|
Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica is a cultural and ecological region spanning Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, defined by the presence of the drought-resistant, culturally significant staple food, the tepary bean ('' Phaseolus acutifolius'').Pratt and Nabhan 419 Its dry, arid climate and geography stand in contrast to the verdant Mesoamerica of present-day central Mexico into Central AmericaCordell and Fowler 85 to the south and east, and the higher, milder "island" of Oasisamerica to the north. Aridoamerica overlaps with both. Because of the relatively hard conditions, the pre-Columbian people in this region developed distinct cultures and subsistence farming patterns. The region has only to of annual precipitation. The sparse rainfall feeds seasonal creeks and waterholes.Bye and Linares 273 The term was introduced by American anthropologist Gary Paul Nabhan in 1985, building on prior work by anthropologists A. L. Kroeber and Paul Kirchhoff to identify a "true cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oasisamerica
Oasisamerica is a cultural region of Indigenous peoples in North America. Their precontact cultures were predominantly agrarian, in contrast with neighboring tribes to the south in Aridoamerica. The region spans parts of Northwestern Mexico and Southwestern United States and can include most of Arizona and New Mexico; southern parts of Utah and Colorado; and northern parts of Sonora and Chihuahua. During some historical periods, it might have included parts of California and Texas as well.Alfredo López Austin and Leonardo López Luján''Mexico's Indigenous Past'' p. 30. The term was first proposed by German-Mexican anthropologist Paul Kirchhoff, who also coined MesoamericaPaul Kirchhoff“Gatherers and Farmers in the Greater Southwest" p. 532. and Aridoamerica, and is used by some scholars, primarily Mexican anthropologists, for the broad cultural area defining pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extends from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Mexico
Northern Mexico ( ), commonly referred as , is an informal term for the northern cultural and geographical area in Mexico. Depending on the source, it contains some or all of the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Durango, Nuevo León, Sinaloa, Sonora and Tamaulipas. There is no specific border that separates the northern states from the southern states in Mexico. For some authors, only states that have a border with the United States are considered as northern Mexico, i.e. Baja California, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Sonora and Tamaulipas. Others also include Durango, Sinaloa and Baja California Sur. Other people consider that the north starts above the Tropic of Cancer, but this description would include some parts of Zacatecas and San Luis Potosí that are not considered northern states. History Before colonization It is not known precisely when the first settlers came to northern Mexico. The harsh climate in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahua People
The Nahuas ( ) are a Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Nahuan ethnicity and one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest Indigenous group in Mexico, as well as the largest population out of any North American Indigenous people group who are native speakers of their respective Indigenous languages of the Americas, Indigenous language. Amongst the Nahua, this is Nahuatl. When ranked amongst all Indigenous languages across the Americas, Nahuas list third after speakers of Guarani language, Guaraní and Quechuan languages, Quechua. The Mexica (Aztecs) are of Nahua ethnic group, ethnicity, as are their historical enemies and allies of the Spaniards: the Tlaxcaltec, Tlaxcallans (Tlaxcaltecs). The Toltecs which predated both groups are often thought to have been Nahua as well. However, in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
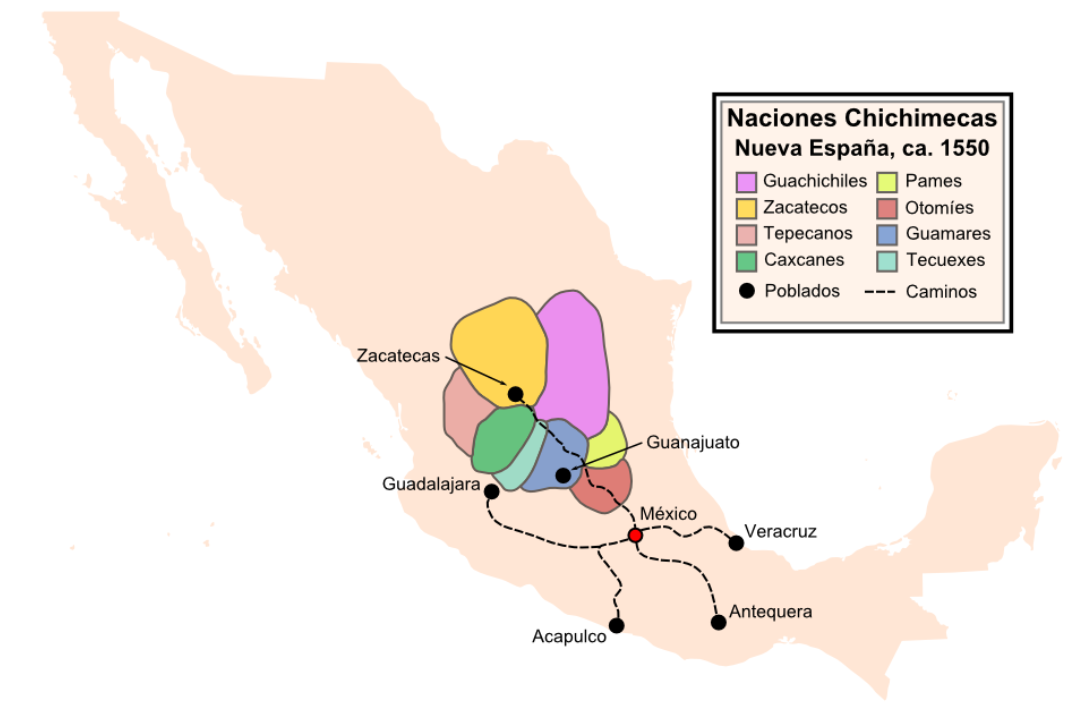
Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. In the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "for the Spanish, the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit."Gradie, Charlotte M. "Discovering the Chichimecas" ''Academy of American Franciscan History'', Vol 51, No. 1 (July 1994), p. 68 Gradie noted that Chichimeca was used as a broad and generalizing term by outsiders, writing, " twas used by both Spanish and Nahuatl speakers to refer collectively to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and northwestern part of Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. In the pre-Columbian era, many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas began on Hispaniola in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Columbian Era
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492. This era encompasses the history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous cultures prior to significant European influence, which in some cases did not occur until decades or even centuries after Columbus's arrival. During the pre-Columbian era, many civilizations developed permanent settlements, cities, agricultural practices, civic and monumental architecture, major Earthworks (archaeology), earthworks, and Complex society, complex societal hierarchies. Some of these civilizations had declined by the time of the establishment of the first permanent European colonies, around the late 16th to early 17th centuries, and are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California (). It has an area of (3.57% of the land mass of Mexico) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the United States on the north and on the south by Baja California Sur. The state has an estimated population of 3,769,020 as of 2020, significantly higher than the sparsely populated Baja California Sur to the south, and similar to San Diego County, California, and Imperial County, California, to its north. Over 75% of the population lives in Mexicali (the state's capital city), Ensenada, or Tijuana (the state's largest city). Other impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uto-Aztecan
The Uto-Aztecan languages are a family of native American languages, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family reflects the common ancestry of the Ute language of Utah and the Nahuan languages (also known as Aztecan) of Mexico. The Uto-Aztecan language family is one of the largest linguistic families in the Americas in terms of number of speakers, number of languages, and geographic extension. The northernmost Uto-Aztecan language is Shoshoni, which is spoken as far north as Salmon, Idaho, while the southernmost is the Nawat language of El Salvador and Nicaragua. ''Ethnologue'' gives the total number of languages in the family as 61, and the total number of speakers as 1,900,412. Speakers of Nahuatl languages account for over 85% of these. The internal classification of the family often divides it into two branches: a northern branch including all the languages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
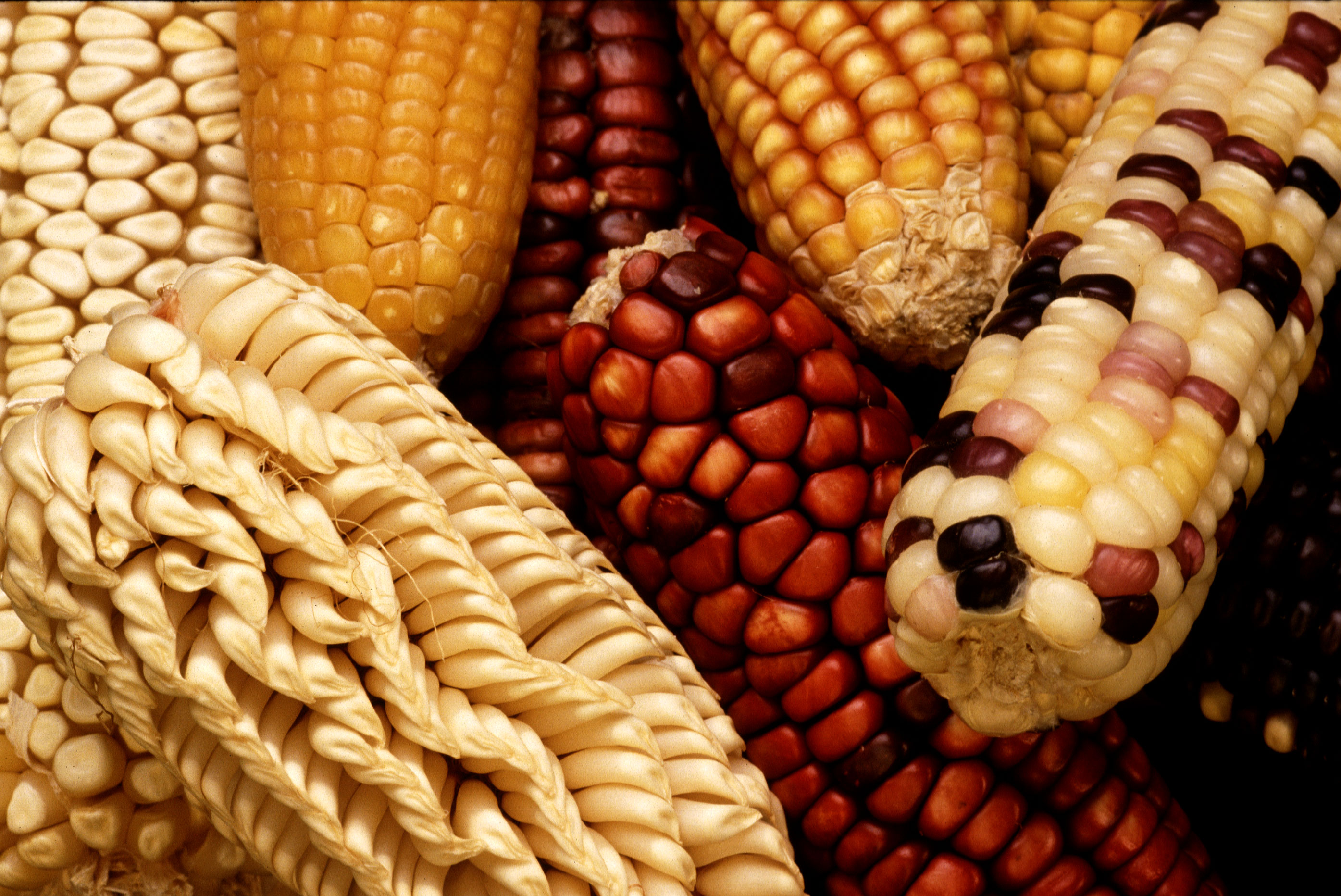
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agave Americana
''Agave americana'', commonly known as the century plant, maguey, or American aloe, is a flowering plant species belonging to the family Asparagaceae. It is native to Mexico and the United States, specifically Texas. This plant is widely cultivated worldwide for its ornamental value and has become naturalized in various regions, including Southern California, the West Indies, South America, the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, the Canary Islands, India, China, Thailand, and Australia. Despite being called "American aloe" in common parlance, ''Agave americana'' is not a member of the same family as ''Aloe'', although it falls under the same order, Asparagales. Description The common name "century plant" stems from its monocarpic nature of flowering only once at the end of its long life. After flowering, the plant dies but produces adventitious shoots from the base, allowing its growth to continue. Although it is called the century plant, it typically lives only 10 to 30 years. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century Plant
''Agave americana'', commonly known as the century plant, maguey, or American aloe, is a flowering plant species belonging to the family Asparagaceae. It is native to Mexico and the United States, specifically Texas. This plant is widely cultivated worldwide for its ornamental value and has become naturalized in various regions, including Southern California, the West Indies, South America, the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, the Canary Islands, India, China, Thailand, and Australia. Despite being called "American aloe" in common parlance, ''Agave americana'' is not a member of the same family as ''Aloe'', although it falls under the same order, Asparagales. Description The common name "century plant" stems from its monocarpic nature of flowering only once at the end of its long life. After flowering, the plant dies but produces adventitious shoots from the base, allowing its growth to continue. Although it is called the century plant, it typically lives only 10 to 30 years. It h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |