|
Arabic Scale
Arabic scale may refer to: *Double harmonic scale, a scale with two augmented seconds *Quarter tone scale, or 24 tone equal temperament * A seventeen tone unequal tuning that was historically used to describe Arabic music *Major locrian scale In music, the major Locrian scale, also called the ''Locrian major scale'', is the scale obtained by sharpening the second and third notes of the diatonic Locrian mode. With a tonic of C, it consists of the notes C D E F G A B. It can be described ..., a scale similar to locrian, also the aeolian mode with 5th and 3rd, Phrygian dominant scale with 5th and 2nd, or Blues Leading-Tone scale with 6th and tonic. {{disambig de:Zigeuner-Dur pt:Escala árabe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Harmonic Scale
The double harmonic major scaleStetina, Troy (1999). ''The Ultimate Scale Book'', p. 59. . is a musical scale with a flattened second and sixth degree. This scale is enharmonic to the Mayamalavagowla raga, Bhairav raga, Byzantine scale, Arabic scale (Hijaz Kar),Christiansen, Mike (2003). ''Mel Bay Complete Guitar Scale Dictionary'', p. 43. . and Gypsy major scale. It can be likened to a gypsy scale because of the diminished step between the 1st and 2nd degrees. ''Arabic scale'' may also refer to any Arabic mode, the simplest of which, however, to Westerners, resembles the double harmonic major scale. : Details The sequence of steps comprising the double harmonic scale is : :half, augmented second, half, whole, half, augmented second, half Or, in relation to the tonic note :minor second, major third, perfect fourth and fifth, minor sixth, major seventh, octave However, this scale is commonly represented with the first and last half step each being represented with qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Tone Scale
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches. Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in Persian traditional music. However, the first evidenced proposal of the equally-tempered quarter tone scale, or 24 equal temperament, was made by 19th-century music theorists Heinrich Richter in 1823Julian Rushton, "Quarter-Tone", ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan, 2001). and Mikhail Mishaqa about 1840. Composers who have written music using this scale include: Pierre Boulez, Julián Carrillo, Mildred Couper, George Enescu, Alberto Ginastera, Gérard Grisey, Alois Hába, Ljubica Marić, Charles Ives, Tristan Murail, Krzysztof P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
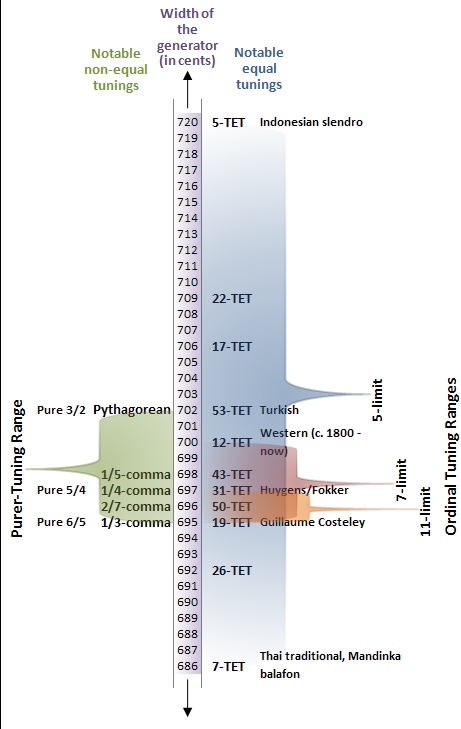
17 Equal Temperament
In music, 17 equal temperament is the musical temperament, tempered scale (music), scale derived by dividing the octave into 17 equal temperament, equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 70.6 cent (music), cents. 17-ET is the tuning of the regular diatonic tuning in which the tempered perfect fifth is equal to 705.88 cents, as shown in Figure 1 (look for the label "17-TET"). History and use Alexander John Ellis, Alexander J. Ellis refers to a tuning of seventeen tones based on perfect fourths and perfect fifth, fifths as the Arabic scale.Alexander John Ellis, Ellis, Alexander J. (1863). "On the Temperament of Musical Instruments with Fixed Tones", ''Proceedings of the Royal Society of London'', vol. 13. (1863–1864), pp. 404–422. In the thirteenth century, Middle-Eastern musician Safi al-Din Urmawi developed a theoretical system of seventeen tones to describe Arabic and Persian music, although the tones were not equally spaced. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Locrian Scale
In music, the major Locrian scale, also called the ''Locrian major scale'', is the scale obtained by sharpening the second and third notes of the diatonic Locrian mode. With a tonic of C, it consists of the notes C D E F G A B. It can be described as a whole tone scale extending from G to E, with F introduced within the diminished third interval from E to G. The scale therefore shares with the Locrian mode the property of having a diminished fifth above the tonic. It can also be the natural minor scale or Aeolian mode with raised third and lowered fifth intervals. It may also be derived from the Phrygian Dominant scale, but this time, the second is major, while the fifth is diminished. In English, Arabian scale may refer to what is known as the major Locrian scale. A version of the major Locrian scale is listed as ''mode 3'' in the French translation of Safi Al-Din's treatise Kitab Al-Adwar. This was a Pythagorean version of the scale. Aside from this Arabic version, interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |