|
Animation In The United States During The Silent Era
The silent age of American animation dates back to at least 1906 when Vitagraph released '' Humorous Phases of Funny Faces''.Jeff Lenburg 1991 The Encyclopedia of Animated Cartoons Although early animations were rudimentary, they rapidly became more sophisticated with such classics as '' Gertie the Dinosaur'' in 1914, Felix the Cat, Oswald the Lucky Rabbit, and Koko the Clown. Originally a novelty, some early animated silents depicted magic acts or were strongly influenced by the comic strip. Later, they were distributed along with newsreels. Early animation films, like their live-action silent cousins, would come with a musical score to be played by an organist or even an orchestra in larger theatres. Silent cartoons became almost entirely obsolete after 1928, when sound synchronized cartoons were introduced with the debut of Walt Disney's Mickey Mouse in ''Steamboat Willie'', thus ushering in the golden age of American animation. History British-American filmmaker J. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitagraph
Vitagraph Studios, also known as the Vitagraph Company of America, was a United States motion picture studio. It was founded by J. Stuart Blackton and Albert E. Smith in 1897 in Brooklyn, New York, as the American Vitagraph Company. By 1907, it was the most prolific American film production company, producing many famous silent films. It was bought by Warner Bros. in 1925. History In 1896, English ''émigré'' Blackton was moonlighting as a reporter/artist for the New York ''Evening World'' when he was sent to interview Thomas Edison about his new film projector. The inventor talked the entrepreneurial reporter into buying a set of films and a projector. A year later, Blackton and business partner Smith founded the American Vitagraph Company in direct competition with Edison. A third partner, distributor William "Pop" Rock, joined in 1899. The company's first studio was located on the rooftop of a building on Nassau Street in Manhattan. Operations were later moved to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamboat Willie
''Steamboat Willie'' is a 1928 American animated short film directed by Walt Disney and Ub Iwerks. It was produced in black-and-white by Walt Disney Animation Studios and was released by Pat Powers (producer), Pat Powers, under the name of Celebrity Productions. The cartoon is considered the public debut of Mickey Mouse and Minnie Mouse, although both appeared months earlier in a test screening of ''Plane Crazy'' and the then unreleased ''The Gallopin' Gaucho''. ''Steamboat Willie'' is the third of Mickey's films to have been produced, but it is the first to have been Film distribution, distributed, because Disney had seen ''The Jazz Singer'' (1927) and became determined to produce one of the first fully synchronized sound cartoons. ''Steamboat Willie'' is one of the first cartoons with Sound film, synchronized sound, and one of the first cartoons to feature a fully Audio post production, post-produced soundtrack, which distinguished it from earlier sound cartoons, such as Fleis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
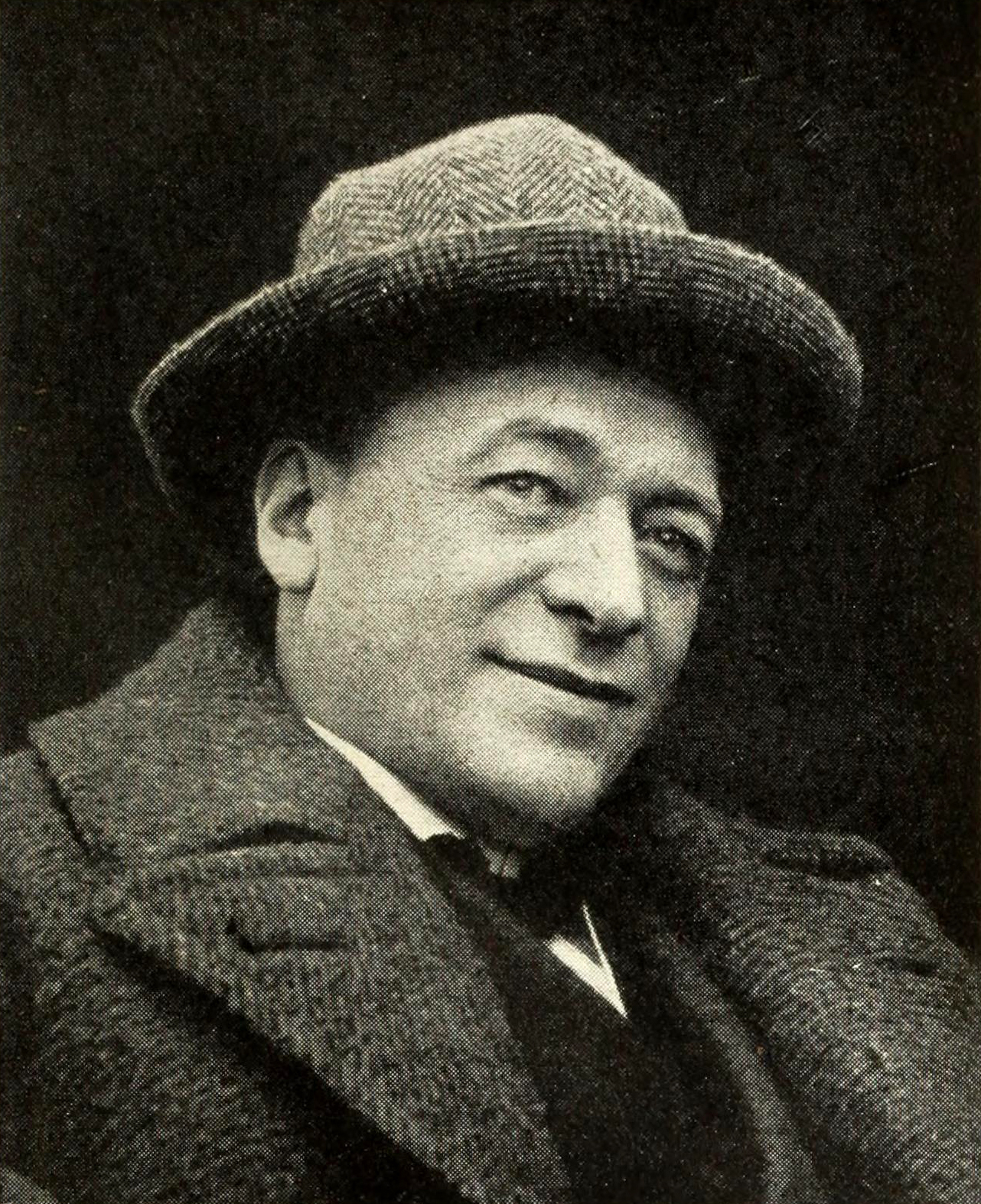
Raoul Barré
Vital Achille Raoul Barré (January 29, 1874 – May 21, 1932) was a Canadian cartoonist, animator of the silent film era, and painter. Initially known as a political cartoonist, he originated the French Canadian comic strip, then crossed over into animated film and started his own studio, a pioneering effort. As a painter, he is considered an Impressionist, evoking atmosphere and light with visible, choppy strokes of paint, whose paintings are in the Musée national des beaux-arts du Québec. Personal history and career Barré was born in Montreal, Quebec, the only artistic child (out of twelve) of a wine merchants and importers. He studied art at the Académie Julian, starting in 1896, and remained there for two years also known as a political cartoonist—he was a loud critic of the unjust trials of Captain Alfred Dreyfus. One of Barré's opponents in the war of words and cartoons was Émile Cohl, writing anonymously. On returning to Canada in 1898, he gave birth to the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movie Theaters
A movie theater (American English) or cinema (Commonwealth English), also known as a movie house, cinema hall, picture house, picture theater, the movies, the pictures, or simply theater, is a business that contains auditoriums for viewing films for public entertainment. Most are commercial operations catering to the general public, who attend by purchasing tickets. The film is projected with a movie projector onto a large projection screen at the front of the auditorium while the dialogue, sounds and music are played through a number of wall-mounted speakers. Since the 1970s, subwoofers have been used for low-pitched sounds. Since the 2010s, the majority of movie theaters have been equipped for digital cinema projection, removing the need to create and transport a physical film print on a heavy reel. A great variety of films are shown at cinemas, ranging from animated films to blockbusters to documentaries. The smallest movie theaters have a single viewing room with a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Sinking Of The Lusitania
''The Sinking of the Lusitania'' (1918) is an American silent film, silent animated short film by cartoonist Winsor McCay. It is a work of propaganda film, propaganda re-creating the never-photographed 1915 Sinking of the RMS Lusitania, sinking of the British liner RMS ''Lusitania''. At twelve minutes, it has been called the longest work of animation at the time of its release. The film is the earliest surviving animated documentary and serious, dramatic work of animation. The National Film Registry selected it for preservation in 2017. On 7 May 1915, a German submarine (SM U-20 (Germany), SM ''U-20'') torpedoed and sank the RMS Lusitania, RMS ''Lusitania'' near Ireland; 128 Americans were among the 1,198 dead. The event outraged McCay, but the newspapers of his employer William Randolph Hearst downplayed the event, as Hearst was opposed to the American entry into World War I, U.S. joining World War I. McCay was required to illustrate anti-war and anti-British editorial cartoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Nemo (1911 Film)
''Winsor McCay: The Famous Cartoonist of the N.Y. Herald and His Moving Comics'', more commonly known as ''Little Nemo'', is a 1911 silent animated short film by American cartoonist Winsor McCay. One of the earliest animated films and McCay's first, it featured characters from McCay's comic strip '' Little Nemo in Slumberland''. Its expressive character animation distinguished the film from the experiments of earlier animators. Inspired by flip books his son brought home, McCay came to see the potential of the animated film medium. He claimed to be the first to make such films, though James Stuart Blackton and Émile Cohl were among those who preceded him. The short's four thousand drawings on rice paper were shot at Vitagraph Studios under Blackton's supervision. Most of the film's running time is made up of a live-action sequence in which McCay bets his colleagues that he can make drawings that move. He wins the bet with four minutes of animation in which the ''Little N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winsor McCay
Zenas Winsor McCay ( – July 26, 1934) was an American cartoonist and animator. He is best known for the comic strip ''Little Nemo'' (1905–1914; 1924–1927) and the animated film ''Gertie the Dinosaur'' (1914). For contractual reasons, he worked under the pen name Silas on the comic strip ''Dream of the Rarebit Fiend''. From a young age, McCay was a quick, prolific, and technically dextrous artist. He started his professional career making posters and performing for dime museums, and in 1898 began illustrating newspapers and magazines. In 1903 he joined the ''New York Herald'', where he created popular comic strips such as ''Little Sammy Sneeze'' and ''Dream of the Rarebit Fiend''. In 1905, his signature strip ''Little Nemo in Slumberland'' debuted—a fantasy strip in an Art Nouveau style about a young boy and his adventurous dreams. The strip demonstrated McCay's strong graphic sense and mastery of color and Perspective (graphical), linear perspective. McCay experimented w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Animation
Traditional animation (or classical animation, cel animation, or hand-drawn animation) is an animation technique in which each frame is drawing, drawn by hand. The technique was the dominant form of animation of the 20th century, until there was a shift to computer animation in the industry, such as Traditional animation#Modern process, digital ink and paint, a modern form of traditional animation methods, and 3D computer animation. Process Writing and storyboarding Animation production usually begins after a story is converted into an animation film script, from which a storyboard is derived. A storyboard has an appearance somewhat similar to comic book panels, and is a shot by shot breakdown of the staging, acting and any camera moves that will be present in the film. The images allow the animation team to plan the flow of the Plot (narrative), plot and the composition of the imagery. Storyboard artists will have regular meetings with the film director, director and may redra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fantasmagorie (1908 Film)
''Fantasmagorie'' (also called '''A Fantasy''') is a 1908 French animated short film by Émile Cohl. It is one of the earliest examples of traditional (hand-drawn) animation, and considered by film historians to be the first animated cartoon. Description The film largely consists of a stick man moving about and encountering all manner of morphing objects, such as a wine bottle that transforms into a flower which becomes an elephant. There are also sections of live action where the animator's hands enter the scene. The main character is drawn by the artist's hand on camera, and the main characters are a clown and a gentleman. Other characters include a woman in a movie theater wearing a large hat with gigantic feathers, and a strongman. The film, in all of its wild transformations, is a direct tribute to the by-then forgotten Incoherent movement. The title is taken from the original French word for "phantasmagoria", a mid-19th century magic lantern The magic lantern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Cohl
Émile Eugène Jean Louis Cohl (; né Courtet; 4 January 1857 – 20 January 1938) was a French caricaturist of the Incoherent Movement, cartoonist, and animator, called "The Father of the Animated Cartoon". Biography Émile's father, Elie, was a rubber salesman, and his mother, Emilie Laure, a linen seamstress. The rubber factory Elie worked for had many ups and downs, causing the family to move from one home in Paris to another. Early years Émile’s father was often busy, and Émile lived with his ailing mother until her death in 1863. In 1864, at the age of 7, he was enrolled at the Ecole professionnelle de Pantin, a boarding school known as the Institute Vaudron after its founder. There his artistic talents were discovered and encouraged. The next year, a cold kept him confined in his father's apartment, where he began stamp collecting, a hobby that would become his sole source of income several times in his life. The chaos caused by the Franco-Prussian War and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théâtre Optique
The Théâtre Optique (Optical Theatre) is an animated moving picture system invented by Charles-Émile Reynaud, Émile Reynaud and patented in 1888. From 28 October 1892 to March 1900 Reynaud gave over 12,800 shows to a total of over 500,000 visitors at the Musée Grévin in Paris. His ''Pantomimes Lumineuses'' series of animated films include ''Pauvre Pierrot'' and ''Autour d'une cabine''. Reynaud's Théâtre Optique predated Auguste and Louis Lumière's first commercial, public screening of the cinematograph on 28 December 1895, which has long been seen as the birth of film. Technology The realized films had 300 to 700 transparent pictures of successive phases of moving figures with black backgrounds. The pictures were hand painted by Reynaud in aniline inks directly on 6 x 6 cm gelatin plates. The plates were coated with shellac and framed in a cardboard strip of which the sides were clad in fabric bands attached with split pins. The horizontal film strip could be up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |