|
Anti-communist Insurgencies In Central And Eastern Europe
Anti-communist insurgencies continued in Central and Eastern Europe during and after World War II. They were suppressed by the Soviet Union and its satellite states. Prominent movements include: *The Ukrainian Insurgent Army fought a guerrilla war until they were defeated in 1956. *Mirdita Tribesmen under Gjon Markagjoni sparked an uprising against the Hoxhaist regime in 1945, and were suppressed in 1950. *The anti-Soviet Hungarian Revolution took place in 1956. Unlike the other movements given here, it was aimed against the domination of the Soviet Union, but not against the ideas of socialism and communism. Hungarian communists were among the leaders of the revolution, and Béla Király, who commanded the National Guard in the revolution, described it as being held by the working class and put emphasis on the revolutionary workers' councils. *Baltic partisans known as the "Forest Brothers" fought until they were defeated in the mid 1950s. * Romanian anti-communist resistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-communism
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism, communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, when the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in an intense rivalry. Anti-communism has been an element of many movements and different political positions across the political spectrum, including anarchism, centrism, conservatism, fascism, liberalism, nationalism, social democracy, socialism, leftism, and libertarianism, as well as broad movements #Evasion of censorship, resisting communist governance. Anti-communism has also been expressed by #Religions, several religious groups, and in art and #Literature, literature. The first organization which was specifically dedicated to opposing communism was the Russian White movement, which fought in the Russian Civil War starting in 1918 against the recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusaders (guerrilla)
The Crusaders (, also known as Škripari) were a Croatian pro-Ustashe anti-communism, anti-communist guerrilla army. Their activities started after the capitulation of the Independent State of Croatia in May 1945, towards the end of World War II. The Crusaders' activities ended in 1950. During World War II The leadership of the Independent State of Croatia was preparing for the impending major battles against the Yugoslav Partisans who were in 1944 reinforced by the Red Army. They wanted to establish a front on the Varaždin-Koprivnica-Sisak-Petrinja-Karlovac line. They also wanted to establish a guerrilla army that would fight behind the front lines. This guerrilla force would also, if necessary, fight the British, Americans, and Soviets. During the penultimate meeting of the Main Ustaše Headquarters, it was discussed whether a guerrilla army should be created, and if so, how this army would fight. A plan for moving the Croatian Army through Bosnia (region), Bosnia was already a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
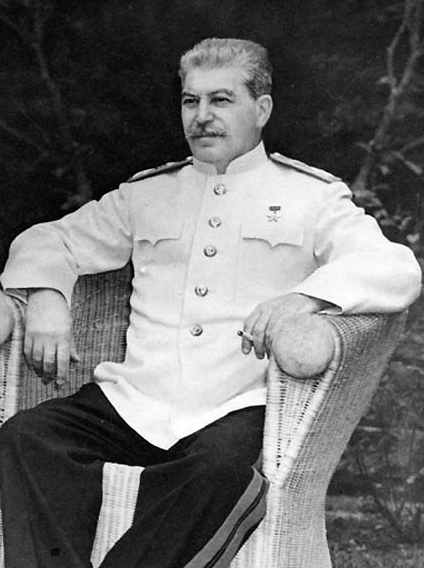
Stalinist
Stalinism (, ) is the totalitarian means of governing and Marxist–Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1927 to 1953 by dictator Joseph Stalin and in Soviet satellite states between 1944 and 1953. Stalinism included the creation of a one man totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory of socialism in one country, forced collectivization of agriculture, intensification of class conflict, a cult of personality, and subordination of the interests of foreign communist parties to those of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, which Stalinism deemed the leading vanguard party of communist revolution at the time. After Stalin's death and the Khrushchev Thaw, a period of de-Stalinization began in the 1950s and 1960s, which caused the influence of Stalin's ideology to begin to wane in the USSR. Stalin's regime forcibly purged society of what it saw as threats to itself and its brand of communism (so-called "enemies of the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
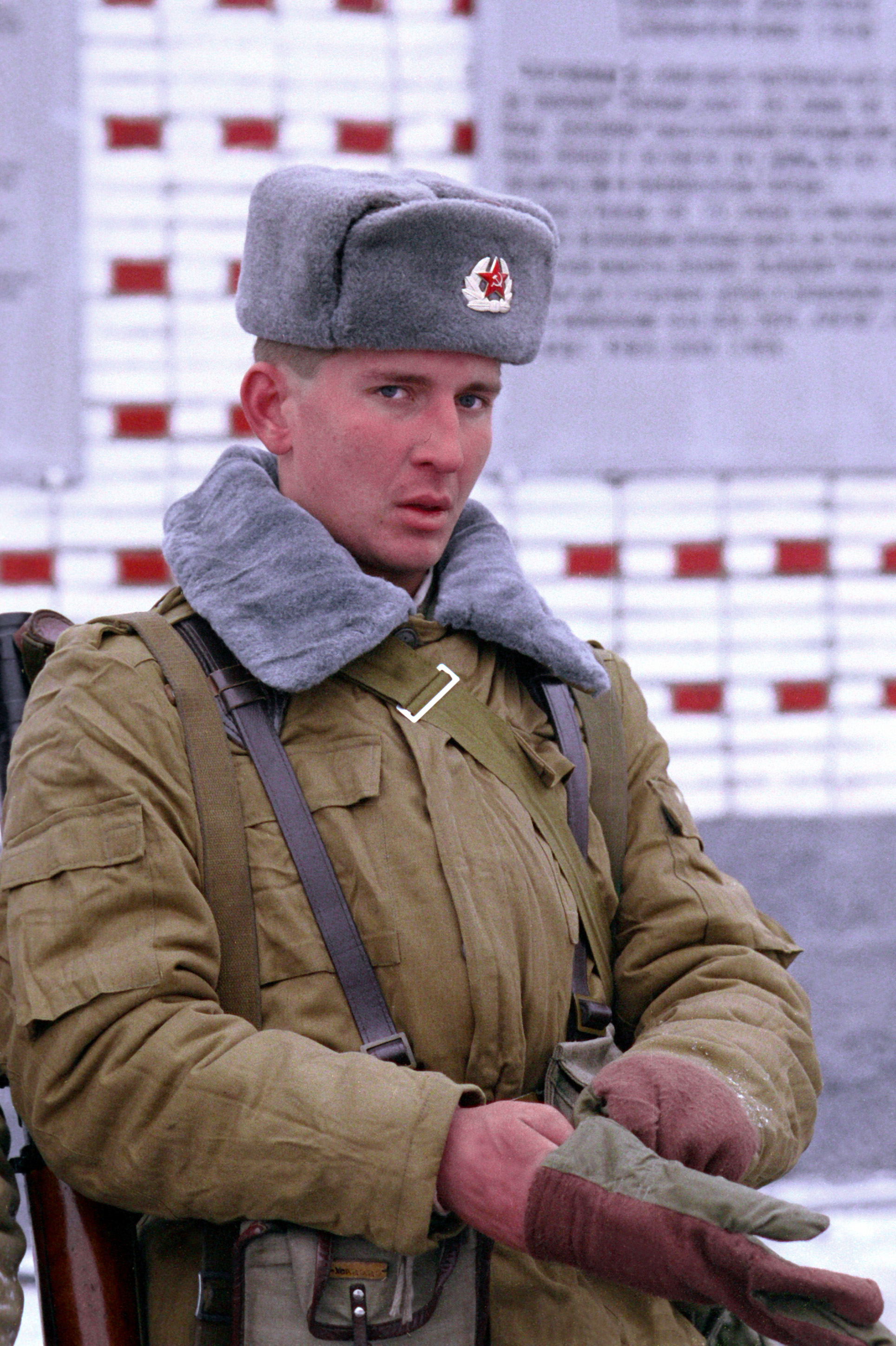
Soviet Army
The Soviet Ground Forces () was the land warfare service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces from 1946 to 1992. It was preceded by the Red Army. After the Soviet Union ceased to exist in December 1991, the Ground Forces remained under the command of the Commonwealth of Independent States until it was formally abolished on 14 February 1992. The Soviet Ground Forces were principally succeeded by the Russian Ground Forces in Russian territory. Outside of Russia, many units and formations were taken over by the post-Soviet states; some were withdrawn to Russia, and some dissolved amid conflict, notably in the Caucasus. While the Ground Forces are commonly referred to in English language sources as the Soviet Army, in Soviet military parlance the term '' armiya'' (army) referred to the combined land and air components of the Soviet Armed Forces, encompassing the Ground Forces as well as the Strategic Rocket Forces, the Air Defence Forces, and the Air Forces. After World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
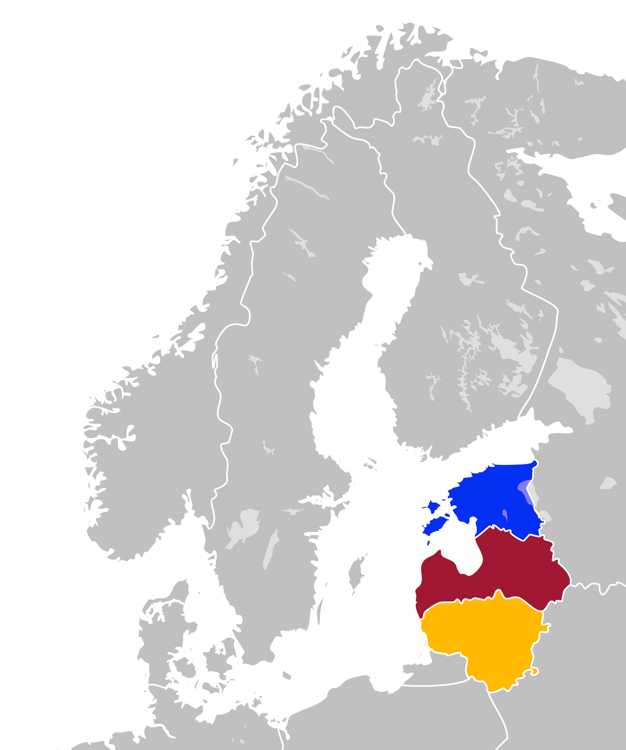
Baltic States
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. The term "Balticum" is sometimes used to describe the region comprising the three states; see e.g All three Baltic countries are classified as World Bank high-income economy, high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. Etymology The term ''Baltic'' stems from the name of the Baltic Sea – a hydronym dating back to at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guerrilla Warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include recruited children, use ambushes, sabotage, terrorism, raids, petty warfare or hit-and-run tactics in a rebellion, in a violent conflict, in a war or in a civil war to fight against regular military, police or rival insurgent forces. Although the term "guerrilla warfare" was coined in the context of the Peninsular War in the 19th century, the tactical methods of guerrilla warfare have long been in use. In the 6th century BC, Sun Tzu proposed the use of guerrilla-style tactics in '' The Art of War''. The 3rd century BC Roman general Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus is also credited with inventing many of the tactics of guerrilla warfare through what is today called the Fabian strategy, and in China Peng Yue is also often regarded as the inventor of guerrilla warfare. Guerrilla wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ants Kaljurand
Ants Kaljurand (20 October 1917 – 13 March 1951) – Metsavennad.esm.ee (in Estonian) popularly known as ''Terrifying Ants'', (), was an Estonian Nazi collaborator, anti-communist, and Forest Brothers, forest brother during and after World War II. Early life Ants Kaljurand was born on 20 October 1917 in Tallinn. His mother Juula was born in 1887. There is no information about his father. Kaljurand grew up in the village of Teesu near Pidula, Pidula Bay on the island of Saaremaa. He graduated from Pidula Primary School. In 1935, he went to Koonga Parish (now Lääneranna Parish) in Pärnu County to work as a farm laborer on Sepa Farm. In 1938, he served in the Estonian Defence Forces, Estonian Defense Forces and then continued on as a laborer on Sepa Farm. Partisan lif ...
|
People's Republic Of Poland
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near the end of its existence, it was the second most-populous communist government, communist and Eastern Bloc country in Europe. It was also where the Warsaw Pact was founded. The largest city and capital was Warsaw, followed by the industrial city of Łódź and cultural city of Kraków. The country was bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north, the Soviet Union to the east, Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, Czechoslovakia to the south, and East Germany to the west. The Polish People's Republic was a unitary state with a Marxist–Leninist government established in the country after the Red Army's takeover of Polish territory from Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German occupation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Franczak
Józef Franczak (17 March 1918 – 21 October 1963) was a soldier of the Polish Army, Armia Krajowa World War II resistance, and last of the cursed soldiers – members of the militant anti-communist resistance in Poland. He used codenames ''Lalek'' (best known), ''Laluś, Laleczka, Guściowa'', and fake name ''Józef Babiński''. He was a resistance fighter for 24 out of 45 years of his life. ''Also in:'' And: Biography Józef Franczak was born in the Polish village of Kozice Górne, some from Lublin. After attending a school for the gendarmerie in Grudziądz, he was stationed as a soldier of the Polish Army in Równe (then in Poland, now Rivne, Ukraine). He was captured during the Soviet invasion of Poland, but escaped and joined one of the first Polish resistance organizations, the Związek Walki Zbrojnej, which later became the Armia Krajowa. Not much is known about Franczak's wartime activities, except that around February 1943, he and two other partisan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish People
Polish people, or Poles, are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation who share a common History of Poland, history, Culture of Poland, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Central Europe. The preamble to the Constitution of the Republic of Poland defines the Polish nation as comprising all the citizenship, citizens of Poland, regardless of heritage or ethnicity. The majority of Poles adhere to Roman Catholicism. The population of self-declared Poles in Poland is estimated at 37,394,000 out of an overall population of 38,512,000 (based on the 2011 census), of whom 36,522,000 declared Polish alone. A wide-ranging Polish diaspora (the ''Polish diaspora, Polonia'') exists throughout Eurasia, the Americas, and Australasia. Today, the largest urban concentrations of Poles are within the Warsaw metropolitan area and the Katowice urban area. Ethnic Poles are considered to be the descendants of the ancient West Slavic Lechites and other tribes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Kuras Ogień
Józef is a Polish variant of the masculine given name Joseph. Art * Józef Chełmoński (1849-1914), Polish painter * Józef Gosławski (1908-1963), Polish sculptor Clergy * Józef Glemp (1929-2013), Polish cardinal * Józef Kowalski (1911-1942), Polish priest * Józef Milik (1922-2006), Polish priest and biblical scholar * Józef Tischner (1931-2000), Polish priest * Józef Andrzej Załuski (1702-1774), Polish priest and Bishop of Kyiv * Józef Życiński (1948-2011), Polish archbishop Literature * Józef Maksymilian Ossoliński (1748-1826), Polish novelist and poet * Józef Wybicki (1747-1822), Polish poet Military * Józef Bem (1794-1850), Polish general and engineer * Józef Grzesiak (1900-1975), Polish resistance member and scoutmaster * Józef Haller (1873-1960), Polish general * Józef Piotrowski (1840-1923), Polish participant in the January Uprising * Józef Poniatowski (1763-1813), Polish general * Józef Sowiński (1777-1831), Polish general * Józ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lokot Autonomy
The Lokot Autonomy () or Lokot Republic (, ) was an autonomous republic in the occupied territories of the Bryansk, Oryol and Kursk Oblasts of the Soviet Union, formed by German Nazi troops, and more specifically by Guderian's 2nd Panzer Army during World War II. The Wehrmacht entered the area in October 1941 and were forced out in August 1943. A local administration and police were appointed by German occupation authorities in November 1941. The autonomous republic was established in July 1942, when six districts were added to the Lokot district. The autonomy's name was derived from the region's administrative center, the urban-type settlement of Lokot in Oryol Oblast (now located in Bryansk Oblast). The autonomy covered the area of eight raions (the present-day Brasovsky, Dmitriyevsky, Dmitrovsky, Komarichsky, Navlinsky, Sevsky, Suzemsky and Zheleznogorsky districts) now divided between Bryansk, Oryol and Kursk Oblasts. The Lokot Autonomy was ruled by a Russian ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |