|
Army Of The Lord
The Army of the Lord ( ro, Oastea Domnului), also known as The Lord's Army, is an evangelical " renewal movement within the Romanian Orthodox Church". The founder of the Army of the Lord, Father Iosif Trifa, as well as consequent leaders, Ioan Marini and Traian Dorz, felt that "people needed to come to the gospel and that the Orthodox Church in Romania needed to return to her true mission: to serve God and to represent God in the midst of our nation." Tom Keppeler writes that "What Wesley was to the Anglican Church, Trifa was to the Romanian Orthodox Church. As Wesley's preaching and ministry drew crowds from the working classes, so Trifa's as well was a ministry that grew among the villagers and workers of the fields." In the 1930s and 1940s, "millions of Romanian Orthodox, including priests and religious, took part in its activities of evangelization, printing and open air meetings." Members of the Army of the Lord greet one another with the phrase "Praise the Lord!", followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and the Malabar coast of South Asia, and ephemerally parts of Persia, Central Asia, the Near East and the Far East. The term does not describe a single communion or religious denomination. Major Eastern Christian bodies include the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Oriental Orthodox Churches, along with those groups descended from the historic Church of the East, as well as the Eastern Catholic Churches (which have either re-established or always retained communion with Rome and maintain Eastern liturgies), and the Eastern Protestant churches (which are Protestant in theology but Eastern in cultural practice). The various Eastern churches do not normally refer to themselves as "Eastern", with the exception of the Assyrian Church of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople. The canonical hours are very long and complicated, lasting about eight hours (longer during Great Lent) but are abridged outside of large monasteries. An iconostasis, a partition covered with icons, separates the area around the altar from the nave. The sign of the cross, accompanied by bowing, is made very frequently, e.g., more than a hundred times during the divine liturgy, and there is prominent veneration of icons, a general acceptance of the congregants freely moving within the church and interacting with each other, and distinctive traditions of liturgical chanting. Some traditional practices are falling out of use in modern times in sundry churches and in the diaspora, e.g., the faithful standing during services, bowing and prostrating frequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Protestantism
The term Eastern Protestant Christianity (or Eastern Reformed Christianity as well as Oriental Protestant Christianity) encompasses a range of heterogeneous Protestant Christian denominations that developed outside of the Occident, from the latter half of the nineteenth century, and yet keep elements of Eastern Christianity, to varying degrees. Some of these denominations came into being, when existing Protestant churches adopted reformational variants of Eastern and Oriental Orthodox liturgy and worship. Some others are the result of reformations of Orthodox beliefs and practices, inspired by the teachings of Western Protestant missionaries. Some Eastern Protestant Churches are in communion with similar Western Protestant Churches. However, Eastern Protestant Christianity does not constitute a single communion. This is due to the diverse polities, practices, liturgies and orientations of the denominations which fall under this category. List of churches * Armenian Evangeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-religious Campaign Of Communist Romania
The anti-religious campaign of Communist Romania was initiated by the People's Republic of Romania and continued by the Socialist Republic of Romania, which under the doctrine of Marxist–Leninist atheism took a hostile stance against religion and set its sights on the ultimate goal of an atheistic society, wherein religion would be recognized as the ideology of the bourgeoisie. Scope Romania's Communist government achieved an incredible degree of control (relative to the other Eastern Bloc nations) of the nation's largest religious community: the Romanian Orthodox Church. This control was used to foster political support for the regime as well as to manipulate Romania's image abroad. In Romania, more than 5,000 Orthodox Christian priests were imprisoned. The Orthodox archdiocese of Cluj contains biographies of 1,700 church personnel jailed. 1945–1965 Cultural background The Communist Party of the Soviet Union, in accordance with Marxist–Leninist interpretation of histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican Church
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The majority of Anglicans are members of national or regional ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, which forms the third-largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. These provinces are in full communion with the See of Canterbury and thus with the Archbishop of Canterbury, whom the communion refers to as its ''primus inter pares'' (Latin, 'first among equals'). The Archbishop calls the decennial Lambeth Conference, chairs the meeting of primates, and is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English cleric, theologian, and evangelist who was a leader of a revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Methodist movement that continues to this day. Educated at Charterhouse and Christ Church, Oxford, Wesley was elected a fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford, in 1726 and ordained as an Anglican priest two years later. At Oxford, he led the " Holy Club", a society formed for the purpose of the study and the pursuit of a devout Christian life; it had been founded by his brother Charles and counted George Whitefield among its members. After an unsuccessful ministry of two years, serving at Christ Church, in the Georgia colony of Savannah, he returned to London and joined a religious society led by Moravian Christians. On 24 May 1738, he experienced what has come to be called his evangelical conversion, when he felt his "heart strangely wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual experiences personal conversion; the authority of the Bible as God's revelation to humanity ( biblical inerrancy); and spreading the Christian message. The word ''evangelical'' comes from the Greek (''euangelion'') word for " good news". Its origins are usually traced to 1738, with various theological streams contributing to its foundation, including Pietism and Radical Pietism, Puritanism, Quakerism, Presbyterianism and Moravianism (in particular its bishop Nicolaus Zinzendorf and his community at Herrnhut).Brian Stiller, ''Evangelicals Around the World: A Global Handbook for the 21st Century'', Thomas Nelson, USA, 2015, pp. 28, 90. Preeminently, John Wesley and other early Methodists were at the root of sparking this new movement d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the 'priesthood', a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred texts and keep temple or church rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; ro, Biserica Ortodoxă Română, ), or Patriarchate of Romania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 1925, the church's Primate bears the title of Patriarch. Its jurisdiction covers the territories of Romania and Moldova, with additional dioceses for Romanians living in nearby Serbia and Hungary, as well as for diaspora communities in Central and Western Europe, North America and Oceania. It is the only autocephalous church within Eastern Orthodoxy to have a Romance language for liturgical use. The majority of Romania's population (16,367,267, or 85.9% of those for whom data were available, according to the 2011 census data), as well as some 720,000 Moldovans, belong to the Romanian Orthodox Church. Members of the Romanian Orthodox Church sometimes refer to Orthodox Christian doctrine as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibiu
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Cibin River, a tributary of the river Olt. Now the capital of the Sibiu County, between 1692 and 1791 and 1849–65 Sibiu was also the capital of the Principality of Transylvania. Nicknamed ''The City with Eyes'', the city is a well-known tourist destination for both domestic and foreign visitors. Known for its culture, history, gastronomy and diverse architecture, which includes the iconic houses with eyes that gave Sibiu its nickname, the city has garnered significant attention since the beginning of the 21st century. In 2004, its historical center began the process of becoming a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Sibiu was designated the European Capital of Culture in 2007. One year later, it was ranked "Europe's 8th-most idyllic place to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
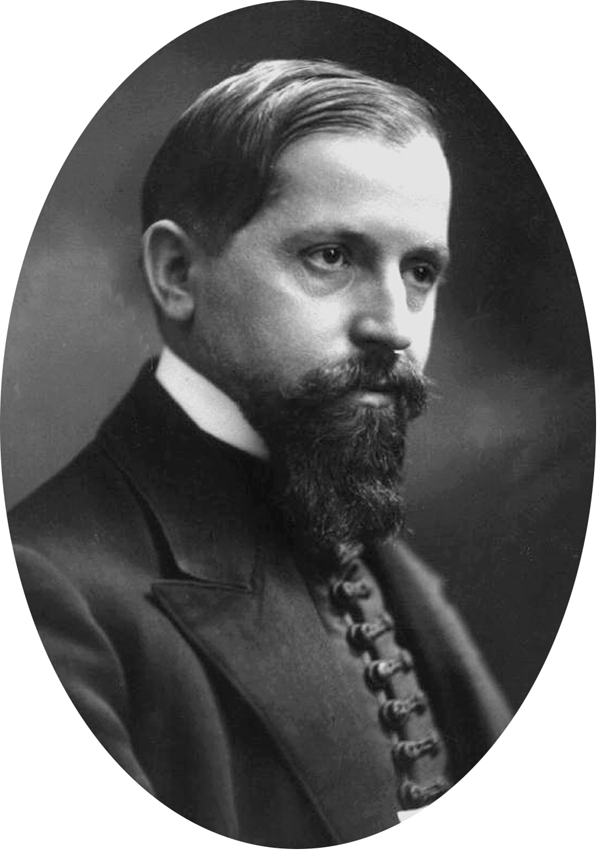
Iosif Trifa
Iosif Trifa (3 March 1888 – 12 February 1938) was a Romanian Orthodox priest and evangelist. He founded " Oastea Domnului" ("The Lord's Army"). He was also the uncle of Valerian Trifa. Trifa placed on the 100 greatest Romanians list. Life Iosif Trifa was born in the family of Dimitrie and Ana Trifa, from the village Certege, Torda-Aranyos County (now Câmpeni, Alba County, Romania). He was the 4th son of a total of 6. He was baptised on 6 March 1888. When he was 7 years old, in 1895, he started elementary school in his village, and in 1900 started gymnasium in Beiuș. Later on, he studied theology in Sibiu. In 1910 he was named a confessional teacher in the town of Vidra de Sus, which is now the town of Avram Iancu, Alba, named after the Transylvanian Romanian national hero. In 1911 he married Iuliana Iancu, niece to the hero Avram Iancu. In the same year he was made priest in Vidra. In 1912 his first child, a girl, Olimpia, was born, but she died the following year. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Language
Romanian (obsolete spellings: Rumanian or Roumanian; autonym: ''limba română'' , or ''românește'', ) is the official and main language of Romania and the Republic of Moldova. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Bulgaria, Hungary, Serbia, and Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 28–29 million people as an L1+ L2, of whom 23–24 millions are native speakers. In Europe, Romanian is rated as a medium level language, occupying the tenth position among thirty-seven official languages. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called ''Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)