|
Anterior Cerebral Artery Syndrome
Anterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes, basal ganglia, anterior fornix and anterior corpus callosum.O'Sullivan, Susan (2007). "Physical Rehabilitation", p.709-711. F.A. Davis, Philadelphia. Depending upon the area and severity of the occlusion, signs and symptoms may vary within the population affected with ACA syndrome. Blockages to the proximal (A1) segment of the vessel produce only minor deficits due to the collateral blood flow from the opposite hemisphere via the anterior communicating artery. Occlusions distal to this segment will result in more severe presentation of ACA syndrome. Contralateral hemiparesis and hemisensory loss of the lower extremity is the most common symptom associated with ACA syndrome. Signs and symptoms # Hemiparesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cerebral Artery
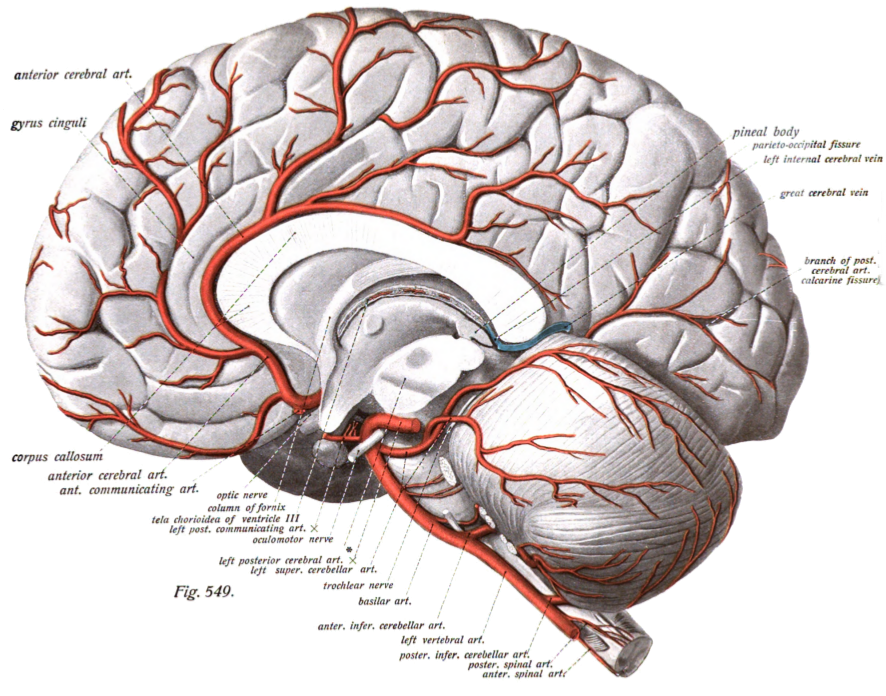
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. *A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supplementary Motor Area
The supplementary motor area (SMA) is a part of the motor cortex of primates that contributes to the control of movement. It is located on the midline surface of the hemisphere just in front of (anterior to) the primary motor cortex leg representation. In monkeys the SMA contains a rough map of the body. In humans the body map is not apparent. Neurons in the SMA project directly to the spinal cord and may play a role in the direct control of movement. Possible functions attributed to the SMA include the postural stabilization of the body, the coordination of both sides of the body such as during bimanual action, the control of movements that are internally generated rather than triggered by sensory events, and the control of sequences of movements. All of these proposed functions remain hypotheses. The precise role or roles of the SMA is not yet known. For the discovery of the SMA and its relationship to other motor cortical areas, see the main article on the motor cortex. Subregi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiballismus
Hemiballismus or hemiballism is a basal ganglia syndrome resulting from damage to the subthalamic nucleus in the basal ganglia. Hemiballismus is a rare hyperkinetic movement disorder, that is characterized by violent involuntary limb movements, on one side of the body, and can cause significant disability. ''Ballismus'' affects both sides of the body and is much rarer. Symptoms can decrease during sleep. Hemiballismus differs from chorea in that the movements occur in the proximal limbs whereas in chorea the limb movements are in the distal limbs. Also in chorea the movements are more dance-like, flowing from one region to another. Presentation ''Ballism'' was defined by Meyers in 1968Meyer, R. (1968) Ballismus. In: Vinken, P.J. and Bruyn, G.W. (Eds.), Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 6, North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, pp. 476-490. as "Repetitive, but constantly varying, large amplitude involuntary movements of the proximal parts of the limbs. This activity is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alteplase
Alteplase (t-PA), a biosynthetic form of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), is a thrombolytic medication, used to treat acute ischemic stroke, acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (a type of heart attack), pulmonary embolism associated with low blood pressure, and blocked central venous catheter. It is given by injection into a vein or artery. Alteplase is the same as the normal human plasminogen activator produced in vascular endothelial cells and is synthesized via recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO). Alteplase causes the breakdown of a clot by inducing fibrinolysis. Medical uses Alteplase is mainly used to treat acute ischemic stroke, acute myocardial infarction, acute massive pulmonary embolism, and blocked catheters. Similar to other thrombolytic drugs, alteplase is used to dissolve clots to restore tissue perfusion, but this can vary depending on the pathology. Generally, alteplase is delivered intravenously into the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621–1675), an English physician. Structure The circle of Willis is a part of the cerebral circulation and is composed of the following arteries: * Anterior cerebral artery (left and right) * Anterior communicating artery * Internal carotid artery (left and right) * Posterior cerebral artery (left and right) * Posterior communicating artery (left and right) The middle cerebral arteries, supplying the brain, are not considered part of the circle of Willis. Origin of arteries The left and right internal carotid arteries arise from the left and right common carotid arteries. The posterior communicating artery is given off as a branch of the internal carotid artery just before it divides into its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucking Reflex
Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli. These reflexes are suppressed by the development of the frontal lobes as a child transitions normally into child development. These primitive reflexes are also called infantile, infant or newborn reflexes. Older children and adults with atypical neurology (e.g., people with cerebral palsy) may retain these reflexes and primitive reflexes may reappear in adults. Reappearance may be attributed to certain neurological conditions including dementia (especially in a rare set of diseases called frontotemporal degenerations), traumatic lesions, and strokes. An individual with cerebral palsy and typical intelligence can learn to suppress these reflexes, but the reflex might resurface under certain conditions (i.e., during extreme startle reaction). Reflexes may also be limited to those areas affecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasp Reflex
Palmar grasp reflex (or grasp reflex) is a primitive and involuntary reflex found in infants of humans and most primates. When an object, such as an adult finger, is placed in an infant's palm, the infant's fingers reflexively grasp the object. Placement of the object triggers a spinal reflex, resulting from stimulation of tendons in the palm, that gets transmitted through motor neurons in the median and ulnar sensory nerves. The reverse motion can be induced by stroking the back or side of the hand. A fetus exhibits the reflex ''in utero'' by 28 weeks into gestation (sometimes, as early as 16 weeks), and persists until development of rudimentary fine motor skills between two to six months of age. Evolutionary significance Biologists have found that the reflex is significantly more frequent in infants of fur carrying primate species. It is theorized that the grasping reflex evolved as it is essential to survival in species, usually primates, where the young are carried in the fur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others. Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: * Urge incontinence due to an overactive bladder * Stress incontinence due to "a poorly functioning urethral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anosmia
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells. Anosmia may be temporary or permanent. It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells. Anosmia can be due to a number of factors, including an inflammation of the nasal mucosa, blockage of nasal passages or a destruction of one temporal lobe. Inflammation is due to chronic mucosa changes in the lining of the paranasal sinus and in the middle and superior turbinates. When anosmia is caused by inflammatory changes in the nasal passageways, it is treated simply by reducing inflammation. It can be caused by chronic meningitis and neurosyphilis that would increase intracranial pressure over a long period of time, and in some cases by ciliopathy, including ciliopathy due to primary ciliary dyskinesia. The term derives from the New Latin ''anosmia'', based on Ancient Greek ἀν- (''an''-) + ὀσμή (''osmḗ'' 'smell'; another related term, hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
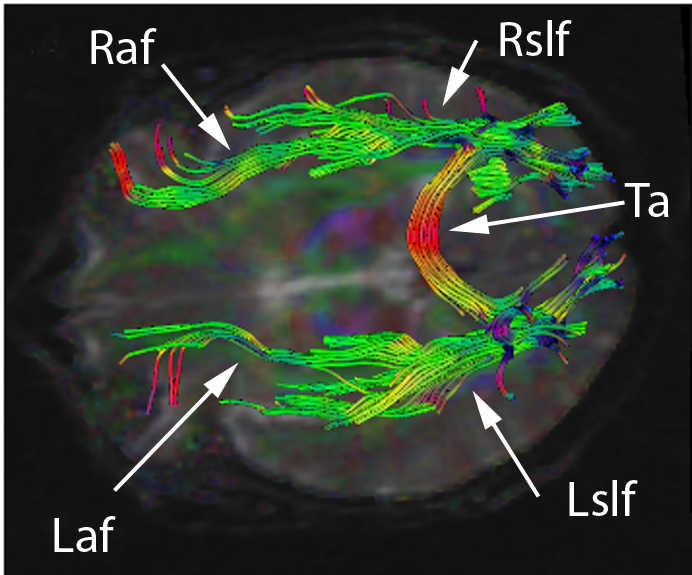
Disconnection Syndrome
Disconnection syndrome is a general term for a collection of neurological symptoms caused – via lesions to associational or commissural nerve fibres – by damage to the white matter axons of communication pathways in the cerebrum (not to be confused with the cerebellum), independent of any lesions to the cortex. The behavioral effects of such disconnections are relatively predictable in adults. Disconnection syndromes usually reflect circumstances where regions A and B still have their functional specializations except in domains that depend on the interconnections between the two regions. Callosal syndrome, or split-brain, is an example of a disconnection syndrome from damage to the corpus callosum between the two hemispheres of the brain. Disconnection syndrome can also lead to aphasia, left-sided apraxia, and tactile aphasia, among other symptoms. Other types of disconnection syndrome include conduction aphasia (lesion of the association tract connecting Broca’s area an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apraxia
Apraxia is a motor disorder caused by damage to the brain (specifically the posterior parietal cortex or corpus callosum), which causes difficulty with motor planning to perform tasks or movements. The nature of the damage determines the disorder's severity, and the absence of sensory loss or paralysis helps to explain the level of difficulty. Children may be born with apraxia; its cause is unknown, and symptoms are usually noticed in the early stages of development. Apraxia occurring later in life, known as ''acquired apraxia'', is typically caused by traumatic brain injury, stroke, dementia, Alzheimer's disease, brain tumor, or other neurodegenerative disorders. The multiple types of apraxia are categorized by the specific ability and/or body part affected. The term "apraxia" comes from the Greek ἀ- ''a-'' ("without") and πρᾶξις ''praxis'' ("action"). Types The several types of apraxia include: * Apraxia of speech (AOS) is having difficulty planning and coordinatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_in_a_two-week-old_female.jpg)