|
Argonaut (lunar Lander)
Argonaut or European Large Logistics Lander (EL3) is a class of lunar landers designed by the European Space Agency (ESA) in partnership with Thales Alenia Space to deliver payloads to the surface of the Moon. The lander is being designed with a versatile set of uses in mind, including use as a power station, support for a rover, cargo delivery, and infrastructure delivery. It is envisioned to launch on an Ariane 64 launch vehicle. The Argonaut lander will consist of the descent element, cargo platform and payload. Capable of delivering up to , the craft will reportedly be able to land with an accuracy of 50–100 meters. First mission: ''ArgoNET'' ''ArgoNET'' will be the first operational flight of the programme, planned for launch in 2031. It will deliver navigation, energy, and telecommunications infrastructure and will serve as a selenodetic reference station for the Moonlight satellite constellation in order to improve navigation capabilities around the lunar south pole. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space () is a joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (company), Leonardo (33%). The company is headquartered in Cannes, France. It provides space-based systems, including satellites and ground segments, used for telecommunications, navigation, earth observation, space exploration and scientific purposes. The company is the second largest industrial participant in the International Space Station (ISS), having produced numerous pressurized modules for the European Space Agency (ESA) including the Cupola (ISS module), Cupola, the node modules Harmony (ISS module), Harmony and Tranquility (ISS module), Tranquility, and the structure of the Columbus (ISS module), Columbus laboratory. It is a key contributor to Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo, a European Satellite navigation, global satellite navigation system, being responsible for the ground segment in particular. In 2021, the company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
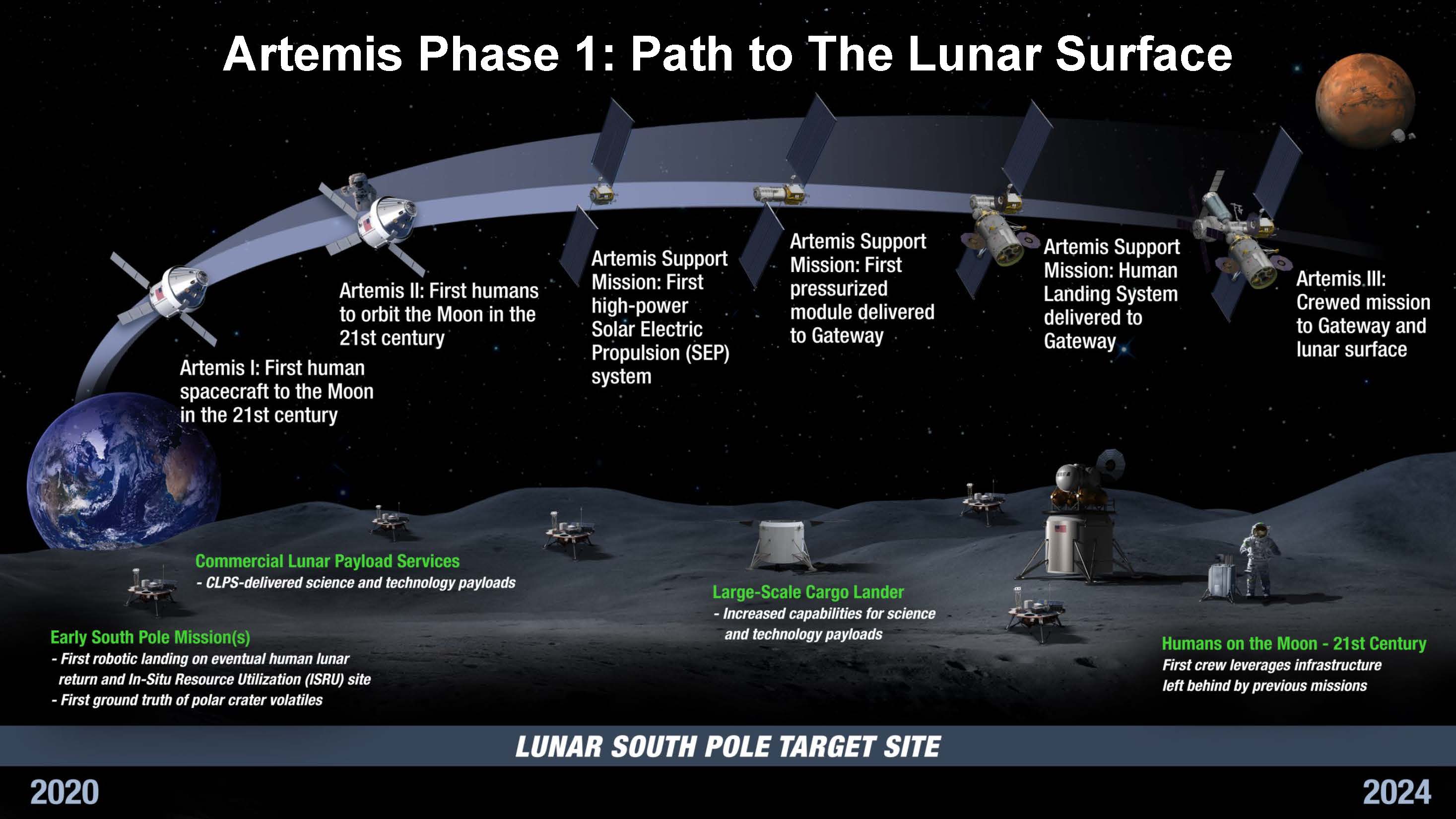
Artemis Program
The Artemis program is a Exploration of the Moon, Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a Moonbase, permanent base on the Moon to facilitate Human mission to Mars, human missions to Mars. It is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 and continue the direct exploration of Mars begun with data from the Mariner 9 probe in the same year. Two principal elements of the Artemis program are derived from the now-cancelled Constellation program: the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft (with the European Service Module, ESM instead of a US-built service module) and the Space Launch System's Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster#Five-segment booster, solid rocket boosters (originally developed for the Ares V). Other elements of the program, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of The Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made a deliberate impact on the surface of the Moon on 14 September, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of lunar exploration had been observations from Earth. The invention of the optical telescope brought about the first leap in the quality of lunar observations. Galileo Galilei is generally credited as the first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes, having made his own telescope in 1609, the mountains and craters on the lunar surface were among his first observations using it. Human exploration of the Moon since Luna 2 has consisted of both crewed and uncrewed missions. NASA's Apollo program has been the only program to successfully land humans on the Moon, which it did six times on the near side in the 20th century. The first human landing took place in 1969, when the Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong touched down on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Lunar Payload Services
Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) is a NASA program to hire companies to send small robotic landers and rovers to the Moon. Most landing sites are near the lunar south pole where they will scout for lunar resources, test in situ resource utilization (ISRU) concepts, and perform lunar science to support the Artemis lunar program. CLPS is intended to buy end-to-end payload services between Earth and the lunar surface using fixed-price contracts. The program achieved the first landing on the Moon by a commercial company in history with the IM-1 mission in 2024. The program was extended to add support for large payloads starting after 2025. The CLPS program is run by NASA's Science Mission Directorate along with the Human Exploration and Operations and Space Technology Mission directorates. NASA expects the contractors to provide all activities necessary to safely integrate, accommodate, transport, and operate NASA payloads, including launch vehicles, lunar lander spacecraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna-Glob
Luna-Glob (, meaning ''Lunar sphere'') is a Moon exploration programme by Roscosmos meant to progress toward the creation of a fully robotic lunar base. When completed, the programme is intended to continue with crewed lunar missions, starting with a crewed orbiter spacecraft called Orel. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Lunar Exploration Program
Korean Lunar Exploration Program () is led by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), which develops lunar orbiters and landers. The plan includes the Danuri, a lunar orbiter launched in 2022, and a future lunar lander, scheduled to be launched in 2032. Lunar orbiter South Korea's first lunar orbiter is named Danuri and its main mission is to perform various scientific and technological missions, including lunar observation. Danuri is equipped with payloads developed by research institutes in South Korea. Major payloads include a high-resolution camera from the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), a wide-field polarimetric camera from the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI), a magnetic field measuring instrument from Kyung Hee University, a gamma-ray spectrometer from the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources, and a space internet from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute. It was launched on August 4, 2022 from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Lunar Exploration Program
The (Japanese) Lunar Exploration Program () is a program of robotic and human missions to the Moon undertaken by the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and its division, the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS). It is also one of the three major enterprises of the JAXA Space Exploration Center (JSPEC). The main goal of the program is "to elucidate the origin and evolution of the Moon and utilize the Moon in the future".Lunar Exploration Program . Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The first spacecraft of the program, the uncrewed lunar orbiter (Kaguya), was launched from |
Chandrayaan Programme
The Chandrayaan programme ( ) (Sanskrit: 'Moon', 'Craft, Vehicle', ) also known as the Indian Lunar Exploration Programme is an ongoing series of outer space missions by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for the exploration of the Moon. The program incorporates a lunar orbiter, an impactor, a soft lander and a rover spacecraft. There have been three missions so far with a total of two orbiters, landers and rovers each. While the two orbiters were successful, the first lander and rover which were part of the Chandrayaan-2 mission, crashed on the surface. The second lander and rover mission Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed on the Moon on 23 August 2023, making India the first nation to successfully land a spacecraft in the lunar south pole region, and the fourth country to soft land on the Moon after the Soviet Union, the United States and China. Background The Indian space programme had begun with no intentions of undertaking sophisticated initiatives like h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Lunar Exploration Program
The Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP; ), also known as the Chang'e Project () after the Chinese Moon goddess Chang'e, is an ongoing series of robotic Moon missions by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). Engineering Program The program encompasses lunar orbiters, landers, rovers and sample return spacecraft, launched using the Long March series of rockets. A human lunar landing component may have been added to the program, after China publicly announced crewed lunar landing plans by the year 2030 during a conference in July 2023. The program's launches and flights are monitored by a telemetry, tracking, and command (TT&C) system, which uses radio antennas in Beijing and antennas in Kunming, Shanghai, and Ürümqi to form a VLBI antenna. A proprietary ground application system is responsible for downlink data reception. In 2019, China National Space Administration head Zhang Kejian announced that China is planning to build a scientific research s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HERACLES (spacecraft)
HERACLES (Human-Enhanced Robotic Architecture and Capability for Lunar Exploration and Science) was a proposed robotic transport system to and from the Moon by Europe (ESA), Japan (JAXA), and Canada ( CSA) that would feature a lander called the European Large Logistic Lander (EL3, or Argonaut), a Lunar Ascent Element, and a rover. The lander could be configured for different operations such as up to 1.5 tons of cargo delivery, sample-returns, or prospecting [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Lander (spacecraft)
The Lunar Lander was a robotic mission intended to send a lander vehicle to the Moon, led by ESA's Human Spaceflight and Operations directorate. The primary objective of the Lunar Lander mission was to demonstrate Europe's ability to deliver payload safely and accurately to the Moon's surface. More specifically the mission would have demonstrated the technologies required to achieve a soft and precise landing while autonomously avoiding surface hazards that can endanger landing and surface mission safety. These technologies will be an asset for future human and robotic exploration missions. However the project was put on hold at the 2012 ESA Ministerial Council. Mission scenario Launch and transfer Launching from Centre Spatial Guyanais, Kourou in late 2018 on a Soyuz launcher, the Lander is injected into a Highly Elliptical Orbit (HEO) by a Fregat-MT upper stage, through a series of intermediate orbits. Following Fregat separation, the lander uses its own propulsion to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of European Space Agency Programmes And Missions
The European Space Agency (ESA) operates a number of space missions, both individually and in collaborations with other space agencies such as Japanese JAXA, U.S. NASA, Chinese CNSA, as well as space agencies of ESA member states (eg. French CNES, Italian ASI, German DLR, Polish POLSA). A staple of the ESA's Science Doctrine is the Cosmic Vision Programme, a series of space science missions chosen by ESA to launch through competitions, similar to NASA's Discovery and New Frontiers programmes. It follows the Horizon 2000 and Horizon 2000+ programmes which launched notable missions such as '' Huygens'' (Titan lander), ''Rosetta'' (comet orbiter and lander), and ''Gaia'' (astrometry telescope). These missions are divided into two categories: "Sun and Solar System", space probes studying the Solar System (eg. Solar Orbiter studying the Sun and JUICE currently on its way to Jupiter) and "Astrophysics", space telescopes contributing to interstellar astronomy (eg. CHEOPS charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |