenian Studies''. Vol. 8, 1995, 5–7. Family Cyril Toumanoff was born on 10 October 1913 in Saint Petersburg, the son of Prince Leo Tumanov, a military officer of the Russian Imperial army. His father, who was born in Yerevan, was descended from the Armeno-Georgian princely family of Tumanishvili (Russified to Tumanov)Rapp, Stephen H. (2003), ''Studies in Medieval Georgian Historiography: Early Texts and Eurasian Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giorgi Melikishvili
Giorgi Aleksandres dze Melikishvili ( ka, გიორგი ალექსანდრეს ძე მელიქიშვილი; ; 30 December 1918 – 19 April 2002) was a Georgian historian known for his fundamental works on the history of Georgia, Caucasia and the Middle East. He earned international recognition for his research on Urartu. Biography Giorgi Melikishvili was born in Tbilisi on 30 December 1918. He graduated from the Faculty of History of Tbilisi State University in 1939. In 1944, he began working at the Department of Georgian History of the Institute of History, Archaeology and Ethnography of the Academy of Sciences of Georgia. In 1954 he defended his doctoral dissertation, titled (Materials from the Ancient East on the history of the peoples of the Transcaucasus). From 1954 to 1988, he chaired the Department of Ancient History of the institute and from 1965 to 1999 served as the institute's director. He remained its honorary director until his deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artsruni Dynasty
The House of Artsruni (; also Ardzruni or Artsrunid) was an ancient princely and, later, royal dynasty of Armenia. Name The name ''Artsruni'' contains the ending , which is widespread in old Armenian family names. The early Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi derives the name from (, ). He implies that the Artsrunis carried standards with eagles on them and makes reference to a legend from Hadamakert (the center of the Artsrunis' home district of Aghbak) in which a bird protects a sleeping boy from the rain and sun; this is presumed to be a legend about the Artsrunis' ancestor (Sanasar, according to Manuk Abeghian) involving an eagle. James Russell notes that the eagle was a totemic animal for the Artsrunis and connects the dynasty's name with Urartian , which is attested as the name of an Urartian king's horse and may derive from Armenian . On this basis, Russell suggests that the Artsrunis may have had Urartian ancestors. Hrach Martirosyan writes that this connection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
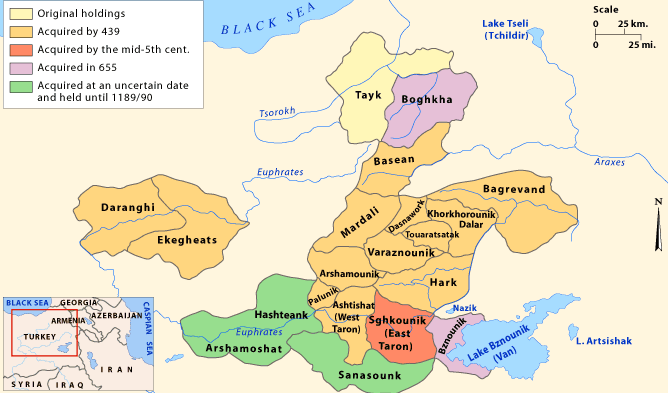
Sasun (historical Region)
Sasun or Sassoun (), also known as Sanasun or Sanasunkʻ (), was a region of historical Armenia. The region is now divided among the modern Turkey, Turkish provinces of Muş Province, Muş, Bingöl Province, Bingöl, Bitlis Province, Bitlis, Siirt Province, Siirt, Batman Province, Batman, and Diyarbakır Province, Diyarbakır, with the modern-day district of Sason District, Sason in Batman Province encompassing only one part of historical Sasun. In antiquity, Sasun was one of the ten districts () of the province of Arzanene, Aghdznikʻ (Arzanene) of the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia. Over time, Sasun came to denote a larger region than the original '. In the 10th century, an independent Armenian principality based in Sasun and ruled by a branch of the Mamikonian dynasty emerged and existed until the 12th century. The region was conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century, and the district (''kaza'') of Sasun was made a part of different administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |