|
Ardito-class Destroyer
The ''Ardito'' class of destroyers consisted of two ships— and —that were built for the Italian (Royal Navy) in the 1910s. Design The ships of the ''Ardito'' class were long at the waterline and long overall, with a beam of and a draft of . They displaced standard and up to at full load. They had a crew of 4 officers and 65 enlisted men. The ships were powered by two Parsons steam turbines, with steam provided by four Thornycroft water-tube boilers. The engines were rated to produce for a top speed of , though in service they reached as high as from . At a more economical speed of , the ships could cruise for . The ships carried an armament that consisted of a single gun and four guns, along with two torpedo tubes. The 102 mm gun was placed on the forecastle and two of the 76 mm guns were mounted abreast the funnels, with the remaining pair at the stern. The torpedo tubes were in single mounts, both on the centerline. Ships Service histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy was abolished, following civil discontent that led to an 1946 Italian institutional referendum, institutional referendum on 2 June 1946. This resulted in a modern Italian Republic. The kingdom was established through the unification of several states over a decades-long process, called the . That process was influenced by the House of Savoy, Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia, which was one of Italy's legal Succession of states, predecessor states. In 1866, Italy Third Italian War of Independence, declared war on Austrian Empire, Austria in Italo-Prussian Alliance, alliance with Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and, upon its victory, received the region of Veneto. Italian troops Capture of Rome, entered Rome in 1870, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Register
A Navy Directory, Navy List or Naval Register is an official list of naval officers, their ranks and seniority, the ships which they command or to which they are appointed, etc., that is published by the government or naval authorities of a country. Background A Navy List fulfills an important function in international law in that warships are required by article 29 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea to be commanded by a commissioned officer whose name appears in the appropriate service list. Past copies of the Navy List are also important sources of information for historians and genealogists. When a ship is removed from the navy list of any country, the ship is said to be " stricken" (from the list). The British Royal Navy publishes annual lists of active and reserve officers, and biennial lists of retired officers. In 2016 ''The Navy List'', which had been officially published under that name since 1814, was renamed ''The Navy Directory''. The equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livorno
Livorno () is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 152,916 residents as of 2025. It is traditionally known in English as Leghorn (pronounced , "Leghorn" in the Oxford Dictionaries Online. or ). During the Italian Renaissance, Renaissance, Livorno was designed as an "ideal town". Developing considerably from the second half of the 16th century by the will of the House of Medici, Livorno was an important free port. Its intense commercial activity was largely dominated by foreign traders. Also the seat of consulates and shipping companies, it became the main port-city of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany. The high status of a multiethnic and multicultural Livorno lasted until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantiere Navale Fratelli Orlando
Cantiere navale fratelli Orlando (Orlando Brothers Shipyard) is a historical Italian shipyard in Livorno. History It was founded by Luigi Orlando and his brothers Giuseppe, Paolo and Salvatore who moved to Livorno from Genoa where in 1858 they had the management of Gio. Ansaldo & C., Ansaldo which produced marine machines and cannons, in 1861 they directed the factory to the construction of ships. Cantiere Navale Fratelli Orlando Luigi Orlando on 31 August 1865 signed a thirty years concession for the buildings and the area of the former ''Lazzaretto di San Rocco'' (Saint Roch lazaret) which was transformed in an arsenal by Tommaso Mati in 1852. The shipyard entered into works the following year, and on July 29, 1867, the first ship was launched, the Ironclad warship, ironclad for the ''Regia Marina''. The shipyard developed and built the gunboats ''Alfredo Cappellini'' (1868) and ''Faa di Bruno'' (1869) for the ''Regia Marina'' and on March 17, 1883 the most difficult launch wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
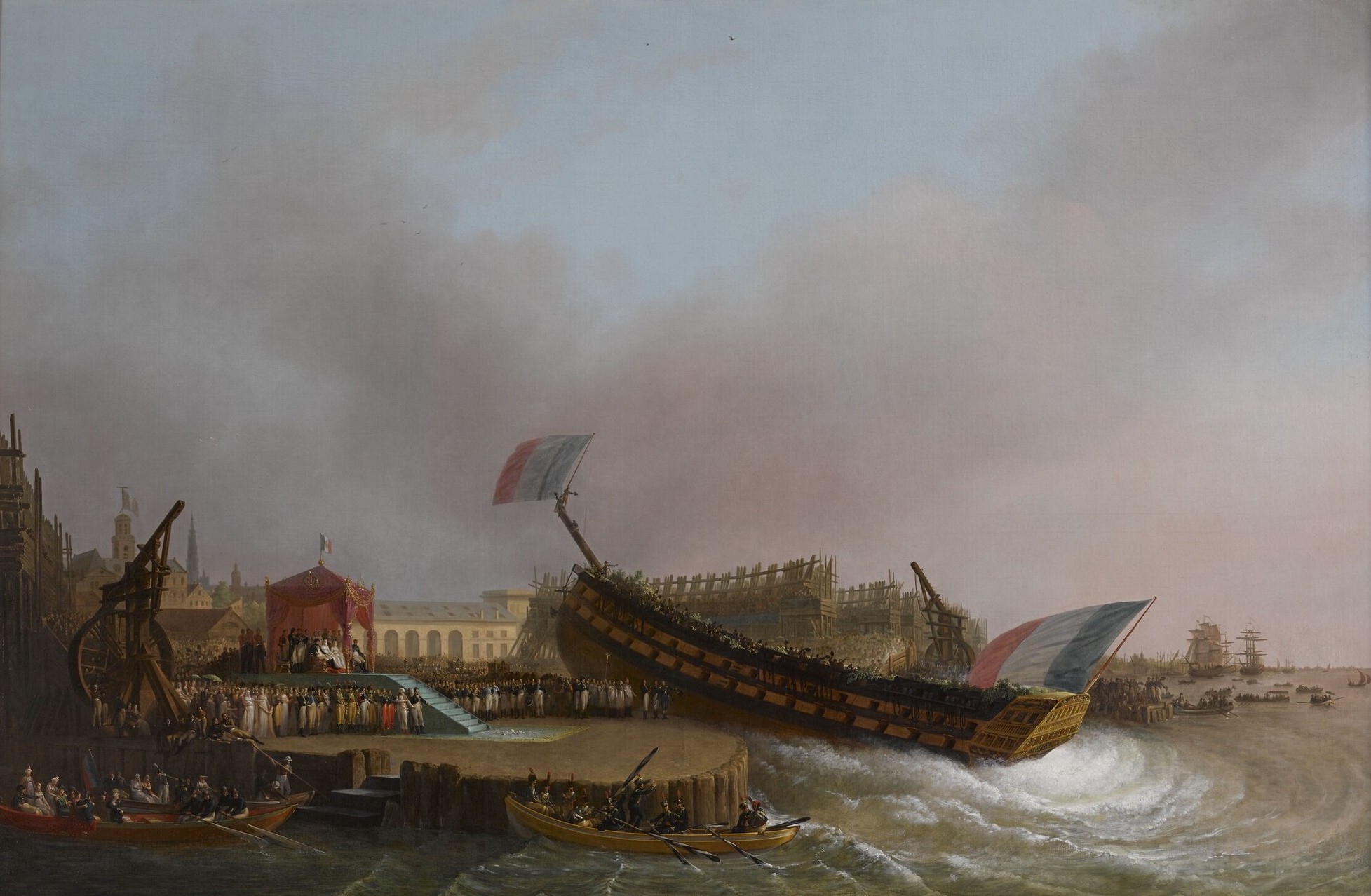
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performing of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back millennia, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and in addition to the size and weight of the vessel represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves Sailors' superstitions, many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as baptism#Boats and ships, christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow (ship), bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel Laying
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a shipbuilding, ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in a ship's life; the others are Ceremonial ship launching, launching, Ship commissioning, commissioning, and Ship decommissioning, decommissioning. Earlier, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centerline (nautical)
Center line, centre line or centerline may refer to: Sports * Center line, marked in red on an ice hockey rink * Centre line (football), a set of positions on an Australian rules football field * Centerline, a line that separates the service courts in Glossary of pickleball#C, pickleball Transportation * Center line, a road surface marking * Center line, a Taxiway#Taxiway markings, taxiway marking * Center line, a Runway#Markings, runway marking * CenterLine (OCTA), failed light-rail project in Orange County, California, U.S. * Centerline (nautical), the dividing line between port and starboard sides of a ship or boat * Centreline, a bus service in Manchester, England, later rebranded Metroshuttle Other uses * Center Line, Michigan, a place in the United States ** Center Line High School * Centre-Line Party, former name of the Australian Democrats political party * Centerline, an Engineering drawing abbreviations and symbols, engineering drawing symbol stylized by an overlapping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
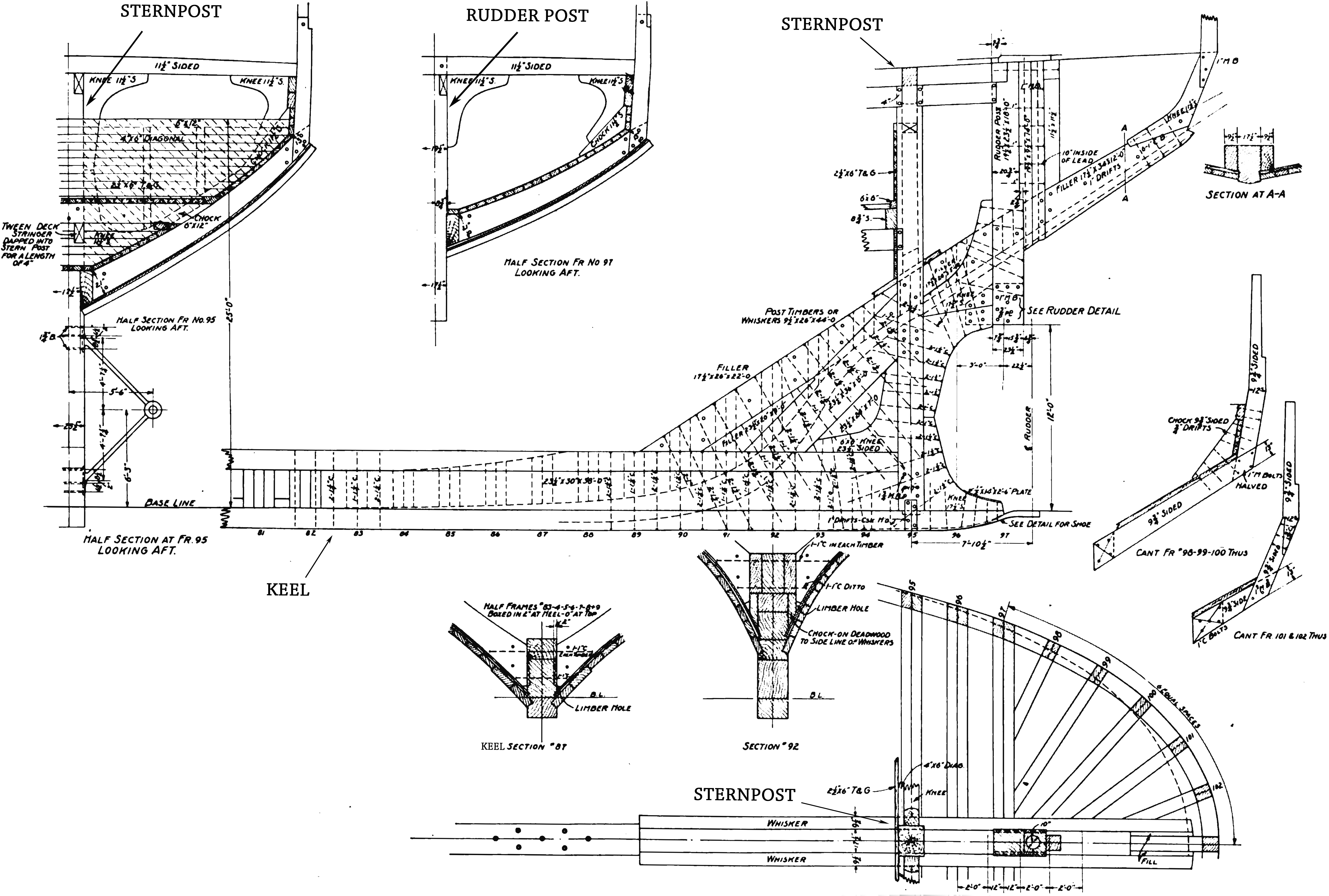
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel (ship)
A funnel is the smokestack or chimney on a ship used to expel boiler steam and smoke or engine exhaust gas, exhaust. They are also commonly referred to as stacks. Purpose The primary purpose of a ship's funnel(s) is to lift the exhaust gases clear of the deck, in order not to foul the ship's structure or decks, and to avoid impairing the ability of the crew to carry out their duties. In steam ships the funnels also served to help induce a boiler draught, convection draught through the boilers. Design Since the introduction of steam-power to ships in the 19th century, the funnel has been a distinctive feature of the silhouette of a vessel, and used for recognition purposes. Funnel area The required funnel cross-sectional area is determined by the volume of exhaust gases produced by the propulsion plant. Often this area is too great for a single funnel. Early steam vessels needed multiple funnels ( had 5 when launched), but as efficiency increased new machinery needed fewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck (ship), deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase "Wiktionary:before the mast, before the mast" which denotes anything related to ordinary sailors, as opposed to a ship's officers. History and design In medieval shipbuilding, a ship of war was usually equipped with a tall, multi-deck castle-like structure in the bow (ship), bow of the ship. It served as a platform for archers to shoot down on enemy ships, or as a defensive stronghold if the ship were boarded. A similar but usually much larger structure, called the aftcastle, was at the aft end of the ship, often stretching all the way from the main Mast (sailing), mast to the stern. Having such tall upper works on the ship was detrimental to sailing performance. As cannons were introduced and gunfire replaced boarding as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornycroft Boiler
Three-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler. The fundamental characteristic of the "three-drum" design is the arrangement of a steam drum above two water drums, in a triangular layout. Water tubes fill in the two sides of this triangle between the drums, and the furnace is in the centre. The whole assembly is then enclosed in a casing, leading to the exhaust flue. Firing can be by either coal or oil. Many coal-fired boilers used multiple firedoors and teams of stokers, often from both ends. Development Development of the three-drum boiler began in the late 19th century, with the demand from naval ships that required high power and a compact boiler. The move to water-tube boilers had already begun, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |