|
Anonychium Africanum
''Anonychium'' is a genus of plant in the pea family (Fabaceae). It includes a single species, ''Anonychium africanum'', a tree native to northern Sub-saharan Africa from Mauritania to Uganda and to Saudi Arabia. It is known by the synonym ''Prosopis africana'', and its common names include African mesquite, iron tree, ''gele'' (in Malinke), ''okpehe'', and ''somb'' tree. Okpehe is the name given by the Idoma and Igala people of Nigeria to both the tree and its fermented seeds. All of the other derivatives such as ''okpeye'' and ''okpiye'' stem from the noun ''okpehe'' used by the Idoma and Igala people of present day Benue State of Nigeria. In the Serer creation myth, it is one of the sacred trees that grew not just first, but also within the primordial swamp on Earth. Logs harvested from mature trees are one of the hardwoods used in crafting the shells of traditional djembes. Seeds of ''P. africana'' are used in Nigeria to prepare daddawa, kpaye, and okpeye, which are ferme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condiment
A condiment is a preparation that is added to food, typically after cooking, to enhance the Flavoring, flavour, to complement the dish or to impart a specific flavor. Such specific flavors generally add sweetness or pungency, or sharp or piquant flavors. The seasonings and spices common in many different cuisine arise from global introductions of foreign trade. Condiments include those added to cooking to impart flavor, such as barbecue sauce and soy sauce, those added before serving such as mayonnaise in a sandwich, and those added tableside to taste, such as ketchup with fast food. Condiments can also provide other health benefits to diets that lack micronutrients. Definition The exact definition of a condiment varies. Some definitions encompass spices and herbs, including salt and pepper, using the term interchangeably with ''seasoning''. Others restrict the definition to include only "prepared food compound[s], containing one or more spices", which are added to food after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of Africa
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Fabaceae Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopine
Prosopine is an alkaloid Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. Alkaloids are produced by a large varie ... found in '' Prosopis africana''. References Alkaloids Alkaloids found in Fabaceae {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gum
Natural gums are polysaccharides of natural origin, capable of causing a large increase in a solution's viscosity, even at small concentrations. They are mostly gum (botany), botanical gums, found in the woody elements of plants or in seed coatings. Human uses Gums are used in the food industry as thickening agents, gelling agents, Emulsion, emulsifying agents, and Food additive#Categories , stabilizers, and in other industrial adhesives, Excipient#Types, binding agents, crystal inhibitors, Brewing#Ingredients, clarifying agents, encapsulating agents, Flocculation , flocculating agents, swelling agents, foam stabilizers, etc. When consumed by humans, many of these gums are fermented by the microbes that inhabit the lower gastrointestinal tract (microbiome) and may influence the ecology and functions of these microscopic communities. Commercial significance Humans have used natural gums for various purposes, including chewing gum , chewing and the manufacturing of a wide rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterotoxin
An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines. They can be chromosomally or plasmid encoded. They are heat labile (> 60 °C), of low molecular weight and water-soluble. Enterotoxins are frequently cytotoxic and kill cells by altering the apical membrane permeability of the mucosal (epithelial) cells of the intestinal wall. They are mostly pore-forming toxins (mostly chloride pores), secreted by bacteria, that assemble to form pores in cell membranes. This causes the cells to die. Clinical significance Enterotoxins have a particularly marked effect upon the gastrointestinal tract, causing traveler's diarrhea and food poisoning. The action of enterotoxins leads to increased chloride ion permeability of the apical membrane of intestinal mucosal cells. These membrane pores are activated either by increased cAMP or by increased calcium ion concentration intracellularly. The pore formation has a direct effect on the osmolarity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-positive Bacillus, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be Aerobic organism, aerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, Metalloproteinase, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit Flagellum, flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens
''Bacillus amyloliquefaciens'' is a species of bacterium in the genus ''Bacillus'' that is the source of the BamHI restriction enzyme. It also synthesizes a natural antibiotic protein barnase, a widely studied ribonuclease that forms a famously tight complex with its intracellular inhibitor barstar, and plantazolicin, an antibiotic with selective activity against ''Bacillus anthracis''. It is used in agriculture, aquaculture, and hydroponics to fight root pathogens such as ''Ralstonia solanacearum,'' ''Pythium'', ''Rhizoctonia solani'', ''Alternaria tenuissima'' and ''Fusarium'' as well improve root tolerance to salt stress. They are considered a growth-promoting rhizobacteria and have the ability to quickly colonize roots. Discovery and name ''Bacillus amyloliquefaciens'' was first isolated from the soil 1943 by the Japanese scientist Juichiro Fukumoto, who gave the bacterium its name because it produced (''faciens'') a liquifying (''lique'') amylase (''amylo''). Uses Alpha a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
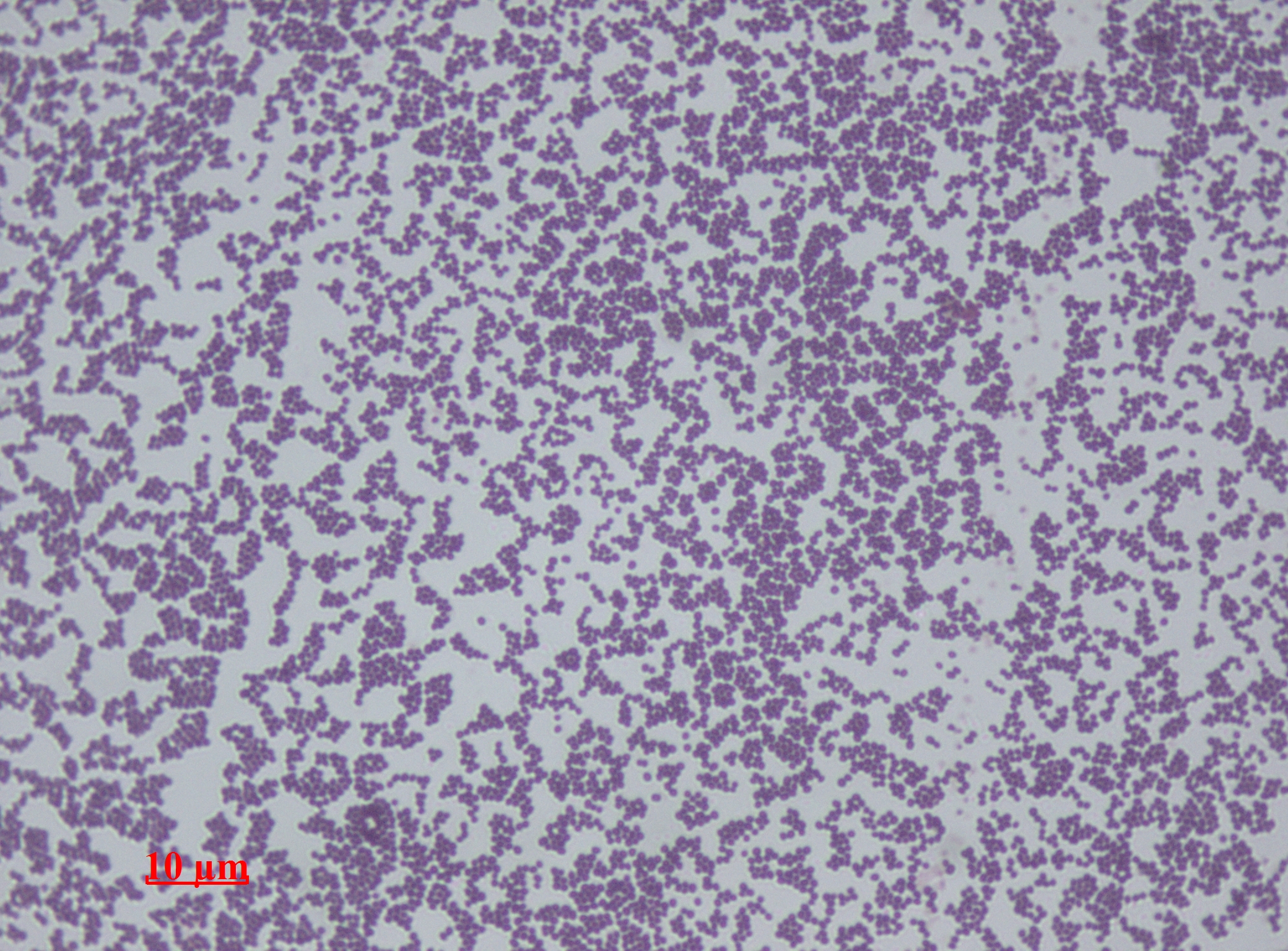
Micrococcus
''Micrococcus'', from Ancient Greek μικρός (''mikrós''), meaning "small", and κόκκος (''kókkos''), meaning "sphere", is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family (biology), family. ''Micrococcus'' occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate test, citrate negative. ''Micrococcus'' has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass. The genome of ''Micrococcus'' is rich in guanine and cytosine (GC), typically exhibiting 65 to 75% GC-content. Micrococci often carry plasmids (ranging from 1 to 100 MDa in size) that provide the organism with useful traits. Some species of ''Micrococcus'', such as ''M. luteus'' (yellow) and ''M. roseus'' (red) produce yellow or pink colonies when grown on mannitol salt agar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. It is part of the human flora, normal human microbiota, typically the skin flora, skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually Pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally Hospital-acquired infection, hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environments. S.I. Paul et al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |