|
Anisocapparis Speciosa
''Morisonia speciosa'', commonly known as , is a species of tree in the family ''Capparaceae''. It is native to the Gran Chaco region of Bolivia, Paraguay, western Brazil, and northern Argentina. It was formerly known under the scientific names ''Anisocapparis speciosa'' and ''Capparis speciosa''. The fruit, seeds, and flowers of ''Morisonia speciosa'' are edible. The fruit is very sweet and has a spicy flavor reminiscent of mangoes. The Toba people, Toba and Wichí peoples traditionally use it both culinarily and medicinally. Taxon and naming ''Morisonia speciosa'' was first described in scientific literature by August Grisebach as ''Capparis speciosa'' as published in ''Abhandlungen der Königlichen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen'' in 1879. It was transferred from the genus ''Capparis'' to the Monotypic taxon, monotypic genus ''Anisocapparis'' following a description by Xavier Cornejo and Hugh Iltis published in a 2008 paper. It was renamed ''Morisonia speciosa'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Grisebach
August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach (; 17 April 18149 May 1879) was a German botanist and phytogeographer. Biography Grisebach studied at the Lyceum in Hanover, the cloister-school at Ilfeld, and the University of Göttingen. He graduated in medicine from the University of Berlin in 1836. He undertook expeditions to Provence, Turkey, the Balkans, and Norway. In 1837 he became associate professor and in 1847 full professor at the medical faculty in Göttingen and was named director of the botanical garden there in 1875. While his main fields of interest were phytogeography and systematics, especially the Gentianaceae and Malpighiaceae, he considered his ''Flora of the British West Indian Islands'' his most important work. Much of his collection, especially the types of species described by him, are housed at the Göttingen University Herbarium. His taxonomic classification is set out in his ''Grundriss der systematischen Botanik'' (1854). His son Eduard was an author, lawyer a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carob
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, which takes the form of seed pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes. The carob tree is native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Portugal is the largest producer of carob, followed by Italy and Morocco. In the Mediterranean Basin, extended to the southern Atlantic coast of Portugal (i.e., the Algarve region) and the Atlantic northwestern Moroccan coast, carob pods were often used as animal feed and in times of famine, as "the last source of umanfood in hard times". The ripe, dried and sometimes toasted pod is often ground into carob powder, which is used as a substitute for cocoa powder; this often occurred in the 1970s natural food movement. The powder and chips can be used as a chocolate alternative in most recipes. The plant's seeds are used to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaguar
Chaguar is the common name of several related species of South American plants of the family Bromeliaceae, among them '' Bromelia serra'', '' Bromelia hieronymi'', '' Deinacanthon urbanianum'' and '' Pseudananas sagenarius'', which are non-woody forest plants with sword-shaped evergreen leaves, resembling yucca. The different varieties grow in the semi-arid parts of the Gran Chaco ecoregion. The term ''chaguar'' is of Quechua origin; in areas where the Guaraní have had an influence, it is also known as caraguatá. This plant is mainly employed by the Wichí tribal groups in the provinces of Salta and Formosa, Argentina, to provide a resistant fiber that can be woven to make bags and purses, ponchos, skirts, fishing nets, string, ropes, hammocks, mats, covers and clothing. Along with those made from hardwoods such as '' quebracho'', chaguar crafts make up an important part of the economy of some Wichí groups, though the profits are scarce.{{cn, date=October 2023 Chaguar is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myiasis
Myiasis ( ), also known as flystrike or fly strike, is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) that grow inside the host while feeding on its Biological tissue, tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly, Calliphoridae, blowfly, and Cochliomyia hominivorax, screwfly) can create an infestation even on unbroken skin. Non-myiatic flies (such as the common housefly) can be responsible for accidental myiasis. Because some animals (particularly non-native domestic animals) cannot react as effectively as humans to the causes and effects of myiasis, Parasitic flies of domestic animals, such infestations present a severe and continuing problem for livestock industries worldwide, causing severe economic losses where they are not mitigated by human action. Although typically a far greater issue for animals, myiasis is also a relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehydration. The cause of dysentery is usually the bacteria from genus '' Shigella'', in which case it is known as shigellosis, or the amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''; then it is called amoebiasis. Other causes may include certain chemicals, other bacteria, other protozoa, or parasitic worms. It may spread between people. Risk factors include contamination of food and water with feces due to poor sanitation. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the intestine, especially of the colon. Efforts to prevent dysentery include hand washing and food safety measures while traveling in countries of high risk. While the condition generally resolves on its own within a week, drinking sufficient fluids such as oral rehydration solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
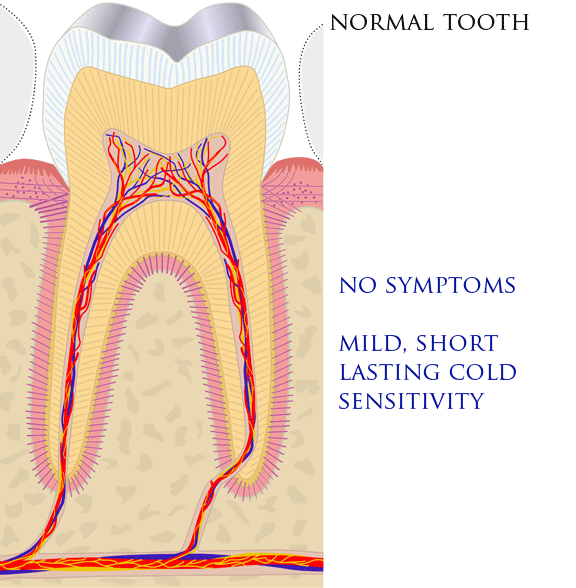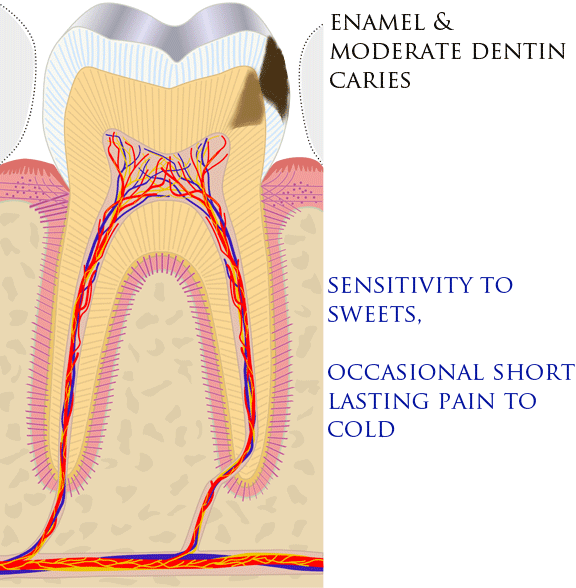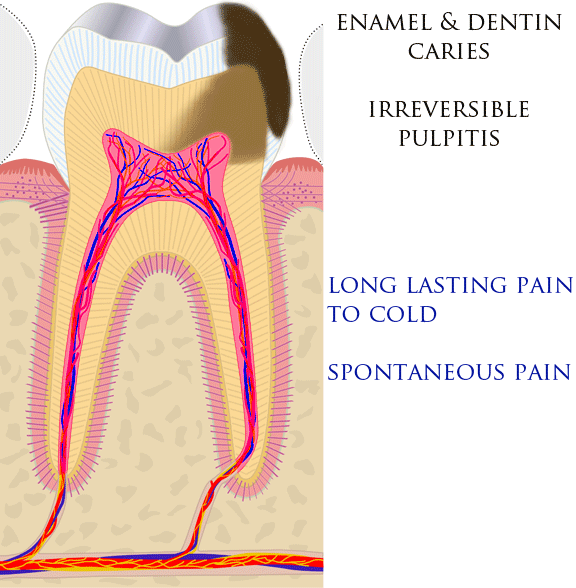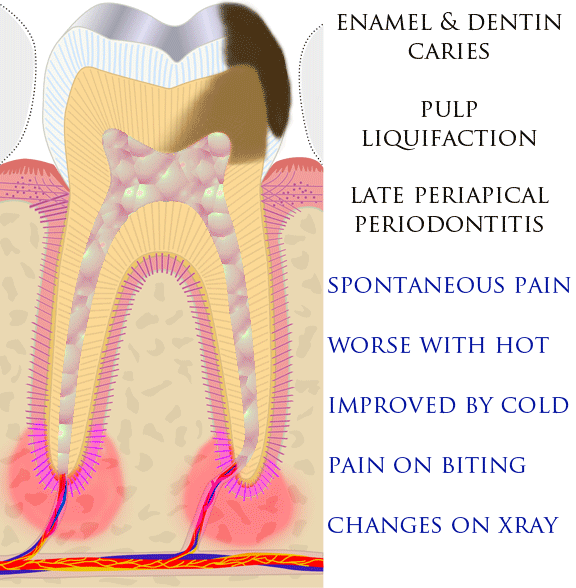
Toothache
Toothaches, also known as dental pain or tooth pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or referred pain, pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities. Common causes include pulpitis, inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to dental caries, tooth decay, dental trauma, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity, apical periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone around the Root apex (dental), root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis ("dry socket", a possible complication of dental extraction, tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder. Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Foods are also treated with antioxidants to prevent Food spoilage, spoilage, in particular the rancidification of Vegetable oil, oils and fats. In Cell (biology), cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol, or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, inhibit damage from oxidative stress. Known diet (nutrition), dietary antioxidants are vitamins vitamin A, A, vitamin C, C, and vitamin E, E, but the term has also been applied to various compounds that exhibit antioxidant properties in vitro, having little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotyledon
A cotyledon ( ; ; "a cavity, small cup, any cup-shaped hollow", gen. (), ) is a "seed leaf" – a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant – and is formally defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." Botanists use the number of cotyledons present as one characteristic to classify the flowering plants (angiosperms): species with one cotyledon are called monocotyledonous ("monocots"); plants with two embryonic leaves are termed dicotyledonous ("dicots"). Many orchids with minute seeds have no identifiable cotyledon, and are regarded as acotyledons. The Dodders (''Cuscuta'' spp) also lack cotyledons, as does the African tree '' Mammea africana'' ( Calophyllaceae). In the case of dicot seedlings whose cotyledons are photosynthetic, the cotyledons are functionally similar to leaves. However, true leaves and cotyledons are developmentally distinct. Cotyledons form during embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peduncle (botany)
In botany, a peduncle is a stalk supporting an inflorescence or a solitary flower, or, after fecundation, an infructescence or a solitary fruit. The peduncle sometimes has bracts (a type of cataphyll) at nodes. The main axis of an inflorescence above the peduncle is the rachis, which hosts flowers (as opposed to directly on the peduncle). When a peduncle arises from the ground level, either from a compressed aerial stem or from a subterranean stem (rhizome, tuber, bulb, corm), with few or no bracts except the part near the rachis or receptacle, it is referred to as a scape. The acorns of the pedunculate oak are borne on a long peduncle, hence the name of the tree. See also *Pedicel (botany) *Scape (botany) In botany, a scape is a peduncle arising from a subterranean or very compressed stem, with the lower internodes very long and hence few or no bracts except the part near the rachis or receptacle. Typically it takes the form of a long, leafl ... Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floral Nectary
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of predacious or parasitoid wasps (e.g., the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely on nectar as a primary food source. In turn, these wasps then hunt agricultural pest insects as food for their young. Nectar is most often associated with flowering plants angiosperms, but it is also produced by other groups, including ferns. Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |