|
Angola White-eye
The Angola white-eye (''Zosterops kasaicus''), is a small passerine bird in the white-eye family Zosteropidae. It is found from central Democratic Republic of the Congo to northern and central Angola. It was formerly considered to be conspecific with the northern yellow white-eye. Taxonomy The Angola white-eye was formally described in 1932 by the American ornithologist James Chapin based on a specimen that had been collected near Luluabourg (now Kananga) in the Kasaï region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Chapin considered his specimen to be a subspecies of the forest white-eye (''Zosterops stenocricotus'') and coined the trinomial name ''Zosterops stenocricotus kasaicus''. The Angola white-eye was formerly considered to be conspecific with the northern yellow white-eye (''Zosterops senegalensis''). The species were split based on the results of a molecular phylogenetic study published in 2020 that found significant genetic divergence between the two species. Three su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Chapin
James Paul Chapin (July 9, 1889 – April 5, 1964) was an American ornithologist and curator of the American Museum of Natural History. Biography Chapin is one of the highest-regarded ornithologists of the twentieth century. He was joint leader (with Herbert Lang) of the Lang–Chapin expedition, which made a biological survey of the Belgian Congo between 1909 and 1915. For his work ''The Birds of the Belgian Congo, Part I'', he was awarded the Daniel Giraud Elliot Medal from the United States National Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Sciences in 1932. He received a bachelor's degree in 1916, master's degree in 1917, and a doctorate in 1932, all from Columbia University, and then began a lengthy career at the American Museum of Natural History. Chapin served as the 17th president of The Explorers Club from 1949 to 1950. Intelligence officer in the Congo In 1942, Chapin was recruited by the Office of Strategic Services intelligence agency as an intelligence officer. Unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest White-eye
The forest white-eye or Cameroon green white-eye (''Zosterops stenocricotus'') is a species of bird in the family Zosteropidae. It is found from southeastern Nigeria to southwestern Central African Republic and northern Gabon. Its natural habitats are subtropical, tropical moist montane forests, and subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... References forest white eye Birds of Central Africa forest white-eye forest white-eye {{Zosteropidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of Sub-Saharan Africa
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zosterops
''Zosterops'' (meaning "eye-Zoster (costume), girdle") is a genus of passerine birds containing the typical white-eyes in the white-eye family Zosteropidae. The genus has the largest number of species in the white-eye family. They occur in the Afrotropical realm, Afrotropical, Indomalayan realm, Indomalayan, and Australasian realms. Typical white-eyes have a length of between . Their most characteristic feature is a conspicuous white feather eye-ring, ring around the eye, though some species lack it. The species in this group vary in the structural adaptations of the tongue. The ''Zosterops'' [''griseotinctus''] group is an example of a "great speciator" inhabiting a vast area and showing a remarkable morphological differentiation on islands, some of which may be as close as apart. Systematics The genus ''Zosterops'' was introduced by the naturalists Nicholas Aylward Vigors, Nicholas Vigors and Thomas Horsfield in 1827. The name combines the Ancient Greek words ''zōstēros'' "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodolphe Meyer De Schauensee
Rodolphe Meyer de Schauensee (; January 4, 1901 – April 24, 1984) was a Swiss-American ornithologist. Early life and education Meyer de Schauensee was born January 4, 1901 in Rome, Italy, one of two sons, to Baron Frederick Meyer de Schauensee and his American-born wife Matilda (née Toland; died 1932). His father was from a well-established Swiss aristocratic family originally from Lucerne that owned Schauensee Castle. In 1913, the family moved to the United States. He attended the Hoosac School in Hoosick, New York. He moved to Wynnewood, Pennsylvania in the 1920s. Career He was the curator of ornithology at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia for nearly fifty years. He was particularly noted for his study of South American birds. He expanded the academy's collection of bird skins, taking part in collecting trips to Brazil, Thailand, Burma, southern Africa, the East Indies, and Guatemala. He wrote about the birds of South America, including the groundbreakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Meise
Wilhelm Meise (12 September 1901 in Essen - 24 August 2002 in Hamburg) was a German ornithology, ornithologist.Haffer, Jurgen (2003)''In memoriam'': Wilhelm Meise, 1901-2002 ''The Auk,'' 120(2): 540. (Apr 2003) He studied at the University of Berlin from 1924 to 1928, where he did his Ph.D. dissertation on the distribution of the carrion crow and the hooded crow, and hybridization between them under the supervision of Professor Erwin Stresemann, (1889–1972). He also analysed taxonomic and historic relationships between the house sparrow and the Spanish sparrow in particular the status of the "Italian sparrow". He was curator of vertebrates at the Museum of Natural History in Dresden from 1929 until World War II. Meise produced the first review of bird species new to science in 1934 at the eighth International Ornithological Congress (IOC), followed by an update at the ninth IOC in 1938. Meise, W. (1934) "Fortschritte der ornithologischen Systematik seit 1920" ''Proc. VIII Cong. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
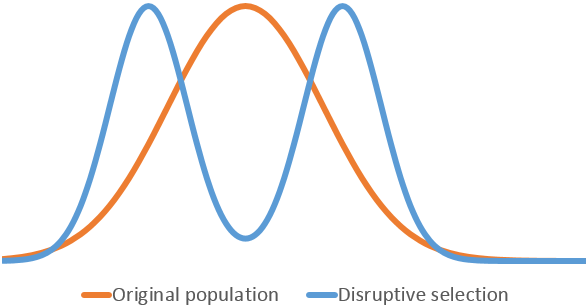
Genetic Divergence
Genetic divergence is the process in which two or more populations of an ancestral species accumulate independent genetic changes ( mutations) through time, often leading to reproductive isolation and continued mutation even after the populations have become reproductively isolated for some period of time, as there is not any genetic exchange anymore. In some cases, subpopulations cover living in ecologically distinct peripheral environments can exhibit genetic divergence from the remainder of a population, especially where the range of a population is very large (see parapatric speciation). The genetic differences among divergent populations can involve silent mutations (that have no effect on the phenotype) or give rise to significant morphological and/or physiological changes. Genetic divergence will always accompany reproductive isolation, either due to novel adaptations via selection and/or due to genetic drift, and is the principal mechanism underlying speciation. On a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinomial Name
In biology, trinomial nomenclature is the system of names for taxa below the rank of species. These names have three parts. The usage is different in zoology and botany. In zoology In zoological nomenclature, a trinomen (), trinominal name, or ternary name is the name of a subspecies. A trinomen is a name with three parts: generic name, specific name and subspecific name. The first two parts alone form the binomen or species name. All three names are typeset in italics, and only the first letter of the generic name is capitalised. No indicator of rank is included: in zoology, subspecies is the only rank below that of species. For example: "''Buteo jamaicensis borealis'' is one of the subspecies of the red-tailed hawk (''Buteo jamaicensis'')." Examples include ''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'' ( Savage and Wyman, 1847) for the western lowland gorilla and ''Gorilla gorilla diehli'' ( Matschie, 1903) for the Cross River gorilla (which are subspecies of ''Gorilla gorilla'', the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerine
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped') which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines generally have an anisodactyl arrangement of their toes (three pointing forward and one back), which facilitates perching. With more than 140 families and some 6,500 identified species, Passeriformes is the largest order of birds and one of the most diverse clades of terrestrial vertebrates, representing 60% of birds.Ericson, P.G.P. et al. (2003Evolution, biogeography, and patterns of diversification in passerine birds ''J. Avian Biol'', 34:3–15.Selvatti, A.P. et al. (2015"A Paleogene origin for crown passerines and the diversification of the Oscines in the New World" ''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'', 88:1–15. Passerines are divided into three suborders: New Zealand wrens; Suboscines, primarily found in North and South America; and songbirds. Passerines originated in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is the List of African countries by area, second-largest country in Africa and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the DR Congo is the most populous nominally List of countries and territories where French is an official language, Francophone country in the world. Belgian French, French is the official and most widely spoken language, though there are Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, over 200 indigenous languages. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, the Cabinda Province, Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west; the Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasaï Region
The Kasaï region (also referred to as the Greater Kasaï region, Greater Kasaï, Grand Kasaï, or simply Kasaï) is a geographic and cultural region in south-central Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a single province, it now comprises the provinces of Kasaï Province, Kasaï-Central, Sankuru, Kasaï-Oriental, and Lomami Province. It shares its name with the Kasai River. Historically, the Kasaï region has been a stronghold for the Union for Democracy and Social Progress (UDPS) party. As an opposition stronghold, it experienced both political and economic marginalization by the central government. This long-running resentment of the central government's remoteness and corruption exploded into a rebellion, triggered by the official rejection of a local chief, Kamwina Nsapu, who in August 2016 was killed by security forces. After UDPS candidate Félix Tshisekedi's victory in the 2018 presidential election, most militia members surrendered and returned to their communities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |