|
Apaseo El Grande
Apaseo el Grande is a city and Municipalities of Guanajuato, municipality located in Guanajuato, Mexico. The municipality covers 415.26 square kilometres (160 sq mi). It is bordered on the north by Comonfort and San Miguel de Allende, on the east by Querétaro City, Querétaro in the State of Querétaro, on the south by Apaseo el Alto, and on the west by Celaya. The municipality had a population of 85,319 inhabitants according to the 2010 census. In pre-Columbian times, the region was known as Andahe ("Close to the water") and Atlayahualco ("Place where water flows") by the Otomi people, Otomí and Nahua peoples, Nahua inhabitants. It was eventually known as Apatzeo ("Yellow flower") by the Purépecha people, Purépecha. Following the Spanish conquest 1525, Apaseo was the first town founded in what is now the state of Guanajuato. It received its present name of Apaseo el Grande in 1957, to avoid confusion with the neighboring town of Apaseo el Alto. Etymology The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otomi Language
Otomi ( ; ) is an Oto-Pamean languages, Oto-Pamean language spoken by approximately 240,000 indigenous Otomi people in the Mexican Plateau, central ''altiplano'' region of Mexico. Otomi consists of several closely related languages, many of which are not mutually intelligible. The word ''Hñähñu'' has been proposed as an endonym, but since it represents the usage of a single dialect, it has not gained wide currency. Linguists have classified the modern dialects into three dialect areas: the Northwestern dialects are spoken in Querétaro, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo and Guanajuato; the Southwestern dialects are spoken in the Mexico (state), State of Mexico; and the Eastern dialects are spoken in the highlands of Veracruz, Puebla, and eastern Hidalgo and villages in Tlaxcala and Mexico states. Like all other Oto-Manguean languages, Otomi is a tonal language, and most varieties distinguish three tones. Nouns are marked only for possessor; the plural number is marked with a definite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
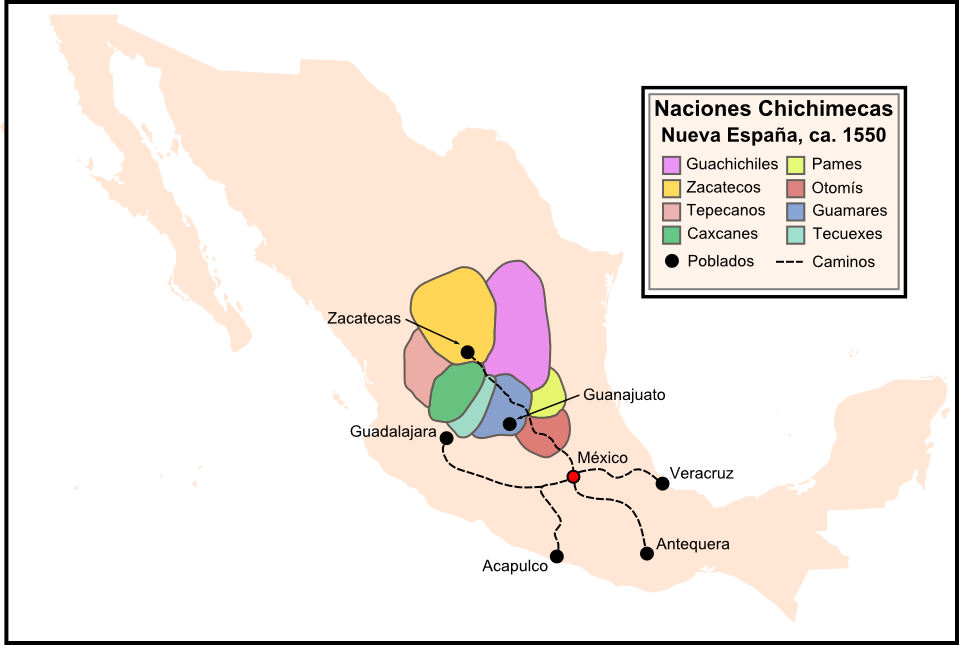
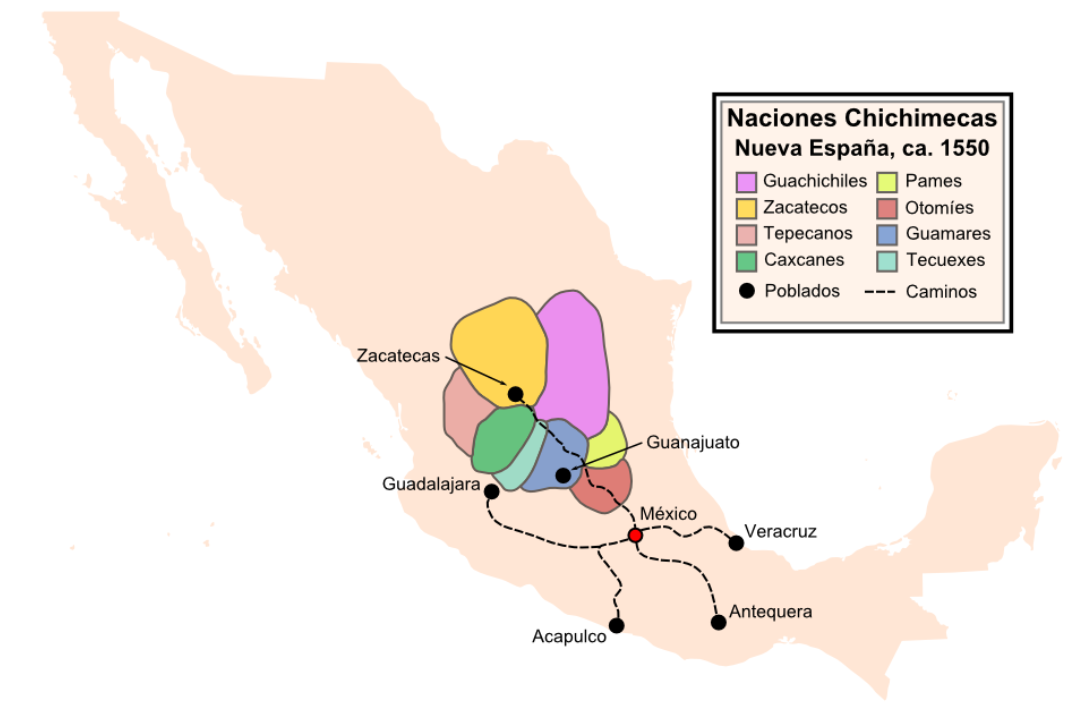
Chichimeca War
The Chichimeca War (1550–1600) was a military conflict between the Spanish Empire and the Chichimeca Confederation established in the territories today known as the Central Mexican Plateau, called by the Conquistadores La Gran Chichimeca. The epicenter of the hostilities was the region now called the Bajío. The Chichimeca War is recorded as the longest and most expensive military campaign confronting the Spanish Empire and indigenous people in Aridoamerica. The forty-year conflict was settled through several peace treaties driven by the Spaniards which led to the pacification and, ultimately, the streamlined integration of the native populations into the New Spain society. The Chichimeca War (1550–1600) began eight years after the two-year Mixtón War. It can be considered a continuation of the rebellion as the fighting did not come to a halt in the intervening years. The war was fought in what are the present-day Mexican states of Zacatecas, Guanajuato, Aguascaliente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. In the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "for the Spanish, the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit."Gradie, Charlotte M. "Discovering the Chichimecas" ''Academy of American Franciscan History'', Vol 51, No. 1 (July 1994), p. 68 Gradie noted that Chichimeca was used as a broad and generalizing term by outsiders, writing, " twas used by both Spanish and Nahuatl speakers to refer collectively to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
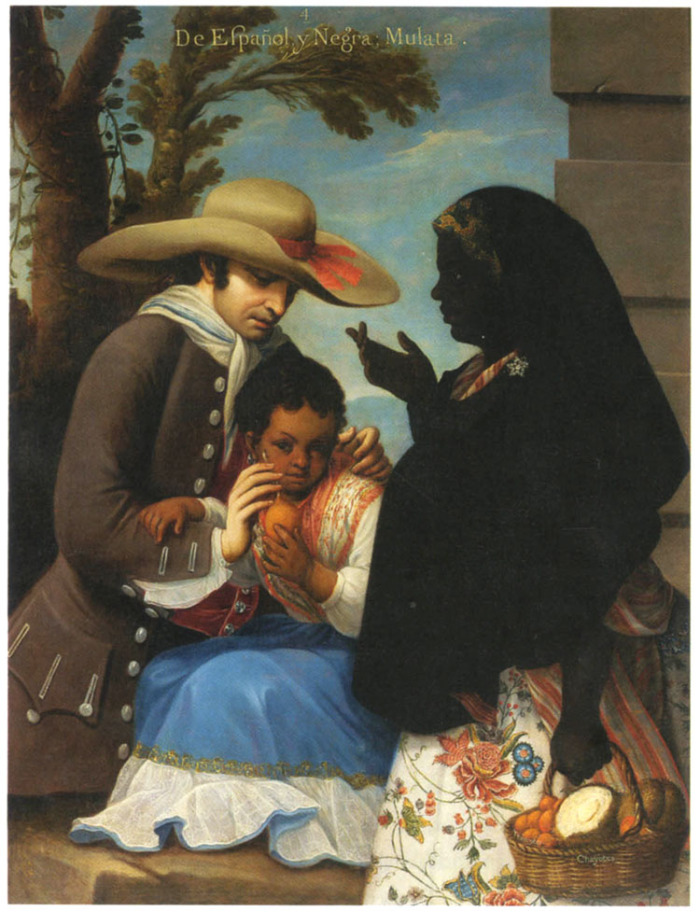
Mulattos
( , ) is a racial classification that refers to people of mixed African and European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the word is (). The use of this term began in the United States shortly after the Atlantic slave trade began and its use was widespread, derogatory and disrespectful. After the post Civil Rights Era, the term is now considered to be both outdated and offensive in the United States. In other Anglophone countries (the English-speaking world) such as English and Dutch-speaking West Indian countries, the word mulatto is still used. Countries with the highest percentages of persons who have equally high European and African ancestry — ''Mulatto'' — are the Dominican Republic (74%) and Cape Verde (71%). Mulattos in many Latin American countries, aside from predominately European and African ancestry, usually also have slight indigenous admixture. Race-mixing has been prevalent in Latin America for centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajío
The Bajío (the ''lowland'') is a cultural and geographical region within the Mexican Plateau, central Mexican plateau which roughly spans from northwest of Greater Mexico City, Mexico City to the main silver mines in the northern-central part of the country. This includes (from south to north) the states of Querétaro, Guanajuato, parts of Jalisco (Centro, Los Altos de Jalisco), Aguascalientes and parts of Zacatecas, San Luis Potosí and Michoacán. Located at the border between Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica, El Bajío saw relatively few permanent settlements and big civilizations during Pre-Columbian era, Pre-Columbian history, being mostly inhabited by the Otomi and semi-nomadic tribes known to the Aztecs as the "Chichimeca" peoples (poorly attested conglomerate of Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Nahua groups, from whom the Toltec and the Aztecs were probably descended). The tribes that inhabited the Bajío proved to be some of the hardest to conquer for the Spanish—peace was ul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn Legitimacy (family law), legitimate child to inheritance, inherit all or most of their parent's estate (law), estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture), or firstborn child (absolute primogeniture). Its opposite analogue is partible inheritance. Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g., male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogenitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fee Tail
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust, established by deed or settlement, that restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents that property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise alienated by the tenant-in-possession, and instead causes it to pass automatically, by operation of law, to an heir determined by the settlement deed. The terms ''fee tail'' and ''tailzie'' are from Medieval Latin , which means "cut(-short) fee". Fee tail deeds are in contrast to "fee simple" deeds, possessors of which have an unrestricted title to the property, and are empowered to bequeath or dispose of it as they wish (although it may be subject to the allodial title of a monarch or of a governing body with the power of eminent domain). Equivalent legal concepts exist or formerly existed in many other European countries and elsewhere; in Scots law tailzie was codified in the Entail Act 1685. Most common law jurisdictions have abolished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuño De Guzmán
Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán (1558) was a Spanish conquistador and colonial administrator in New Spain. He was the governor of the province of Pánuco (province), Pánuco from 1525 to 1533 and of Nueva Galicia from 1529 to 1534, and president of the first Royal Audiencia of Mexico – the high court that governed New Spain – from 1528 to 1530. He founded several cities in Northwestern Mexico, including Guadalajara. Originally a bodyguard of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles I of Spain, he was sent to Mexico to counterbalance the influence of the leader of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, Hernán Cortés, since the King worried he was becoming too powerful. As Governor of Pánuco, Guzmán cracked down hard on the supporters of Cortés, stripping him and his supporters of property and rights. He conducted numerous expeditions of conquest into the northwestern areas of Mexico, enslaving thousands of Indians and shipping them to the Spanish West Indies, Caribbean colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, and his small army of European soldiers and numerous indigenous allies, overthrowing one of the most powerful empires in Mesoamerica. Led by the Aztec ruler Moctezuma II, the Aztec Empire had established dominance over central Mexico through military conquest and intricate alliances. Because the Aztec Empire ruled via hegemonic control by maintaining local leadership and relying on the psychological perception of Aztec power — backed by military force — the Aztecs normally kept subordinate rulers compliant. This was an inherently unstable system of governance, as this situation could change with any alteration in the status quo. A combination of factors including superior weaponry, strategic alliances with oppresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |