|
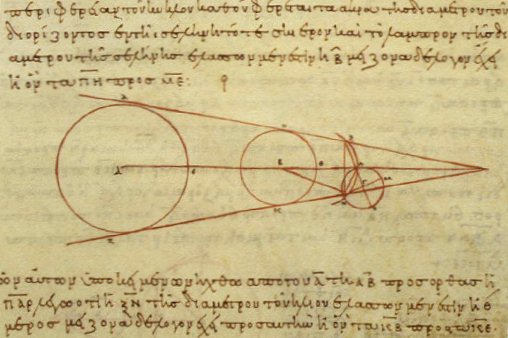
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle University Of Thessaloniki
The Aristotle University of Thessaloniki ( AUTh; ), often called the University of Thessaloniki, is the second oldest tertiary education institution in Greece. Named after the philosopher Aristotle, who was born in Stageira, about east of Thessaloniki, it is the largest university in Greece and its campus covers in the centre of Thessaloniki, with additional educational and administrative facilities elsewhere. As of 2023, it has approximately 88,283 active students enrolled at the university (77,198 at the undergraduate level and 6,588 in postgraduate programmes of which 3,952 at doctoral level) and 2,366 faculty members. There are additionally 248 members of the Laboratory Teaching Staff and 213 members of the Special Technical Laboratory Staff. The administrative staff consists of 400 permanent employees and 528 subcontractor employees that are contracted by the university. The language of instruction is Greek, although there are programs in foreign languages and courses f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundial
A sundial is a horology, horological device that tells the time of day (referred to as civil time in modern usage) when direct sunlight shines by the position of the Sun, apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat plate (the ''dial'') and a gnomon, which casts a shadow onto the dial. As the Sun diurnal motion, appears to move through the sky, the shadow aligns with different hour-lines, which are marked on the dial to indicate the time of day. The ''style'' is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, though a single point or ''nodus'' may be used. The gnomon casts a broad shadow; the shadow of the style shows the time. The gnomon may be a rod, wire, or elaborately decorated metal casting. The style must be polar alignment, parallel to the axis of the Earth's rotation for the sundial to be accurate throughout the year. The style's angle from horizontal is equal to the sundial's geographical latitude. The term ''sundial'' can r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is an academic publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University. It is a member of the Association of University Presses. Its director since 2017 is George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint (trade name), imprint, which it inaugurated in May 1954 with the publication of the ''Harvard Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal For The History Of Astronomy
''Journal for the History of Astronomy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that covers the history of astronomy from earliest times to the present, and in history in the service of astronomy. The journal's founding editor-in-chief was Michael Hoskin (Cambridge University) and it is currently edited by James Evans ( University of Puget Sound). History The journal was established in 1970 and was published by Science History Publications through to 2013, and since 2014 by SAGE Publishing. From 1979 to 2002, ''Archaeoastronomy'' was published as a supplement, but was incorporated in 2003. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Scopus and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Sand-Reckoner
''The Sand Reckoner'' (, ''Psammites'') is a work by Archimedes, an Ancient Greek mathematician of the 3rd century BC, in which he set out to determine an upper bound for the number of grains of sand that fit into the universe. In order to do this, Archimedes had to estimate the size of the universe according to the contemporary model, and invent a way to talk about extremely large numbers. The work, also known in Latin as ''Arenarius'', is about eight pages long in translation and is addressed to the Syracusan king Gelo II (son of Hiero II). It is considered the most accessible work of Archimedes.Archimedes, The Sand Reckoner 511 R U, by Ilan Vardi accessed 28-II-2007. Naming large numbers [Baidu] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenistic Sicily, Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, based on his surviving work, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity, and one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and mathematical analysis, analysis by applying the concept of the Cavalieri's principle, infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove many geometry, geometrical theorem, theorems, including the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Archimedes' other math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owen Gingerich
Owen Jay Gingerich (; March 24, 1930 – May 28, 2023) was an American astronomer who had been professor emeritus of astronomy and of the history of science at Harvard University and a senior astronomer emeritus at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. In addition to his research and teaching, he had written many books on the history of astronomy. Gingerich was also a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the American Philosophical Society, and the International Academy of the History of Science. A committed Christian, he had been active in the American Scientific Affiliation, a society of evangelical scientists.Stephen C. Meyer.Owen Gingerich. ''Eternity''. May 1986. He served on the board of trustees of the Templeton Foundation. Early life Gingerich was born March 24, 1930, to Melvin and Verna (Roth) Gingerich, a Mennonite family in Washington, Iowa, but was raised on the prairies of Kansas where he first became interested in astronomy. His father taught his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 (2023), with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596, and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Kraków Old Town, Old Town was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the world's first sites granted the status. The city began as a Hamlet (place), hamlet on Wawel Hill and was a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. In 1038, it became the seat of King of Poland, Polish monarchs from the Piast dynasty, and subsequently served as the centre of administration under Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings and of the Polish–Lithuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagiellonian Library
The Jagiellonian Library (, popular nickname ''Jagiellonka'') is the library of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków and with almost 6.7 million volumes, one of the largest libraries in Poland, serving as a public library, university library and part of the Polish national library system.Official national library of Poland is the National Library of Poland in Warsaw; however Jagiellonian Library is considered a part of the ''Narodowy Zasób Biblioteczny''. It was ''the'' National Library before the creation of the National Library in Warsaw, and today it contains the National Library collection for the period before 1801. It has a large collection of medieval manuscripts, for example the Autograph of Nicolaus Copernicus' De revolutionibus, autograph of Copernicus' ''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, De Revolutionibus'' and Jan Długosz's ''Banderia Prutenorum'', and a large collection of Counterculture, underground literature (so-called ''drugi obieg'' or samizdat) from the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its center. Copernicus likely developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an List of ancient Greek astronomers, ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus' model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a semiautonomous and multilingual region created within the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from lands regained from the Teutonic Order after the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War. A Poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |