|
Antimatter Comet
Antimatter comets and antimatter meteoroids are hypothetical comets and meteoroids composed solely of antimatter instead of ordinary matter. Although never actually observed, and unlikely to exist anywhere within the Milky Way, they have been hypothesized to exist, and their existence, on the presumption that hypothesis is correct, has been put forward as one possible explanation for various observed natural phenomena over the years. Hypothesized existence The hypothesis of comets made of antimatter can be traced back to the 1940s, when physicist Vladimir Rojansky proposed, in his paper "The Hypothesis of the Existence of Contraterrene Matter", the possibility that some comets and meteoroids could be made from "contraterrene" matter (i.e. antimatter). Such objects, Rojanski stated, would (if they existed at all) have their origins outside the Solar System. He hypothesized that if there were an antimatter object in orbit in the Solar System, it would exhibit the behavior of come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, a hyperbolic trajectory or hyperbolic orbit is the trajectory of any object around a central body with more than enough speed to escape the central object's gravitational pull. The name derives from the fact that according to Newtonian theory such an orbit has the shape of a hyperbola. In more technical terms this can be expressed by the condition that the orbital eccentricity is greater than one. Under simplistic assumptions a body traveling along this trajectory will coast towards infinity, settling to a final excess velocity relative to the central body. Similarly to parabolic trajectories, all hyperbolic trajectories are also escape trajectories. The specific energy of a hyperbolic trajectory orbit is positive. Planetary flybys, used for gravitational slingshots, can be described within the planet's sphere of influence using hyperbolic trajectories. Parameters describing a hyperbolic trajectory Like an elliptical orbit, a hyperbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatter counterpart) of the electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more photons. Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material. History Theory In 1928, Paul Dirac published a paper proposing that electrons can have both a positive and negative charge. This paper introduced the Dirac equation, a unification of quantum mechanics, special relativity, and the then-new concept of electron Spin (physics), spin to explain the Zeeman effect. The paper did not explicitly predict a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Volt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV), also written electron-volt and electron volt, is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equal to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 revision of the SI, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences, because a particle with electric charge ''q'' gains an energy after passing through a voltage of ''V''. Definition and use An electronvolt is the amount of energy gained or lost by a single electron when it moves through an electric potential difference of one volt. Hence, it has a value of one volt, which is , multiplied by the elementary charge Therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Lightning
Ball lightning is a rare and unexplained phenomenon described as Luminosity, luminescent, spherical objects that vary from pea-sized to several meters in diameter. Though usually associated with thunderstorms, the observed phenomenon is reported to last considerably longer than the split-second flash of a lightning strike, lightning bolt, and is a phenomenon distinct from St. Elmo's fire and will-o'-the-wisp. Some 19th-century reports describe balls that eventually explode and leave behind an odor of sulfur. Descriptions of ball lightning appear in a variety of accounts over the centuries and have received attention from scientists. An optical spectrum of what appears to have been a ball lightning event was published in January 2014 and included a video at high frame rate. Nevertheless, scientific data on ball lightning remain scarce. Although laboratory experiments have produced effects that are visually similar to reports of ball lightning, how these relate to the supposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Energy Research Establishment
The Atomic Energy Research Establishment (AERE), also known as Harwell Laboratory, was the main Headquarters, centre for nuclear power, atomic energy research and development in the United Kingdom from 1946 to the 1990s. It was created, owned and funded by the British Government. A number of early research reactors were built here starting with GLEEP in 1947 to provide the underlying science and technology behind the design and building of Britain's nuclear reactors such as the Windscale Piles and Calder Hall nuclear power station. To support this an extensive array of research and design laboratories were built to enable research into all aspects of nuclear reactor and fuel design, and the development of pilot plants for fuel reprocessing. The site became a major employer in the Oxford area. In the 1990s demand for government-led research had significantly decreased and the site was subsequently gradually diversified to allow private investment, and was known from 2006 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culham Laboratory
The Culham Centre for Fusion Energy (CCFE) is the UK's national laboratory for fusion research. It is located at the Culham Science Centre, near Culham, Oxfordshire, and is the site of the Mega Ampere Spherical Tokamak (MAST) and the now closed Joint European Torus (JET) and Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak (START). Formerly known as UKAEA Culham, the laboratory was renamed in October 2009 as part of organisational changes at its parent body, the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA). Since 2016, the director has been Professor Ian Chapman, and the centre has been engaged in work towards the final detailed design of ITER as well as preparatory work in support of DEMOnstration Power Plant (DEMO). In 2014 it was announced the centre would house the new Remote Applications in Challenging Environments (RACE). Culham Campus The centre occupies the site of the former Royal Navy airfield RNAS Culham (HMS ''Hornbill''), which was transferred to UKAEA in 1960. The UKAEA co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clyde Cowan
Clyde Lorrain Cowan Jr (December 6, 1919 – May 24, 1974) was an American physicist and the co-discoverer of the neutrino along with Frederick Reines. The discovery was made in 1956 in the neutrino experiment. Reines received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995. Early life Born the oldest of four children in Detroit, Detroit, Michigan, Cowan's family moved to St. Louis, Missouri, St. Louis, Missouri, where he began his education attending Public school (government funded), public schools. While attending the Missouri University of Science and Technology, Missouri School of Mines and Metallurgy in Rolla, Missouri, Cowan was Editor-in-Chief of the Missouri Miner newspaper from 1939–1940, and graduated in 1940 with a Bachelor of Science, BS in chemical engineering. Military career Cowan was a Captain (United States), captain in the United States Army Air Forces, where he earned a Bronze Star Medal, bronze star in World War II. From 1936–1940 he was in the Reserve Office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willard Libby
Willard Frank Libby (December 17, 1908 – September 8, 1980) was an American physical chemist noted for his role in the 1949 development of radiocarbon dating, a process which revolutionized archaeology and palaeontology. For his contributions to the team that developed this process, Libby was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1960. A 1931 chemistry graduate of the University of California, Berkeley, from which he received his doctorate in 1933, he studied radioactive elements and developed sensitive Geiger counters to measure weak natural and artificial radioactivity. During World War II he worked in the Manhattan Project's Substitute Alloy Materials (SAM) Laboratories at Columbia University, developing the gaseous diffusion process for uranium enrichment. After the war, Libby accepted a professorship at the University of Chicago's Institute for Nuclear Studies, where he developed the technique for dating organic compounds using carbon-14. He also discovered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
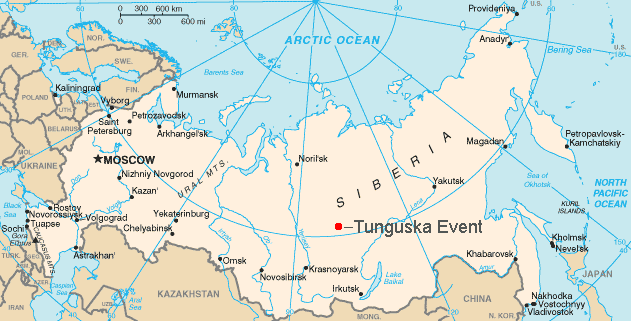
Tunguska Event
The Tunguska event was a large explosion of between 3 and 50 TNT equivalent, megatons that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of 30 June 1908. The explosion over the sparsely populated East Siberian taiga felled an estimated 80 million trees over an area of of forest, and eyewitness accounts suggest up to three people may have died. The explosion is attributed to a meteor air burst, the atmospheric explosion of a stony asteroid about wide. The asteroid approached from the east-south-east, probably with a relatively high speed of about . Though the incident is classified as an impact event, the object is thought to have exploded at an altitude of rather than hitting the Earth's surface, leaving no impact crater. The Tunguska event is the largest impact event on Earth in recorded history, though List of impact craters on Earth, much larger impacts are believed to have occurred in prehistoric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida State University
Florida State University (FSU or Florida State) is a Public university, public research university in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida and a preeminent university in the state. Chartered in 1851, it is located on Florida's oldest continuous site of higher education. Florida State University maintains 17 colleges, as well as 58 centers, facilities, labs, institutes, and professional training programs. In 2023, the university enrolled 43,701 students from all 50 states and 135 countries. Florida State is home to Florida's only national laboratory, the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, and was instrumental in the commercial development of the anti-cancer drug Taxol. Florida State University also operates the John & Mable Ringling Museum of Art, the State Art Museum of Florida and one of the nation's largest museum/university complexes. The university is accredited by the Southern Association of College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |