|
Arame Of Urartu
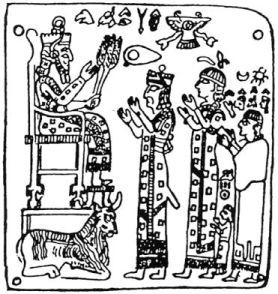
Arame or Aramu () was the first known king of the state of Urartu. Living at the time of King Shalmaneser III of the Neo Assyrian Empire (), Arame fought unsuccessfully against the Assyrian Empire. His capital at Arzashkun was captured by Shalmaneser. Sagunia, a previous capital, which was also captured by Shalamaneser, seems to have been located in the vicinity of Lake Van or Lake Urmia. Subsequent Urartian rulers probably came from a different dynasty than Arame. Arame has been suggested as the prototype of both Aram (and, correspondingly the popular given name Aram) and Ara the Beautiful, two of the legendary but not historically attested forefathers of the Armenian people. Khorenatsi's ''History'' (1.5) puts them six and seven generations after Hayk. It has been hypothesized that Aramu was a military leader of Aramean origin, the earliest recording of the name Aram referring to the Semitic speaking Aramean people of the Levant and southern Anatolia, appearing du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Urartu
This article lists the kings of Urartu (Ararat or Kingdom of Van), an Iron Age kingdom centered on Lake Van in eastern Asia Minor. Kings See also *List of Mesopotamian dynasties References *Boris Piotrovskii, ''The Ancient Civilization of Urartu'', London, 1969. *Igor Diakonoff, ''The Pre-History of the Armenian People'', Caravan Books, New York, 1988. *M. Chahin, ''The Kingdom of Armenia'', Curzon, London, 2001. External links Urartu {{DEFAULTSORT:Kings of Urartu Kings of Urartu, Lists of monarchs in Asia, Urartu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ara The Beautiful
Ara the Handsome (or the Beautiful, ) is a legendary Armenians, Armenian hero and king. He is the son of the legendary king Aram and a descendant of the Armenian patriarch Hayk. Scholars believe that Ara, Aram and Hayk were originally deities who were later reinterpreted as legendary human heroes. Ara represented a Dying-and-rising deity, dying-and-rising agricultural god and is thought to have embodied fertility within the Proto-Indo-European mythology, Indo-European triad of sovereignty, war, and fertility, along with Hayk and Aram. Ara is the subject of a popular legend in which the Akkadian queen Semiramis (''Shamiram'' in Armenian), desiring the handsome Armenian king, wages war against Armenia to capture him and bring him back to her, alive. Ara is killed in the war, and Semiramis attempts to bring him back to life. Name The etymology of the name ''Ara'' (also spelled , ) is uncertain, but it is phonologically similar to the Armenian descendants of Proto-Indo-European , such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Marshall Lang
David Marshall Lang (6 May 1924 – 20 March 1991), was a Professor of Caucasian Studies, School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London. He was one of the most productive British scholars who specialized in Georgian, Armenian and ancient Bulgarian history. Biography Lang was born in Bromley and was educated at Monkton Combe School and St John’s College, Cambridge where he was a Major Scholar and later held a Fellowship. As a 20-year-old graduate, he was serving as an officer in Iran in 1944 when he was appointed as acting Vice-Consul in Tabriz, Iran. He met many of the city's Armenian people and leaders. In 1949 he was a member of staff of the School of Oriental and African Studies at University of London. He began as lecturer in Georgian language, then as reader and in 1964 became professor of Caucasian studies. In 1953 he held a Senior Fellowship at the Russian Institute of Columbia University and in 1965 he was a visiting professor in Caucasian Studies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Agusi
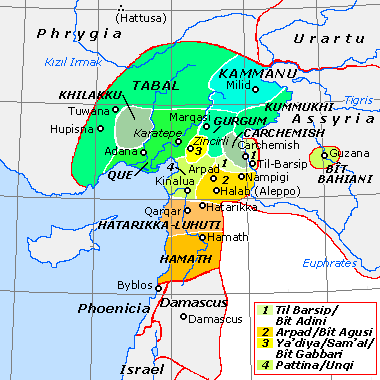
Bit Agusi or Bit Agushi (also written Bet Agus) was an ancient Aramaean Syro-Hittite state, established by Gusi of Yakhan at the beginning of the 9th century BC. It had included the cities of Arpad, Nampigi (Nampigu) and later on Aleppo Arpad was the capital of the state-kingdom. Bit Agusi stretched from the A'zaz area in the north to Hamath in the south. Chronology According to Dan'el Kahn, there were seven stages of Bit Agusi history in Northern Syria in the ninth and eighth centuries BC. * Stage 1 (858–ca. 842 BC). Early on, Bit Agusi was apparently free of political alliances with neighbors. Arame, the second king of Bit Agusi, submitted to Assyria freely in 858 BCE, along with many other rulers of the region, including the southern Anatolia. * Stage 2 (841–823 BC). A period of Bit Agusi subjugation to Assyria. * Stage 3. Around 823 BC, or maybe a little later, Bit Agusi leads a local alliance opposing Assyrian hegemony, and achieves independence. * Stage 4. Also, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramu
Arame or Aramu () was the first known king of the state of Urartu. Living at the time of King Shalmaneser III of the Neo Assyrian Empire (), Arame fought unsuccessfully against the Assyrian Empire. His capital at Arzashkun was captured by Shalmaneser. Sagunia, a previous capital, which was also captured by Shalamaneser, seems to have been located in the vicinity of Lake Van or Lake Urmia. Subsequent Urartian rulers probably came from a different dynasty than Arame. Arame has been suggested as the prototype of both Aram (and, correspondingly the popular given name Aram) and Ara the Beautiful, two of the legendary but not historically attested forefathers of the Armenian people. Khorenatsi's ''History'' (1.5) puts them six and seven generations after Hayk. It has been hypothesized that Aramu was a military leader of Aramean origin, the earliest recording of the name Aram referring to the Semitic speaking Aramean people of the Levant and southern Anatolia, appearing du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramean
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered central regions of what is now Syria. The Arameans were not a single nation or group; Aram was a region with local centers of power spread throughout the Levant. That makes it almost impossible to establish a coherent ethnic category of "Aramean" based on extralinguistic identity markers, such as material culture, lifestyle, or religion. The people of Aram were called "Arameans" in Assyrian texts and the Hebrew Bible, but the terms "Aramean" and “Aram” were never used by later Aramean dynasts to refer to themselves or their country, except the king of Aram-Damascus, since his kingdom was also called Aram. "Arameans" is merely an appellation of the geographical term Aram given to 1st millennium BCE inhabitants of Syria. At the beginn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered central regions of what is now Syria. The Arameans were not a single nation or group; Aram was a region with local centers of power spread throughout the Levant. That makes it almost impossible to establish a coherent ethnic category of "Aramean" based on extralinguistic identity markers, such as material culture, lifestyle, or religion. The people of Aram were called "Arameans" in Assyrian texts and the Hebrew Bible, but the terms "Aramean" and “Aram” were never used by later Aramean dynasts to refer to themselves or their country, except the king of Aram-Damascus, since his kingdom was also called Aram. "Arameans" is merely an appellation of the geographical term Aram given to 1st millennium BCE inhabitants of Syria. At the begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayk
Hayk (, ), also known as Hayk Nahapet (, , ), is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the ''History of Armenia'' attributed to the Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi and in the ''Primary History'' traditionally attributed to Sebeos. Fragments of the legend of Hayk are also preserved in the works of other authors, as well as in Armenian folk tradition. Etymology The name of the patriarch, ''Hayk'' (), is not exactly homophonous with the Armenian name for "Armenia," ''Haykʻ'' (). In Classical Armenian, ''Haykʻ'' is the nominative plural of ''hay'' ( հայ), the Armenian word for "Armenian." While Robert W. Thomson considers the etymology of ''Haykʻ'' (Հայք) from ''Hayk'' (Հայկ) to be impossible, other scholars consider the connection between the two to be obvious and derive ''Hayk'' from ''hay''/''Haykʻ'' via the suffix ''-ik''. Martirosyan, Hrach (2010). ''Etymological Dictionary of the Armenian Inherited Lexicon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Armenia (Moses Of Chorene)
The ''History of Armenia'' (), attributed to Movses Khorenatsi, is an early account of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, covering the legendary origins of the Armenian people as well as Armenia's interaction with Sassanid, Byzantine and Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, Arsacid empires down to the 5th century. It contains unique material on ancient Armenian legends, and such information on pagan (pre-Christian) Armenian as has survived. It also contains plentiful data on the history and culture of contiguous countries. The book had an enormous impact on Armenian historiography. In the text, the author self-identifies as a disciple of Mesrop Mashtots, Saint Mesrop, and states that he composed his work at the request of Isaac (Sahak), the Bagratuni dynasty, Bagratuni prince who fell in battle in 482. The traditional 5th-century dating of this work of Armenian literature has elicited much discussion and a recent, plausible proposal places the final version after 775. Khorenatsi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |