|
Artery To The Ductus Deferens
The artery to the ductus deferens (deferential artery) is an artery in males that provides blood to the ductus deferens. Anatomy Origin The artery arises from the superior vesical artery (usually), or from the inferior vesical artery. Course, anastomoses, and distribution It accompanies the ductus deferens into the testis, where it anastomoses with the testicular artery; in this way it also supplies blood to the testis and epididymis. A small branch also supplies the ureter. See also * Spermatic cord The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ... Additional images File:Slide12Khi.JPG, Artery to the ductus deferens. Deep dissection. Lateral view. References External links * - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: Layers of the Spermatic Cord" {{Authority contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
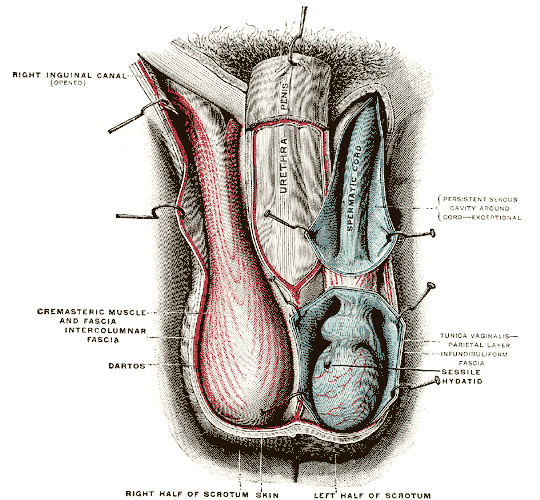
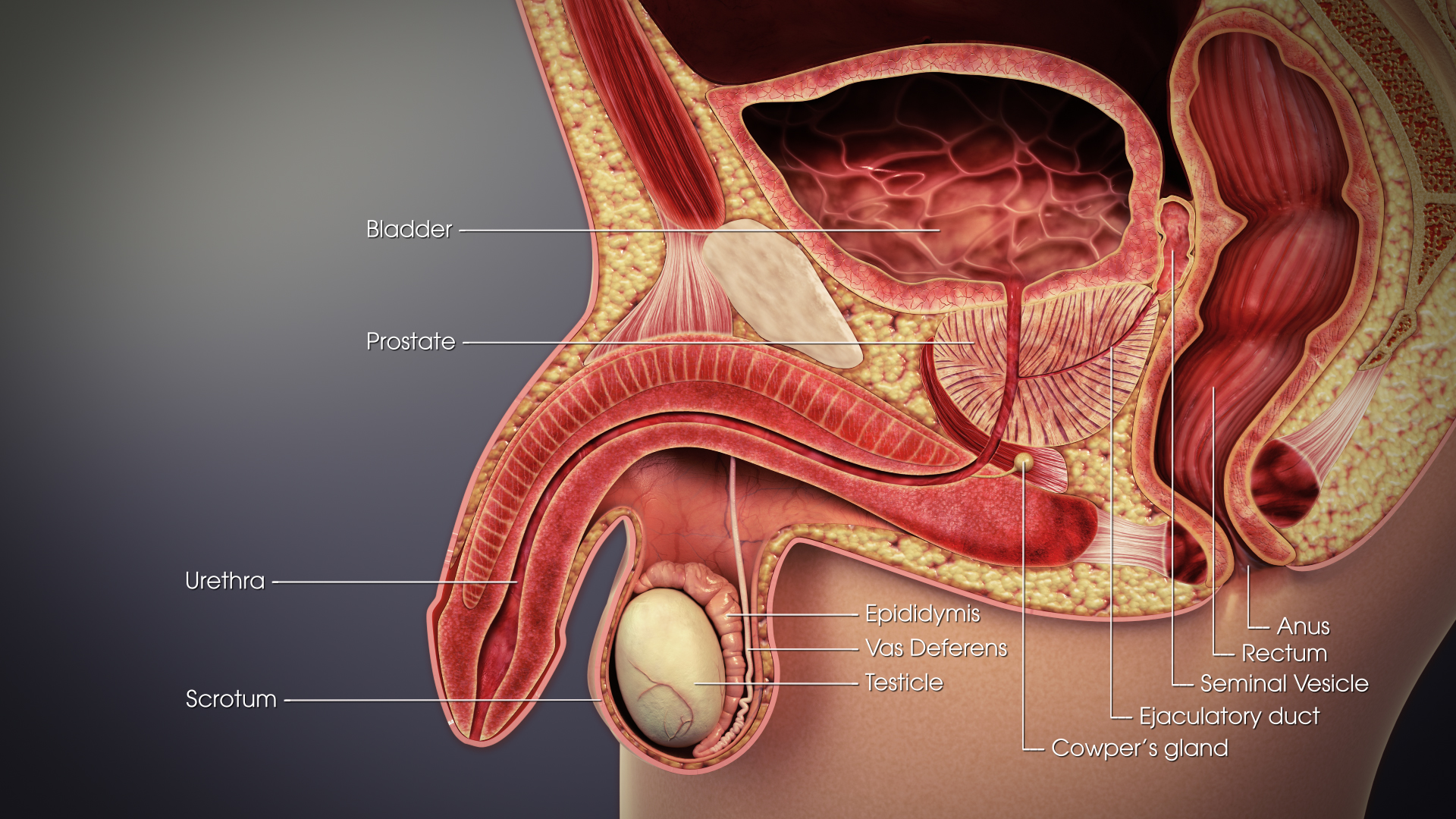
Scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures. The scrotum is homologous to the labia majora in females. Structure In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of skin and muscular tissue containing the testicles and the lower part of the spermatic cords. It is located behind the penis and above the perineum. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical ridge of skin that expands from the anus and runs through the middle of the scrotum front to back. The scrotum is also a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
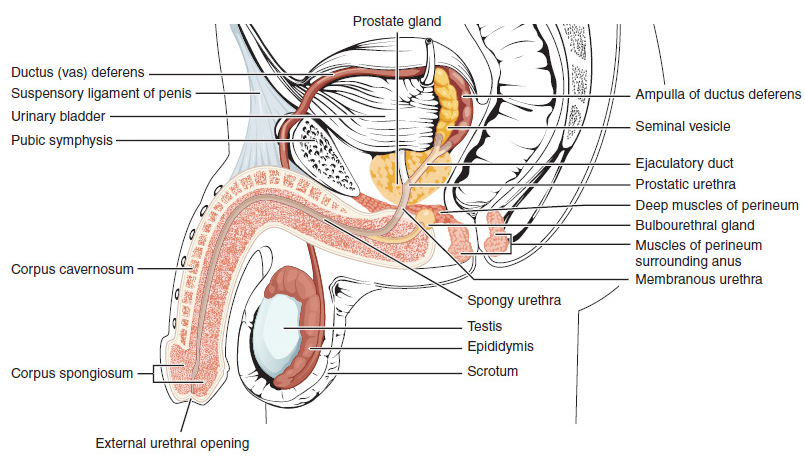
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vesical Artery
The superior vesical artery supplies numerous branches to the upper part of the bladder. This artery often also gives branches to the vas deferens and can provide minor collateral circulation for the testicles. Structure The superior vesical artery, a vital component of the pelvic vascular system, stems from the umbilical artery, which serves as a conduit for oxygenated blood during fetal development. Emerging typically as a single vessel, the superior vesical artery exhibits consistent anatomical features across individuals. Its trajectory leads it towards the superior aspect of the bladder, where it branches intricately to supply blood to this organ and surrounding structures. In males, a noteworthy branch arising from the superior vesical artery is the vesiculo-prostatic artery. This branch extends its reach to the prostate gland, contributing to its vascularization. The consistent presence of this arterial branch underscores its significance in male pelvic anatomy and physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vesical Artery
The inferior vesical artery (or inferior vesical artery) is an artery of the pelvis which arises from the internal iliac artery and supplies parts of the urinary bladder as well as other structures of the urinary system and structures of the male reproductive system. Some sources consider this vessel to be present only in males, and cite the vaginal artery as the homologous structure in females; others consider it to be present in both sexes, with the vessel taking the form of a small branch of a vaginal artery in females. Structure Origin The inferior vesical artery is a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It frequently has a common origin with the middle rectal artery. Course The inferior vesical artery passes medially across the pelvic floor. Distribution The inferior vesical artery is distributed to the trigone and inferior portion of the urinary bladder, the ureter, prostate, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles.vas deferens The vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididymal duct. The end of the epididymis is connected to the vas deferens. The vas deferens ends with an opening into the ejaculatory duct at a point where the duct of the seminal vesicle also joins the ejaculatory duct. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel" while ''ductus deferens'', also Latin, means "carrying-away duct". Structure The human vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis, and exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms a dilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vesical Artery
The superior vesical artery supplies numerous branches to the upper part of the bladder. This artery often also gives branches to the vas deferens and can provide minor collateral circulation for the testicles. Structure The superior vesical artery, a vital component of the pelvic vascular system, stems from the umbilical artery, which serves as a conduit for oxygenated blood during fetal development. Emerging typically as a single vessel, the superior vesical artery exhibits consistent anatomical features across individuals. Its trajectory leads it towards the superior aspect of the bladder, where it branches intricately to supply blood to this organ and surrounding structures. In males, a noteworthy branch arising from the superior vesical artery is the vesiculo-prostatic artery. This branch extends its reach to the prostate gland, contributing to its vascularization. The consistent presence of this arterial branch underscores its significance in male pelvic anatomy and physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductus Deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididymal duct. The end of the epididymis is connected to the vas deferens. The vas deferens ends with an opening into the ejaculatory duct at a point where the duct of the seminal vesicle also joins the ejaculatory duct. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel" while ''ductus deferens'', also Latin, means "carrying-away duct". Structure The human vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis, and exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms a dilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicular Artery
The testicular artery (the male gonadal artery, also called the internal spermatic arteries in older texts) is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles. It is the male equivalent of the ovarian artery. Because the testis is found in a different location than that of its female equivalent, it has a different course than the ovarian artery. They are two slender vessels of considerable length, and arise from the front of the aorta a little below the renal arteries. Each passes obliquely downward and lateralward behind the peritoneum, resting on the psoas major, the right lying in front of the inferior vena cava and behind the middle colic and ileocolic arteries and the terminal part of the ileum, the left behind the left colic and sigmoid arteries and the iliac colon. Each crosses obliquely over the ureter and the lower part of the external iliac artery to reach the abdominal inguinal rin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; uncoiled the tube would be approximately 6 m (20 feet) long. It connects the testicle to the vas deferens in the male reproductive system. The epididymis serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Its primary function is the storage, maturation and transport of sperm cells. Structure The human epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head (). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children. The ureters have been identified for at least two thousand years, with the word "ureter" stemming from the stem relating to urinating and seen in written records since at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * '' external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * '' cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * '' internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |