|
Arab Conquest Of Sindh
The Umayyad conquest of Sindh took place in 711 AD and resulted in Sindh being incorporated as a province into the Umayyad Caliphate. The conquest resulted in the overthrow of the last Hindu dynasty of Sindh, the Brahmin dynasty, after the death of Raja Dahir. Background Although there was no connection between Arabia and Sindh, the war being started was due to events of piracy that plagued the Arabian Sea, at the time the Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate offered Raja Dahir protection and sovereignty if he would help him in quelling the piracy. Raja Dahir of Sindh had refused to return Arab rebels from SindhFredunbeg, Mirza Kalichbeg, "The Chachnama: An Ancient History of Sind", pp57 and '' Meds'' and others.Wink (2002), pg.164 ''Med'' pirates shipping from their bases at Kutch, Debal and Kathiawar during one of their raids had kidnapped Muslim women traveling from Sri Lanka to Arabia, thus providing a ''casus belli'' against Sindhi King Dahir. Raja Dahir expressed his inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin Dynasty Of Sindh
The Brahmin dynasty (), also known as the Chacha dynasty or Silaij dynasty, was a Sindhi Hindu dynasty that ruled the Sindh region, after usurping and overthrowing the Buddhist Rai dynasty of Sindh. Most of the information about its existence comes from the ''Chach Nama'', a historical account of the Chach-Brahmin dynasty. The members of the dynasty continued to administer parts of Sindh under the Umayyad Caliphate's Caliphal province of Sind after it Umayyad conquest of Sindh, fell in 712. These rulers include Hullishāh and Shishah. History The dynasty was founded by a Brahmin named Chach of Aror after he married the widow of Rai Sahasi II and usurped the Buddhist Rai dynasty. His claim was further secured by the killing of Rai Sahasi II's brother. The casus belli for the Ummayad invasion was Sindhi pirates seizing tribute sent from the king of Serendib to the Ummayad Caliph. For the campaign Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan granted a large army to the governor Al-Hajjaj ibn Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casus Belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bound by a mutual defense pact. Either may be considered an A declaration of war usually contains a description of the ''casus belli'' that has led the party in question to declare war on another party. Terminology The term ''casus belli'' came into widespread use in Europe in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries through the writings of Hugo Grotius (1653), Cornelius van Bynkershoek (1707), and Jean-Jacques Burlamaqui (1732), among others, and due to the rise of the political doctrine of '' jus ad bellum'' or " just war theory". The term is also used informally to refer to any "just cause" a nation may claim for entering into a conflict. It is used to describe the case for war given before the term came into wide use, and to descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloomsbury Publishing
Bloomsbury Publishing plc is a British worldwide publishing house of fiction and non-fiction. Bloomsbury's head office is located on Bedford Square in Bloomsbury, an area of the London Borough of Camden. It has a US publishing office located in New York City, an India publishing office in New Delhi, an Australian sales office in Sydney CBD, and other publishing offices in the UK, including in Oxford. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. History The company was founded in 1986 by Nigel Newton, who had previously been employed by other publishing companies. It was floated as a public registered company in 1994, raising £5.5 million, which was used to fund expansion of the company into paperback and children's books. A rights issue of shares in 1998 further raised £6.1 million, which was used to expand the company, in particular to found a U.S. branch. In 1998, Bloomsbury USA was established. Bloomsbury USA Books for Young Read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Muhallab Ibn Abi Sufra
Abū Saʿīd al-Muhallab ibn Abī Ṣufra al-Azdī (; 702) was an Arab general from the Azd tribe who fought in the service of the Rashidun, Umayyad and Zubayrid caliphs between the mid-640s and his death. He served successive terms as the governor of Fars (685–686), Mosul, Arminiya and Adharbayjan (687–688) and Khurasan (698–702). Al-Muhallab's descendants, known as the Muhallabids, became a highly influential family, many of whose members held high office under various Umayyad and Abbasid caliphs, or became well-known scholars. Throughout his early military career, he participated in the Arab campaigns against the Persians in Fars, Ahwaz, Sistan and Khurasan during the successive reigns of caliphs Umar (), Uthman (), Ali () and Mu'awiya I (). By 680, his tribe, the Azd of Oman, had become a major army faction in the Arabs' Basra garrison, the launchpad for the Persian conquest. Following the collapse of Umayyad rule in Iraq and Khurasan in 683–684, during the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kikan, Iran
Kikan (, also Romanized as Kīkan and Kīken; also known as Kīkin) is a village in Khav and Mirabad Rural District, Khav and Mirabad District, Marivan County, Kurdistan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 234, in 52 families. The village is populated by Kurds Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri .... References Towns and villages in Marivan County Kurdish settlements in Kurdistan province {{Marivan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The History Of India, As Told By Its Own Historians
''The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians'' is a book comprising translations of medieval Persian chronicles based on the work of Henry Miers Elliot. It was originally published as a set of eight volumes between 1867–1877 in London. The translations were in part overseen by Elliot, whose efforts were then extended and edited posthumously by John Dowson. The book has been reprinted several times, and is also available online. Elliot was keen to contrast what he saw as the justice and efficiency of the British rule compared to cruelty and despotism of Muslim rule. He expressed hope that it "will make our native subjects more sensible of the immense advantages accruing to them under the mildness and equity of our rule." Background Henry Miers Elliot was born in 1808. He was an administrator who worked for the British East India Company (EIC) and rose to the position of foreign secretary under the Governor-Generalships of Henry Hardinge and James Broun-Ramsay, 1st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the Muslim community and polity from the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (in 632 AD), to the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate (in 661 AD). The reign of these four caliphs is considered in Sunni Islam to have been "rightly-guided", meaning that it sunnah, constitutes a model to be followed and emulated from a religious point of view. This term is not used by Shia Muslims, who reject the rule of the first three caliphs as illegitimate. Following Muhammad's death in June 632, Muslim leaders debated who Succession to Muhammad, should succeed him. Unlike later caliphs, Rashidun were often chosen by some form of a small group of high-ranking companions of the Prophet in () or appointed by their predecessor. Muhammad's close companion A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role in early Islamic history. During his reign as caliph, he was known for ordering the official compilation of the standardized version of the Quran, known as Uthman's Quran, that is still being used today. Before his predecessor, Caliph Umar (), died in office, he appointed a committee of trustees to elect a successor. Uthman, who was then aged 68–71 years, was elected to succeed him and became the oldest person to hold such a high position. During his premiership, the Caliphate expanded further into Persia in 650 and reached as far as the provinces of Khorasan in 651. Uthman instituted centralized reforms in order to create a more cohesive administrative structure and fostered rapid economic growth. However, the last years of his re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
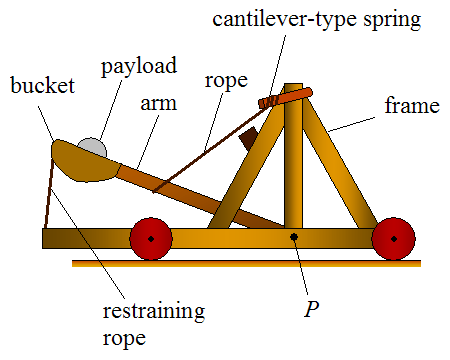
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert Tension (mechanics), tension or Torsion (mechanics), torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms which allow the catapult to launch a projectile such as rocks, cannon balls, or debris. During wars in the ancient times, the catapult was usually known to be the strongest heavy weaponry. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for Aircraft catapult, launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Bin Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqafī (; –) was an Arabs, Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His military exploits led to the establishment of the Sind (caliphal province), Islamic province of Sindh, and the takeover of the region from the Brahmin dynasty of Sindh, Sindhi Brahman dynasty and its ruler, Raja Dahir, who was subsequently decapitated with his head sent to al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf in Basra. With the capture of the then-capital of Aror by Arab forces, Muhammad ibn al-Qasim became the first Muslims, Muslim to have successfully captured Indian land, which marked the beginning of Islamic rulers in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim rule in South Asia. Muhammad ibn al-Qasim belonged to the Banu Thaqif, an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe that is concentrated around the city of Taif in western Arabian Peninsula, Arabia. After the Muslim conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camelry
Camel cavalry, or camelry (, ), is a generic designation for armed forces using camels as a means of transportation. Sometimes warriors or soldiers of this type also fought from camel-back with spears, bows, or firearms. Camel cavalry was a common element in desert warfare throughout history in the Middle East, due in part to the animals' high level of adaptability. They were better suited to working and surviving in arid environments than the horses of conventional cavalry. The smell of the camel, according to Herodotus, alarmed and disoriented horses, making camels an effective anti-cavalry weapon of the Achaemenid Persians in the Battle of Thymbra. Early history The first recorded use of the camel as a military animal was by the Qedarite Arab king Gindibu, said to have employed as many as 1,000 camels at the Battle of Qarqar in 853 BC. They were reportedly later used in the Battle of Thymbra in 547 BC, between Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire and Croesus of Lydia. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia is a historical region of Mesopotamia. It is located in the alluvial plain of Iraq from the Hamrin Mountains to the Faw Peninsula near the Persian Gulf. In the Middle Ages it was also known as the '' Sawad'' and al-Jazira al-sflia ("Lower Jazira"), which strictly speaking designated only the southern alluvial plain, and Arab Iraq, as opposed to Persian Iraq, the Jibal. Lower Mesopotamia was home to Sumer and Babylonia. Delimitation The medieval Arab geographers placed the northern border between Iraq and Upper Mesopotamia (the ''Jazirah'') in a line running from Anbar on the Euphrates to Tikrit on the Tigris, although later it was shifted to a line running due west from Tikrit, thus including several towns on the Euphrates past Anbar into Iraq. Geography An alluvial plain begins north of Tikrit Near Hamrin Mountains and extends to the Persian Gulf. Here the Tigris and Euphrates lie above the level of the plain in many places, and the whole area is a rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |