|
Aptostichus Angelinajolieae
''Aptostichus angelinajolieae'', the Angelina Jolie trapdoor spider, is a species of Euctenizidae, nocturnal arthropods who seize their prey after leaping out of their burrows and inject it with venom. It was described by the Auburn University professor Jason Bond in 2008, who named it after the American actress Angelina Jolie in recognition of her work on the United Nations High Commission for Refugees. It was one of only seven described species of '' Aptostichus'' until 2012, when it was joined by Bono's Joshua Tree trapdoor spider and 32 other species. Identification and distribution It is difficult to identify an individual as being an ''A. angelinajolieae'' specimen due to the species' morphological similarity to '' A. atomarius'' and '' A. stanfordianus''. A set of unique mitochondrial DNA nucleotide substitutions sets the species apart and allows a diagnosis. ''A. angelinajolieae'' inhabits the north of Monterey County, California, restricted to the Santa Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jason Bond
Jason E. Bond is a Professor of Entomology and the Schlinger Chair in Insect Systematics at the University of California, Davis. He was previously Professor of Biology, Chair of the Department of Biological Sciences and Director of the Auburn University Museum of Natural History at Auburn University. When he was an associate professor with the Department of Biology at East Carolina University, he discovered the spider '' Myrmekiaphila neilyoungi'' and numerous other species in the genus '' Aptostichus''. He went to undergraduate school at Western Carolina University, majoring in biology in 1993. He then went to receive his M.S. in Biology (1995) and Ph.D. in Evolutionary Systematics and Genetics (1999) from Virginia Tech. On August 6, 2008, Bond appeared on ''The Colbert Report'', where he named the spider ''Aptostichus stephencolberti'' after host Stephen Colbert. See also * Entomology * Arachnology Arachnology is the scientific study of arachnids, which comprise spiders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
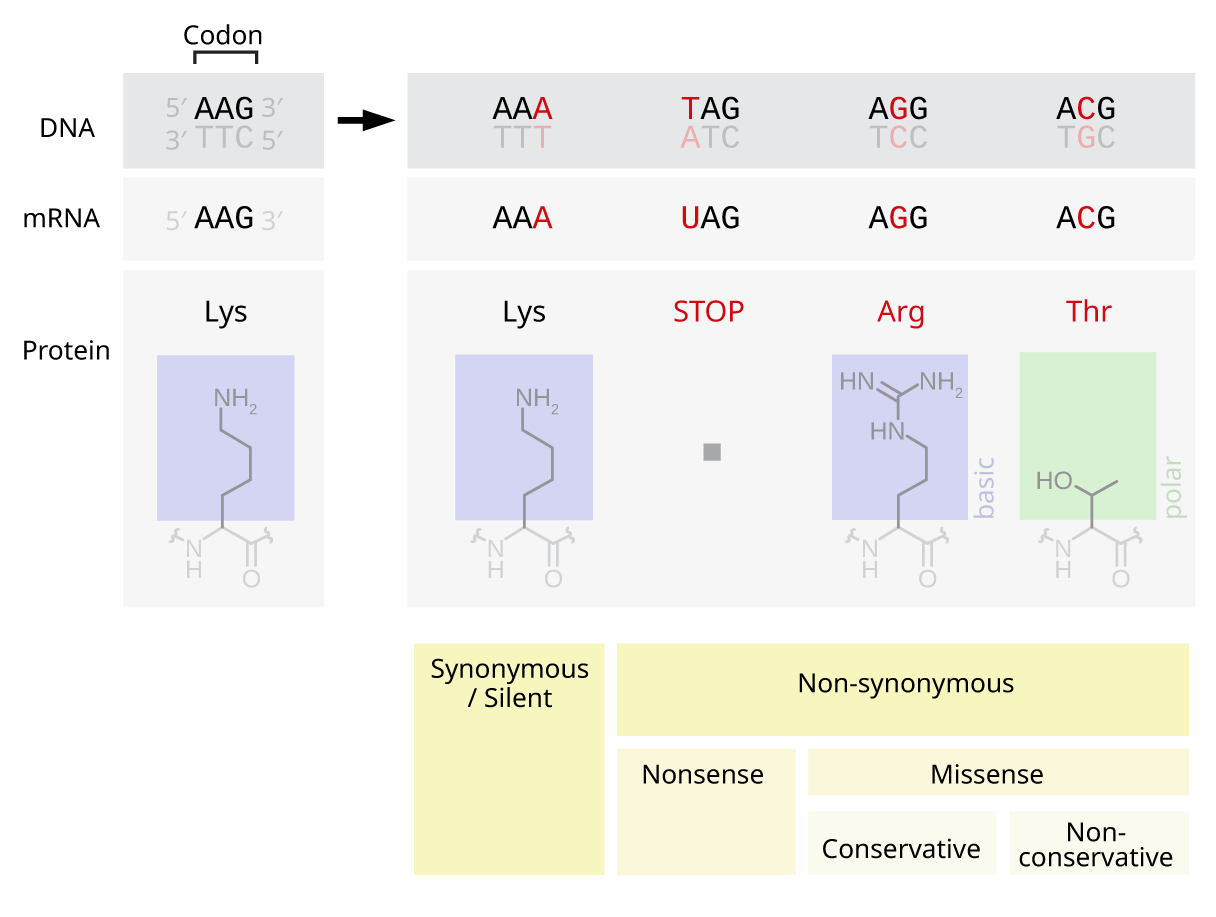
Nucleotide Substitution
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aptostichus Dantrippi
''Aptostichus'' is a genus of North American mygalomorph spiders in the family Euctenizidae, and was first described by Eugène Simon in 1891. They are found predominantly in southern California, United States. Behavior Members of the North American genus, ''Aptostichus'', assemble tunnels with side chambers, but they do not close these chambers with additional trapdoors. Species it contains forty-one species in the United States and Mexico: *''Aptostichus aguacaliente'' Bond, 2012 – USA *''Aptostichus angelinajolieae'' Bond, 2008 – USA *''Aptostichus anzaborrego'' Bond, 2012 – USA *''Aptostichus asmodaeus'' Bond, 2012 – USA *''Aptostichus atomarius'' Simon, 1891 (type) – USA *'' Aptostichus barackobamai'' Bond, 2012 – USA *''Aptostichus bonoi'' Bond, 2012 – USA *'' Aptostichus cabrillo'' Bond, 2012 – USA, Mexico *'' Aptostichus cahuilla'' Bond, 2012 – USA *'' Aptostichus cajalco'' Bond, 2012 – USA *'' Aptostichus chavezi'' Bond, 2012 – USA *'' Aptost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibling Species
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as bacterial strains or plant varieties), that is complex but it is not a species complex. A species complex is in most ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohesion Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes in zoologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore can be considered a single effective population. It has been shown that it takes only "one migrant per generation" to prevent populations from diverging due to drift. Populations can diverge due to selection even when they are exchanging alleles, if the selection pressure is strong enough. Gene flow is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. Migrants change the distribution of genetic diversity among populations, by modifying allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). High rates of gene flow can reduce the genetic differentiation between the two groups, increasing homogeneity. For this reason, gene flow has been thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aptostichus Stephencolberti
''Aptostichus stephencolberti'' is a species of spider in the family Euctenizidae, named after the American satirist Stephen Colbert. The spider was discovered on the California coastline in 2007. Spider ''Aptostichus stephencolberti'' is found on coastal dunes that extend from the Big Sur area to the San Francisco Peninsula at Point Lobos and Golden Gate. Compared to closely related species such as '' Aptostichus angelinajolieae'' (named after Angelina Jolie), ''Aptostichus stephencolberti'' is lighter in color. The male holotype and the female paratype both have brownish yellow legs, carapace and chelicerae, while the abdomen is lighter with dusky stripes. The male has six teeth, while the female has five. Naming The spider was named after Colbert after he reported on his television series ''The Colbert Report'' that Jason Bond, a professor of biology at East Carolina University, named a different species of spider ''Myrmekiaphila neilyoungi'', after the Canadian rock s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat regions covered with wind-swept sand or dunes with little or no vegetation are called '' ergs'' or ''sand seas''. Dunes occur in different shapes and sizes, but most kinds of dunes are longer on the stoss (upflow) side, where the sand is pushed up the dune, and have a shorter ''slip face'' in the lee side. The valley or trough between dunes is called a ''dune slack''. Dunes are most common in desert environments, where the lack of moisture hinders the growth of vegetation that would otherwise interfere with the development of dunes. However, sand deposits are not restricted to deserts, and dunes are also found along sea shores, along streams in semiarid climates, in areas of glacial outwash, and in other areas where poorly cemented s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant community and geographical feature found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intensity crown fires. Chaparral features summer-drought-tolerant plants with hard sclerophyllous evergreen leaves, as contrasted with the associated soft-leaved, drought-deciduous, scrub community of coastal sage scrub, found often on drier, southern facing slopes within the chaparral biome. Three other closely related chaparral shrubland systems occur in central Arizona, western Texas, and along the eastern side of central Mexico's mountain chains (mexical), all having summer rains in contrast to the Mediterranean climate of other chaparral formations. Chaparral comprises 9% of California's wildland vegetation and contains 20% of its plant species. The name comes fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to both the movement of individuals (animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, etc.) from their birth site to their breeding site ('natal dispersal'), as well as the movement from one breeding site to another ('breeding dispersal'). Dispersal is also used to describe the movement of propagules such as seeds and spores. Technically, dispersal is defined as any movement that has the potential to lead to gene flow. The act of dispersal involves three phases: departure, transfer, settlement and there are different fitness costs and benefits associated with each of these phases. Through simply moving from one habitat patch to another, the dispersal of an individual has consequences not only for individual fitness, but also for population dynamics, population genetics, and species distribution. Understanding dispersal and the consequences both for evolutionary strategies at a species level, and for processes at an ecosystem level, requires understanding on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinas Valley
The Salinas Valley is one of the major valleys and most productive agricultural regions in California. It is located west of the San Joaquin Valley and south of San Francisco Bay and the Santa Clara Valley. The Salinas River, which geologically formed the fluvial valley and generated its human history, flows to the northwest or 'up' along the principal axis and the length of the valley. The valley was named during the late 18th-century Spanish colonial Alta California period, and in Spanish ''Salina'' is the term for a salt marsh, salt lake, or salt pan. The seasonal Salinas River had brackish tule ponds in broad depressed areas, and more salinity during summer and when drought lowered flows. The valley runs in a southeast to northwest alignment. It begins south of San Ardo, framed by the central inner California Coast Ranges, continues northwestward continuously defined on the west by the Santa Lucia Range, on the east by the Gabilan Range, to its end and the river's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)