|
Aphelia Peramplana
''Aphelia peramplana'' is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found from Portugal to Greece, as well as in North Africa ( Morocco, Tunisia), Malta, Crete, Iraq, from Iran east to Transcaucasia and in Siberia and Asia Minor. The wingspan is 25–31.5 mm., 2009: A brief study on the tribes Tortricini and Archipini (Lepidoptera: Tortricinae) from Iran. ''Entomofauna'' Band 30, Heft 10: 137–152. The larvae feed on '' Salix'', '' Anemone'', '' Ononis'' and '' Asphodelus'' species, as well as '' Pulsatilla pratensis'' and '' Calendula arvensis''. Larvae can be found in April and May. References Moths described in 1816 Aphelia (moth) Moths of Europe Moths of Asia Moths of Africa {{Archipini-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Hübner
Jacob Hübner (20 June 1761 – 13 September 1826, in Augsburg) was a German entomologist. He was the author of ''Sammlung Europäischer Schmetterlinge'' (1796–1805), a founding work of entomology. Scientific career Hübner was the author of ''Sammlung Europäischer Schmetterlinge'' (1796–1805), a founding work of entomology. He was one of the first specialists to work on the European Lepidoptera. He described many new species, for example ''Sesia bembeciformis'' and ''Euchloe tagis'', many of them common. He also described many new genera. He was a designer and engraver and from 1786 he worked for three years as a designer and engraver at a cotton factory in Ukraine. There he collected butterflies and moths including descriptions and illustrations of some in ''Beiträge zur Geschichte der Schmetterlinge'' (1786–1790) along with other new species from the countryside around his home in Augsburg. Hübner's masterwork "Tentamen" was intended as a discussion document. Inadver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Europe
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphelia (moth)
''Aphelia'' is a genus of tortrix moths in tribe Archipini.Archipini Species *'' Aphelia aglossana'' (Kennel, 1899) *'' Aphelia albidula'' Bai, 1992 *'' Aphelia albociliana'' (Herrich-Schaffer, 1851) *'' Aphelia alleniana'' (Fernald, 1882) *'' Aphelia caradjana'' (Caradja, 1916) *'' Aphelia caucasica'' Kostyuk, 1975 *'' Aphelia christophi'' Obraztsov, 1955 *'' Aphelia cinerarialis'' Bai, 1992 *'' Aphelia conscia'' Razowski, 1981 *'' Aphelia corroborata'' (Meyrick, 1918) *'' Aphelia deserticolor'' Diakonoff, 1983 *'' Aphelia disjuncta'' (Filipjev, 1924) *'' Aphelia effigies'' (Obraztsov, 1968) *'' Aphelia euxina'' (Djakonov, 1929) *'' Aphelia finita'' (Meyrick, 1924) *'' Aphelia flexiloqua'' Razowski, 1984 *'' Aphelia fuscialis'' Bai, 1992 *'' Aphelia galilaeica'' Obraztsov, 1968 *'' Aphelia gregalis'' Razowski, 1981 *'' Aphelia icteratana'' (Staudinger, 1880) *'' Aphelia ignoratana'' (Staudinger, 1880) *'' Aphelia imperfectana'' (Lederer, 1859) *'' Aphelia insincera'' (Meyrick, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Described In 1816
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendula Arvensis
''Calendula arvensis'' is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family known by the common name field marigold. It is native to central and southern Europe, and it is known across the globe as an introduced species. ''Calendula arvensis'' is an annual or biennial herb tall. The leaves are lance-shaped and borne on petioles from the slender, hairy stem. The inflorescence is a single flower head up to four centimeters wide with bright yellow to yellow-orange ray florets around a center of yellow disc florets. The fruit is an achene An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and indehiscent (they do not op ... which can take any of three shapes, including ring-shaped, that facilitate different methods of dispersal. Achene ''Calendula arvensis'' produce three types of achenes (fruits of the sunflower fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
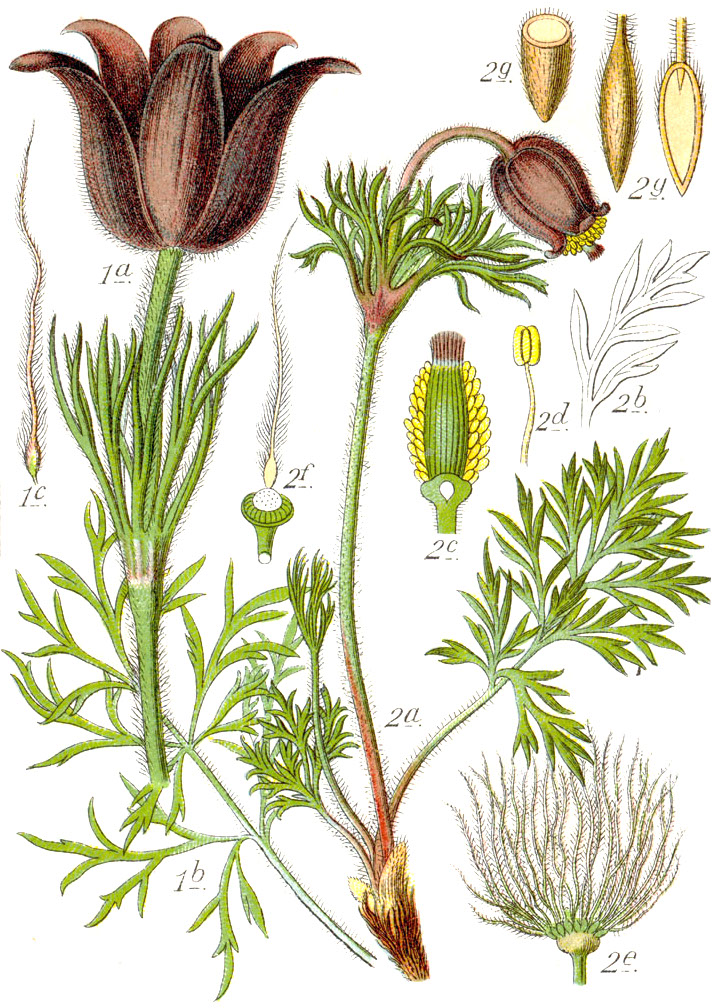
Pulsatilla Pratensis
''Pulsatilla pratensis'' (syn. ''Anemone pratensis''), the small pasque flower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ranunculaceae, native to central and eastern Europe, from southeast Norway and western Denmark south and east to Bulgaria. It grows from near sea level in the north of the range, up to in the south of its range.Flora Europaeapratensis''/ref>Blamey, M. & Grey-Wilson, C. (1989). ''Flora of Britain and Northern Europe''. . Name The Latin specific epithet ''pratensis'' means "from the meadow", referring to one of its typical habitats. Description It is a herbaceous perennial plant growing to tall. The leaves are finely divided and thread-like, and densely covered with silvery hairs. The flowers are long, pendulous, bell-like, the tepals with reflexed tips; flower colour varies from purple in the north of the species' range to greenish-violet in the south. The flowers are hermaphrodite, and are pollinated by bees; flowering is from early to mid spring. Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
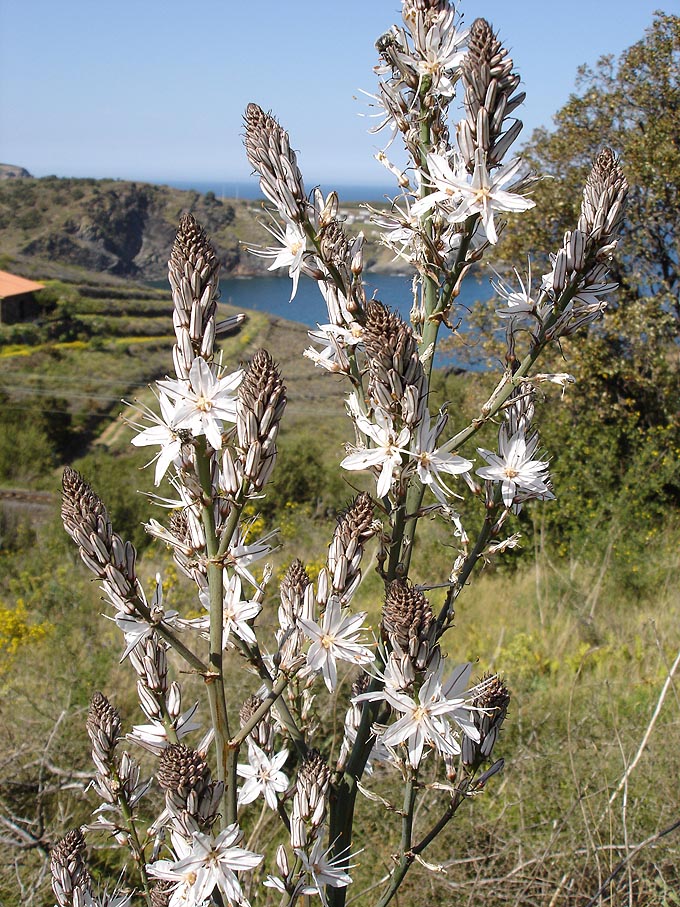
Asphodelus
''Asphodelus'' is a genus of mainly perennial flowering plants in the asphodel family Asphodelaceae that was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The genus was formerly included in the lily family (Liliaceae). The genus is native to temperate Europe, the Mediterranean, Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian Subcontinent, and some species have been introduced to, and are now naturalized in, other places such as New Zealand, Australia, Mexico and southwestern United States. Many asphodels are popular garden plants, which grow in well-drained soils with abundant natural light. Character The plants are hardy herbaceous perennials with narrow tufted radical leaves and an elongated stem bearing a handsome spike of white or yellow flowers. '' Asphodelus albus'' and '' A. fistulosus'' have white flowers and grow from high; '' A. ramosus'' is a larger plant, the large white flowers of which have a reddish-brown line in the middle of each segment. Etymology The genus name is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ononis
''Ononis'' is a large genus of perennial herbs and shrubs from the legume family Fabaceae. The members of this genus are often called restharrows as some species grow as weeds on arable lands whose tough stems would stop the harrow. They are natively distributed in Europe. In herbalism restharrow is used to treat bladder and kidney problems and water retention. The active ingredients in restharrow are essential oils, flavonoid-glycosides, and tannins. Restharrows are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the grey pug and '' Coleophora ononidella'' (which feeds exclusively on ''O. arvensis''). Species of ''Ononis'' The genus ''Ononis'' includes the following accepted species: * '' Ononis adenotricha'' Boiss. * '' Ononis alba'' Poir. * '' Ononis alopecuroides'' L., foxtail restharrow * '' Ononis angustissima'' Lam. * '' Ononis antiquorum'' L. * '' Ononis arvensis'' L., field restharrow * '' Ononis avellana'' Pomel * '' Ononis baetica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemone
''Anemone'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. Plants of the genus are commonly called windflowers. They are native to the temperate and subtropical regions of all continents except Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica. The genus is closely related to several other genera including '' Anemonoides'', '' Anemonastrum'', ''Hepatica'', and '' Pulsatilla''. Some botanists include these genera within ''Anemone''. Description ''Anemone'' are perennials that have basal leaves with long leaf-stems that can be upright or prostrate. Leaves are simple or compound with lobed, parted, or undivided leaf blades. The leaf margins are toothed or entire. Flowers with 4–27 sepals are produced singly, in cymes of 2–9 flowers, or in umbels, above a cluster of leaf- or sepal-like bracts. Sepals may be any color. The pistils have one ovule. The flowers have nectaries, but petals are missing in the majority of species. The fruits are ovoid to obovo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salix
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wingspan
The wingspan (or just span) of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the other wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777–200 has a wingspan of , and a wandering albatross (''Diomedea exulans'') caught in 1965 had a wingspan of , the official record for a living bird. The term wingspan, more technically extent, is also used for other winged animals such as pterosaurs, bats, insects, etc., and other aircraft such as ornithopters. In humans, the term wingspan also refers to the arm span, which is distance between the length from one end of an individual's arms (measured at the fingertips) to the other when raised parallel to the ground at shoulder height at a 90º angle. Former professional basketball player Manute Bol stood at and owned one of the largest wingspans at . Wingspan of aircraft The wingspan of an aircraft is always measured in a straight line, from wingtip to wingtip, independently of wing shape or sweep. Implications for aircraft design an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |