|
Armadillidium Maculatum
''Armadillidium maculatum'', also known as the zebra isopod or zebra pillbug is an '' Armadillidium'' species of woodlouse, named for its black and white patterns. It is native to southern France. It is quite popular as pets or vivarium cleaners, due to their ability to break down various waste. Description and Life Cycle ''Armadillidium maculatum'' is average sized for its genus and can grow up to 1.8 centimeters or 11/16 inches. Like other members of its family, it can conglobate or roll into a ball when disturbed or to conserve moisture. Its striped appearance is thought to be an example of Batesian mimicry, mimicking the pill millipede '' Glomeris marginata'' which secretes noxious chemicals and is native to the same range. ''Armadillidium maculatum'', like all other woodlice, have 7 pairs of legs and 7 main body segments ( pleon) Being an arthropod, ''A. maculatum'' has an exoskeleton which it must shed ( molt) as it grows. Unlike most other arthropods, ''A. maculatum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillidium
''Armadillidium'' () is a genus of the small terrestrial crustacean known as the woodlouse. It is one of 18 genera nested within the family Armadillidiidae. ''Armadillidium'' is also one of the groups commonly known as pill woodlice, leg pebbles, pill bugs, roly-poly, or potato bugs, and are often confused with pill millipedes such as '' Glomeris marginata''. They are characterised by their ability to roll into a ball (" volvation") when disturbed. With a penchant for damp and dark places, species in the ''Armadillidium'' genus can typically be found under rocks, in leaf litter, and in or around the soil. Aided by their dorsoventrally flattened body and small size – usually growing no bigger than 2.5 cm – these pill bugs are able to squeeze into tight cracks and are common household pests as a result. Description Unlike other terrestrial ''arthropods'' such as insects and spiders, pill bugs do not have a waxy cuticle that would reduce evaporation from their bodies. Pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Pouch (Peracarida)
The marsupium or brood pouch, is a characteristic feature of Peracarida, including the orders Amphipoda, Isopoda, and Cumacea Cumacea is an order (biology), order of small marine crustaceans of the superorder Peracarida, occasionally called hooded shrimp or comma shrimp. Their unique appearance and uniform body plan makes them easy to distinguish from other crustaceans. .... It is an egg chamber formed by oostegites, which are appendages that are attached to the coxae (first segment) of the first pereiopods. Females lay their eggs directly into the brood chamber, and the young will develop there, undergoing several moults before emerging as miniature adults referred to as mancae. Males have no marsupium. References {{malacostraca-stub Crustacean anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodlice
Woodlice are terrestrial isopods in the suborder Oniscidea. Their name is derived from being often found in old wood, and from louse, a parasitic insect, although woodlice are neither parasitic nor insects. Woodlice evolved from marine isopods which are presumed to have colonised land in the Carboniferous, though the oldest known fossils are from the Cretaceous period. This makes them quite unique among the crustaceans, being one of the few lineages to have transitioned into a fully terrestrial environment. Woodlice have many common names and although often referred to as terrestrial isopods, some species live semiterrestrially or have recolonised aquatic environments like those of the genus ''Ligia''. Woodlice in the families Armadillidae, Armadillidiidae, Eubelidae, Tylidae and some other genera can roll up into a roughly spherical shape (:wiktionary:conglobate, conglobate) as a defensive mechanism or to conserve moisture; others have partial rolling ability, but most cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desiccation
Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. The word desiccation comes . Industry Desiccation is widely employed in the oil and gas industry. These materials are obtained in a hydrated state, but the water content leads to corrosion or is incompatible with downstream processing. Removal of water is achieved by cryogenics, cryogenic condensation, absorption into glycols, and absorption onto desiccants such as silica gel. Laboratory A desiccator is a heavy glass or plastic container, now somewhat antiquated, used in practical chemistry for drying or keeping small amounts of materials very dry. The material is placed on a shelf, and a drying agent or ''desiccant'', such as dry silica gel or anhydrous sodium hydroxide, is placed below the shelf. Often some sort of humidity indicator is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillidium Vulgare
''Armadillidium vulgare'', the common pill-bug, common pill woodlouse, roly-poly, slater, doodle bug, or carpenter, is a widespread European species of woodlouse. It is the most extensively investigated terrestrial isopod species. It is native to Mediterranean Europe, but as an introduced species they have become naturalized in almost all suitable ecosystems. They are kept as pets by hobbyists for their wide range of possible color variations. Description ''Armadillidium vulgare'' may reach a length of , and is capable of rolling into a ball when disturbed; this ability, along with its general appearance, gives it the name ''pill-bug'' and also creates the potential for confusion with pill millipedes such as '' Glomeris marginata''. It can be distinguished from '' Armadillidium nasatum'' and '' Armadillidium depressum'' by the gap that ''A. nasatum'' and ''A. depressum'' leave when rolling into a ball; ''A. vulgare'' does not leave such a gap. Ecology ''Armadillidium vulgare'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both aquatic species and terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax called the marsupium. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or the bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture like species in the family Armadilli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritivore
Detritivores (also known as detrivores, detritophages, detritus feeders or detritus eaters) are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as feces). There are many kinds of invertebrates, vertebrates, and plants that eat detritus or carry out coprophagy. By doing so, all these detritivores contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles. Detritivores should be distinguished from other decomposers, such as many species of bacteria, fungi and protists, which are unable to ingest discrete lumps of matter. Instead, these other decomposers live by absorbing and metabolizing on a molecular scale (saprotrophic nutrition). The terms ''detritivore'' and ''decomposer'' are often used interchangeably, but they describe different organisms. Detritivores are usually arthropods and help in the process of remineralization. Detritivores perform the first stage of remineralization, by fragmenting the dead plant matter, allowing decomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manca
The manca (plural: ''mancae'') is the post-larval juvenile in some crustaceans. The term is derived from Latin ''mancus'', meaning "defective, imperfect." The manca stage is the defining characteristic of a clade called Mancoida which comprises all the members of the Peracarida except the Mysidacea and the Amphipoda. Mancae closely resemble the adult form, but for the absence of the last pair of pereiopods. In some isopods, specifically the family Gnathiidae, the manca stage is a parasite Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ... of fish, and is also known as the praniza. References Crustaceans Developmental biology Larvae {{crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is a process by which an animal casts off parts of its body to serve some beneficial purpose, either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times, it was also known as "mewing" (from the French verb "muer", to moult), a term that lives on in the name of Britain's Royal Mews where the King's hawks used to be kept during moulting time before becoming horse stables after Tudor times. Moulting can involve shedding the Epidermis (skin), epidermis (skin), pelage (hair, feathers, fur, wool), or other external layer. In some groups, other body parts may be shed, for example, the entire exoskeleton in arthropods, including the wings in some insects. Examples In birds In birds, moulting is the periodic replacement of feathers by shedding old feathers while producing new ones. Feathers are dead struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodlouse
Woodlice are terrestrial isopods in the suborder Oniscidea. Their name is derived from being often found in old wood, and from louse, a parasitic insect, although woodlice are neither parasitic nor insects. Woodlice evolved from marine isopods which are presumed to have colonised land in the Carboniferous, though the oldest known fossils are from the Cretaceous period. This makes them quite unique among the crustaceans, being one of the few lineages to have transitioned into a fully terrestrial environment. Woodlice have many common names and although often referred to as terrestrial isopods, some species live semiterrestrially or have recolonised aquatic environments like those of the genus ''Ligia''. Woodlice in the families Armadillidae, Armadillidiidae, Eubelidae, Tylidae and some other genera can roll up into a roughly spherical shape (:wiktionary:conglobate, conglobate) as a defensive mechanism or to conserve moisture; others have partial rolling ability, but most cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
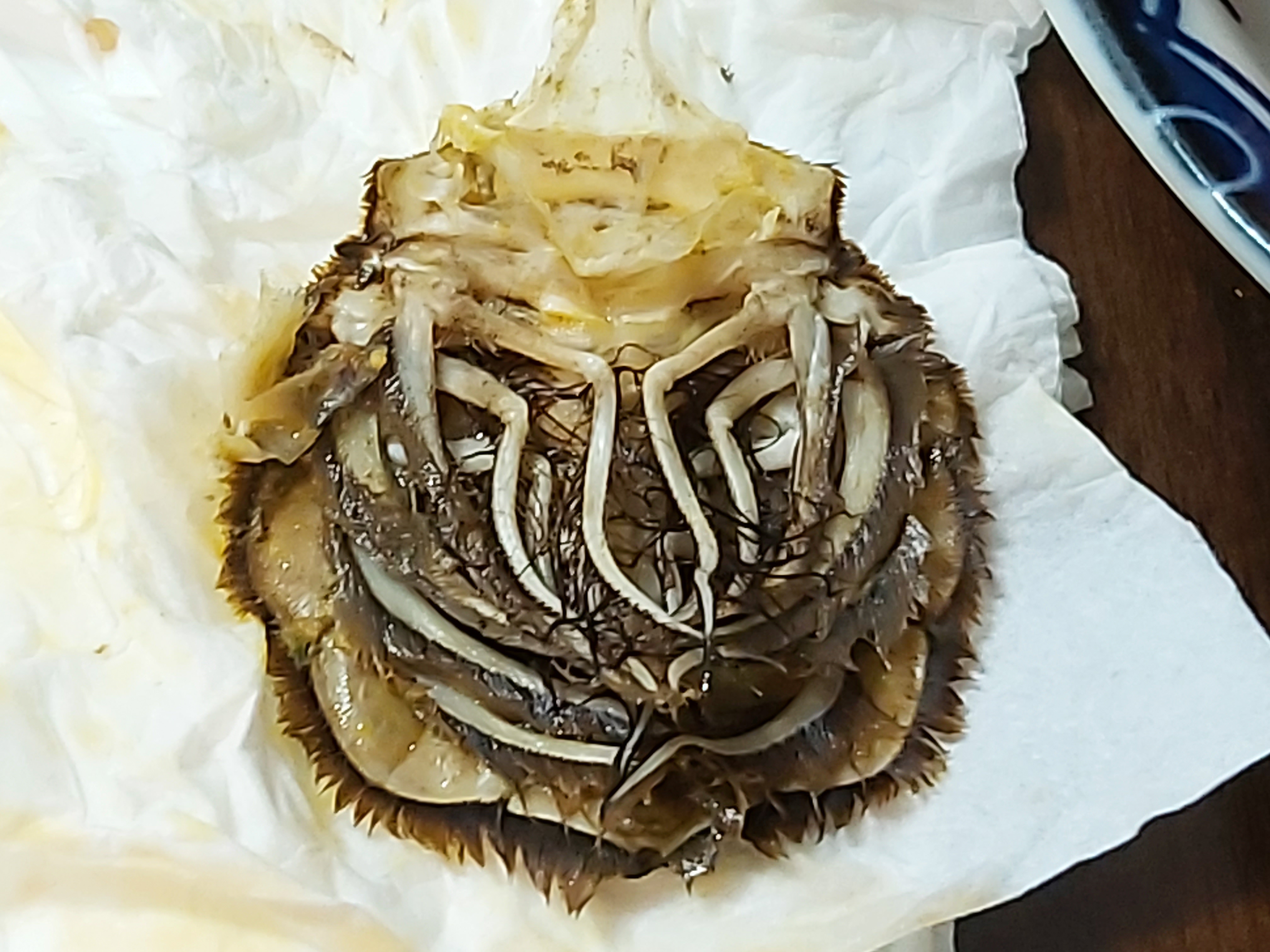
Decapod Anatomy
The anatomy of a decapod consists of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment – often called a somite – may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae # mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods take their name. Those pereiopods which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |