|
Archaeology Of Denmark
The archaeology of Denmark presents an extraordinary rich and varied abundance of archaeological artifacts, exceptionally preserved by the climate and natural conditions in Denmark proper – including boglands, shallow waters, a cold and relatively unvarying climate. At the same time, archaeological ''study'' in Denmark has continually and fundamentally influenced the young science of archaeology from its very beginnings. History and excavations The prehistory of Denmark (Jutland) reveals that (following earlier Clactonian relics) many different cultures were to settle there and leave archaeological footprints since the end of the last ice age. Their discovery parallels the ongoing evolution of Danish archaeology itself, which began in the early nineteenth century with the establishment of the National Museum of Denmark, organised by Christian Thomsen. It was he who introduced the three-age system – Stone, Bronze and Iron ages - to European archaeology, thus for the first tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerthus
In Germanic paganism, Nerthus is a goddess associated with a ceremonial wagon procession. Nerthus is attested by first century A.D. Roman historian Tacitus in his ethnographic work ''Germania''. In ''Germania'', Tacitus records that a group of Germanic peoples were particularly distinguished by their veneration of the goddess. Tacitus describes the wagon procession in some detail: Nerthus's cart is found on an unspecified island in the "ocean", where it is kept in a sacred grove and draped in white cloth. Only a priest may touch it. When the priest detects Nerthus's presence by the cart, the cart is drawn by heifers. Nerthus's cart is met with celebration and peacetime everywhere it goes, and during her procession no one goes to war and all iron objects are locked away. In time, after the goddess has had her fill of human company, the priest returns the cart to her "temple" and slaves ritually wash the goddess, her cart, and the cloth in a "secluded lake". According to Tacitus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
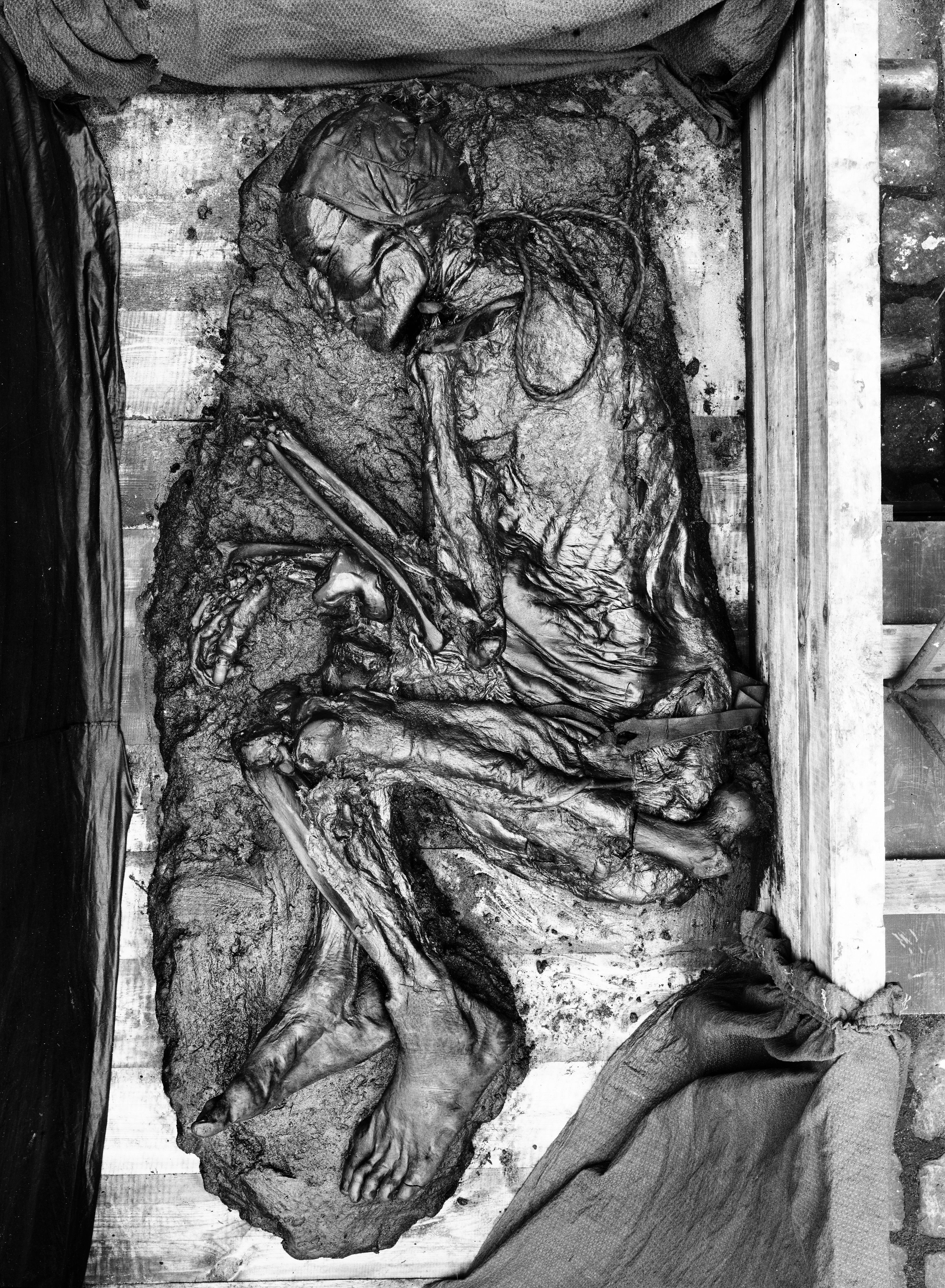
Tollund Man
The Tollund Man (died 405–384 BC) is a naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 5th century BC, during the period characterised in Scandinavia as the Pre-Roman Iron Age. He was found in 1950, preserved as a bog body near Silkeborg on the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The man's physical features were so well preserved that he was mistaken for a recent murder victim. Twelve years before his discovery, another bog body, Elling Woman, was found in the same bog. The cause of death has been determined to be by hanging. There is insufficient evidence to determine if the reason for the killing was a ritual sacrifice or a punitive execution. Discovery On 8 May 1950, peat cutters Viggo and Emil Hojgaard discovered a corpse in the peat layer of the Bjældskovdal peat bog, west of Silkeborg, Denmark, which was so well preserved that they at first believed they had discovered a recent murder victim. The Tollund Man lay away from firm ground, buried under of peat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, and Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, and Athens in Central Greece, and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the south-west coast of Asia Minor, and on Cyprus, while Mycenaean-influenced settlements appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corded Ware Culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between – 2350 BC, thus from the Late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded Ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine in the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. Autosomal genetic studies suggest that the Corded Ware culture originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures, evolving in parallel with (although under significant influence from) the Yamnaya; while the idea of direct male-line descent between them has not received significant support yet, IBD-sharing between the populations of these two cultures indicates that, at the very least, they came from a recent common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maglemosian Culture
Maglemosian ( 9000 – 6000 BC) is the name given to a culture of the early Mesolithic period in Northern Europe. In Scandinavia, the culture was succeeded by the Kongemose culture. Environment and location The name originates from the Danish archeological site ''Maglemose'', situated near Gørlev and Høng on western Zealand, southwest of lake Tissø. Here the first settlement of the culture was excavated in 1900, by George Sarauw. During the following century a long series of similar settlements were excavated from England to Poland and from Skåne in Sweden to northern France. When the Maglemosian culture flourished, sea levels were much lower than now and what is now mainland Europe and Scandinavia were linked with Britain. The cultural period overlaps the end of the last ice age, when the ice retreated and the glaciers melted. It was a long process and sea levels in Northern Europe did not reach current levels until almost 6000 BC, by which time they had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in Epipaleolithic Near East, the Levant and Epipaleolithic Caucasus, Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 Before Present, BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present, BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |