|
Appeal To The Stone
Appeal to the stone, also known as argumentum ad lapidem, is a logical fallacy that dismisses an argument as untrue or absurd. The dismissal is made by stating or reiterating that the argument is absurd, without providing further argumentation. This theory is closely tied to proof by assertion due to the lack of evidence behind the statement and its attempt to persuade without providing any evidence. Appeal to the stone is a logical fallacy. Specifically, it is an informal fallacy, which means that it relies on inductive reasoning in an argument to justify an assertion. Informal fallacies contain erroneous reasoning in content of the argument and not the form or structure of it, as opposed to formal fallacies, which contain erroneous reasoning in argument form. History Origin The name "appeal to the stone" originates from an argument between Dr. Samuel Johnson and James Boswell over George Berkeley's theory of subjective idealism (known previously as "immaterialism"). Subjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvitur Ambulando
() is a Latin phrase which means "it is solved by walking", referring to an anecdotal, practical solution to a seemingly complex philosophical problem. It is often attributed to Saint Augustine in a refutation of Zeno's paradoxes of motion. Philosophy Zeno's paradoxes state that if one were to examine individual moments of an object moving in a given direction, (as with an arrow flying towards a target) or overtaking a second, slower object, (as with Achilles challenging a tortoise to a race) one would not actually be able to find a moment of the act of change or motion taking place, thus proving Zeno's view of motion as illusory and impossible. The literal originates with Diogenes the Cynic in an account by Simplicius of Cilicia of a debate against Zeno; upon hearing his opponent's argument, Diogenes silently rose and walked away, thus implying the reality of motion to be so self-evident that any attempt to debate it is meaningless. The debate is retold by Pushkin in his eigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Hominem
, short for , refers to several types of arguments that are usually fallacious. Often currently this term refers to a rhetorical strategy where the speaker attacks the character, motive, or some other attribute of the person making an argument rather than the substance of the argument itself. This avoids genuine debate by creating a diversion often using a totally irrelevant, but often highly charged attribute of the opponent's character or background. The most common form of this fallacy is "A" makes a claim of "fact", to which "B" asserts that "A" has a personal trait, quality or physical attribute that is repugnant thereby going off-topic, and hence "B" concludes that "A" has their "fact" wrongwithout ever addressing the point of the debate. Other uses of the term are more traditional, referring to arguments tailored to fit a particular audience, and may be encountered in specialized philosophical usage. These typically refer to the dialectical strategy of using the target' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denialism
In the psychology of human behavior, denialism is a person's choice to denial, deny reality as a way to avoid believing in a psychologically uncomfortable truth. Denialism is an essentially irrational action that withholds the validation of a historical experience or event when a person refuses to accept an empirically verifiable reality. In the sciences, denialism is the rejection of basic facts and concepts that are undisputed, well-supported parts of the scientific consensus on a subject, in favor of ideas that are radical, controversial, or fabricated. The terms ''Holocaust denial'' and ''AIDS denialism'' describe the denial of the facts and the reality of the subject matters, and the term ''climate change denial'' describes denial of the Scientific opinion on climate change, scientific consensus that the climate change of planet Earth is a real and occurring event primarily caused in geologically recent times by human activity. The forms of denialism present the common feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Nauseam
' is a Latin term for an argument or other discussion that has continued to the figurative point of nausea. Dictionary.com For example, "this has been discussed '" indicates that the topic has been discussed extensively and those involved have grown sick of it. The fallacy of dragging the conversation to an ''ad nauseam'' state in order to then assert one's position as correct due to it not having been contradicted is also called ' ( to infinity) and argument from repetition. The term is defined by the '' |
Begging The Question
In classical rhetoric and logic, begging the question or assuming the conclusion (Latin: ) is an informal fallacy that occurs when an argument's premises assume the truth of the conclusion. Historically, begging the question refers to a fault in a dialectical argument in which the speaker assumes some premise that has not been demonstrated to be true. In modern usage, it has come to refer to an argument in which the premises assume the conclusion without supporting it. This makes it an example of circular reasoning.Herrick (2000) 248. Some examples are: *“Wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire because wool sweaters have higher wool content". ** The claim in this quote is that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire. However, the justification of this claim begs the question because it ''presupposes'' that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets: in other words, wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets because wool is better than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductio Ad Absurdum
In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical argument'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absurdity or contradiction. This argument form traces back to Ancient Greek philosophy and has been used throughout history in both formal mathematical and philosophical reasoning, as well as in debate. In mathematics, the technique is called ''proof by contradiction''. In formal logic, this technique is captured by an axiom for "Reductio ad Absurdum", normally given the abbreviation RAA, which is expressible in propositional logic. This axiom is the introduction rule for negation (see ''negation introduction''). Examples The "absurd" conclusion of a ''reductio ad absurdum'' argument can take a range of forms, as these examples show: * The Earth cannot be flat; otherwise, since the Earth is assumed to be finite in extent, we would find peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebuttal
In law, rebuttal is a form of evidence that is presented to contradict or nullify other evidence that has been presented by an adverse party. By analogy the same term is used in politics and public affairs to refer to the informal process by which statements, designed to refute or negate specific arguments (see Counterclaim) put forward by opponents, are deployed in the media. In law, special rules apply to rebuttal; rebuttal evidence or rebuttal witnesses must be confined solely to the subject matter of the evidence rebutted. New evidence on other subjects may not be brought in rebuttal. However, rebuttal is one of the few vehicles whereby a party may introduce surprise evidence or witnesses. The basic process is as follows: both sides of a controversy are obliged to declare in advance of trial what witnesses they plan to call, and what each witness is expected to testify to. When either a plaintiff (or prosecutor) or defendant brings direct evidence or testimony Testimo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Modifier
In linguistics, a modifier is an optional element in phrase structure or clause structure which ''modifies'' the meaning of another element in the structure. For instance, the adjective "red" acts as a modifier in the noun phrase "red ball", providing extra details about which particular ball is being referred to. Similarly, the adverb "quickly" acts as a modifier in the verb phrase "run quickly". Modification can be considered a high-level domain of the functions of language, on par with predication and reference. Premodifiers and postmodifiers Modifiers may come before or after the modified element (the ''head''), depending on the type of modifier and the rules of syntax for the language in question. A modifier placed before the head is called a premodifier; one placed after the head is called a postmodifier. For example, in ''land mines'', the word ''land'' is a premodifier of ''mines'', whereas in the phrase ''mines in wartime'', the phrase ''in wartime'' is a postmodifier of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
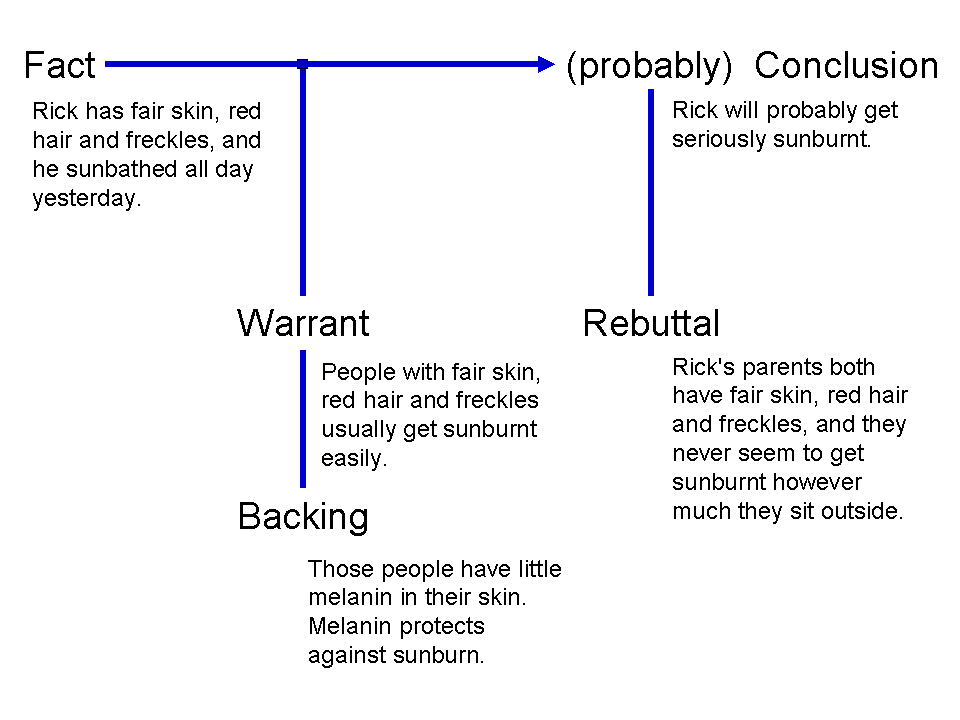
Toulmin Map
Stephen Edelston Toulmin (; 25 March 1922 – 4 December 2009) was a British philosopher, author, and educator. Influenced by Ludwig Wittgenstein, Toulmin devoted his works to the analysis of moral reasoning. Throughout his writings, he sought to develop practical arguments which can be used effectively in evaluating the ethics behind moral issues. His works were later found useful in the field of rhetoric for analyzing rhetorical arguments. The Toulmin model of argumentation, a diagram containing six interrelated components used for analyzing arguments, and published in his 1958 book ''The Uses of Argument'', was considered his most influential work, particularly in the field of rhetoric and communication, and in computer science. Biography Stephen Toulmin was born in London, UK, on 25 March 1922 to Geoffrey Edelson Toulmin and Doris Holman Toulmin. He earned his Bachelor of Arts degree from King's College, Cambridge, in 1943, where he was a Cambridge Apostle. Soon after, Tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulmin Argumentation Example
Toulmin is a surname and given name. Notable people with the name include: *Evelyn Toulmin (1877–1945), Anglo-Argentine cricketer *George Toulmin (1857–1923), British journalist, newspaper proprietor, and politician *George Hoggart Toulmin (1754–1817), English physician and geological thinker *Harry Toulmin (Unitarian minister) (1766–1823), son of Joshua Toulmin; served as president of Transylvania Seminary, Kentucky Secretary of State, and U.S. federal judge in Alabama *Harry Aubrey Toulmin, Sr. (1858–1942), American lawyer *Harry Theophilus Toulmin (1838–1916), U.S. federal judge *Joshua Toulmin (1740–1815), British theologian *Joshua Toulmin Smith (1816–1869), British political theorist, lawyer, and historian *Lucy Toulmin Smith (1838–1911), Anglo-American antiquarian and librarian *Stephen Toulmin (1922–2009), British philosopher, author, and educator *Theophilus Toulmin Garrard (1812–1902), American politician and Civil War Union general *Toulmin Smith, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |