|
Archbishopric Of Sardica
The Diocese of Sofia and Plovdiv () is a Latin diocese of the Catholic Church"Diocese of Sofia e Plovdiv" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved October 7, 2016"Diocese of Sofia e Plovdiv" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved October 7, 2016 which includes the whole southern part of . The remainder of Bulgaria falls within the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of St Louis, Plovdiv
The Cathedral of St Louis (, ''katedrala „Sveti Ludvig“'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the city of Plovdiv, Bulgaria. Co-cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Sofia and Plovdiv, Diocese of Sofia and Plovdiv together with the Cathedral of St Joseph, Sofia, Cathedral of St Joseph in Sofia, it is one of the largest and most important Roman Catholic places of worship in the country. It was named after Louis IX of France, commonly known as "Saint Louis". The cathedral was constructed in the 1850s, during the time of vicar Andrea Canova. The first organ (music), organ in Bulgaria was installed in the cathedral in 1861, later replaced with a newer and larger one. A fire severely damaged the cathedral in 1931 and destroyed the wood-carved ceiling. The cathedral was reconstructed, with Krastyo Stamatov creating the frescoes and Kamen Petkov being the main architect. The cathedral was once again inaugurated on 8 May 1932. Architecturally, it features an Eclecticism, eclectic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelo Sodano
Angelo Raffaele Sodano (23 November 1927 – 27 May 2022) was an Italian prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as the Dean of the College of Cardinals from 2005 to 2019 and previously as the Cardinal Secretary of State from 1991 to 2006; Sodano was the first person since 1828 to serve simultaneously as Dean and Secretary of State. On 22 June 2006, Pope Benedict XVI accepted Sodano's resignation as Secretary of State, effective 15 September 2006. He had served in the foreign relations of the Holy See, diplomatic corps of the Holy See since 1959, including a decade as nuncio to Chile from 1978 to 1988. On 21 December 2019, it was reported that Sodano shielded sexually abusive clergy in the Legion of Christ. On the same day, Pope Francis accepted Sodano's resignation as Dean of the College of Cardinals. Early life The second of six children, Sodano was born on 23 November 1927 in Isola d'Asti, Piedmont, to Giovanni and Delfina Sodano. His father (1901–1991) was a Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
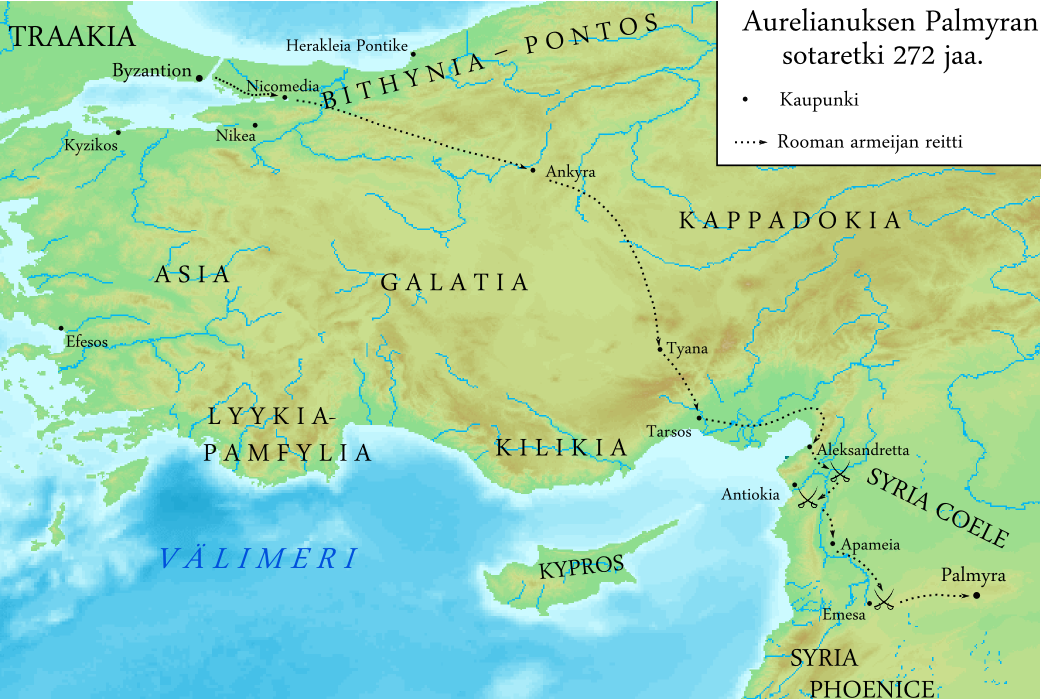
Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in modest circumstances, most likely in Moesia, Moesia Superior, he entered the Roman army in 235 and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' Gallienus#Assassination, assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus then ruled for three months, before Aurelian took the empire for himself. Aurelian was chosen Roman emperor by the Illyrians, Illyriciani as one of themselves. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi (people), Carpi. Aurelian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulpia Serdica
Ulpia may refer to: People * Ulpia gens, ancient Roman family which produced the emperor Trajan (98–117) Places A number of Roman settlements, mostly named in honour of the Emperor Trajan: * Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, the capital of Roman Dacia, located near modern Tapae in Romania * Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum, modern Nijmegen, Netherlands. * Colonia Ulpia Traiana, modern Xanten, Germany. * Civitas Ulpia Sueborum Nicretum, modern Ladenburg, Germany. * Colonia Ulpia Traiana Poetovio, modern Ptuj, Slovenia. * Ulpia Serdica, another name for Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. * Colonia Ulpia Oescensium or Oescus, near modern Pleven, Bulgaria. * Colonia Ulpia Ratiaria, near modern Archar, Bulgaria. * Marcianopolis Ulpia, another name for Marcianopolis, Bulgaria. * Ulpia Nicopolis, another name for Nicopolis ad Istrum, near modern Veliko Tarnovo, Bulgaria. * Ulpia Topira, another name for Topeiros, near modern Evlalo, northeastern Greece. * Colonia Concordia Ulpia Trajana Augusta Frug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history, during which, by the time of his death, the Roman Empire reached its maximum territorial extent. He was given the title of ('the best') by the Roman Senate. Trajan was born in the of Italica in the present-day Andalusian province of province of Seville, Seville in southern Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his came from the town of Todi, Tuder in the Regio VI Umbria, Umbria region of central Italy. His namesake father, Marcus Ulpius Traianus (father of Trajan), Marcus Ulpius Traianus, was a general and distinguished senator. Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of Domitian; in AD 89, serving as a in , he supported t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
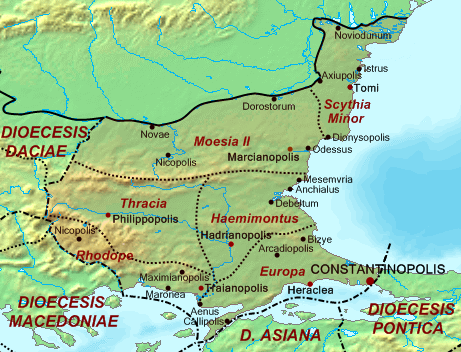
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkans, Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical Greece, Classical and Hellenistic period, Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia and Scythia Minor (Dobruja), Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Odrysia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Rome
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of classical Roman civilisation beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective oligarchy, not a democracy; a small number of powerful families largely monopolised the magistracies. Roman institutions underwent considerable chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal State
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to the era of the Egyptian, Hittite, and Mitanni conflict, as well as in ancient China. The relationships between vassal rulers and empires were dependent on the policies and agreements of each empire. While the payment of tribute and military service was common amongst vassal states, the degree of independence and benefits given to vassal states varied. Today, more common terms are puppet state, protectorate, client state, associated state, or satellite state. Historical examples Ancient Egypt The reign of Thutmose III (1479 BC – 1425 BC) laid the foundations for the systems that functioned during the Amarna period of Egypt. Vassal states in the Levant became fully integrated in Egypt's economy with the construction of harbours � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Kingdom (Roman Vassal State)
The Thracian kingdom, also called the Sapaean kingdom, was an ancient Thracian state in the southeastern Balkans that existed from the middle of the 1st century BC to 46 AD. Succeeding the Classical and Hellenistic era Odrysian kingdom of Thrace, it was dominated by the Sapaean tribe, who ruled from their capital Bizye in what is now northwestern Turkey. Initially only of limited relevance, its power grew significantly in the ancient Roman world as a client state of the late Roman Republic. After the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, Octavian (later emperor Augustus) installed a new dynasty that proved to be highly loyal and expansive. Conquering and ruling much of Thrace on behalf of the Roman Empire, it lasted until 46 AD, when Emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom and made Thracia into a Roman province. History In the late 2nd and early 1st century BC, Thrace was politically fractured and subject to constant fighting between local and foreign powers. As a result of a pau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome". Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Irving.Richest People in History Ancient Roman Crassus. Trivia-Library. '' The People's Almanac''. 1975–1981. Web. 23 December 2009."Often named as the richest man ever, a more accurate conversion of sesterce would put his modern figure between $200 million and $20 billion." Peter L. BernsteinThe 20 Richest People Of All Time/ref> Crassus began his public career as a military commander under Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his civil war. Following Sulla's assumption of the dictatorship, Crassus amassed an enormous fortune through property speculation. Crassus rose to political prominence following his victory over the slave revolt led by Spartacus, sharing the consulship with his rival Pompey the Great. A political and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |