|
Andaman And Nicobar Command
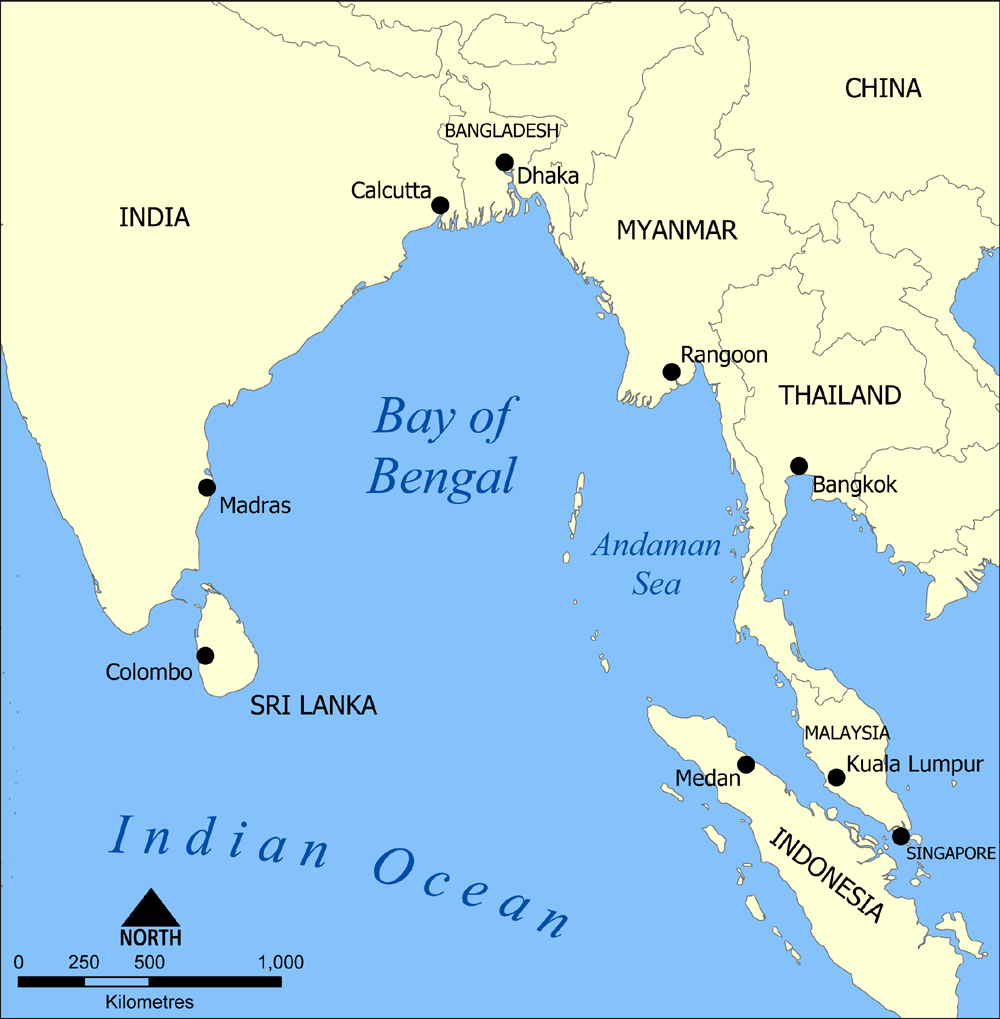
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is a integrated tri-services command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the region. It provides logistical and administrative support to naval ships which are sent on deployment to East Asia and the Pacific Ocean.Rajat Pandit (2010), '. The Times of India, 6 February 2010. Accessed on 23 July 2012. Background Strategic Importance of ANC According to the International Hydrographic Organization's (IHO) definitions of the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (A&N) fall on the maritime boundary of these two. Indian exclusive economic zone (EEZ) to the north and west of A&N falls within the Bay of Bengal and to east of A&N falls within the Andaman Sea. Various straits (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
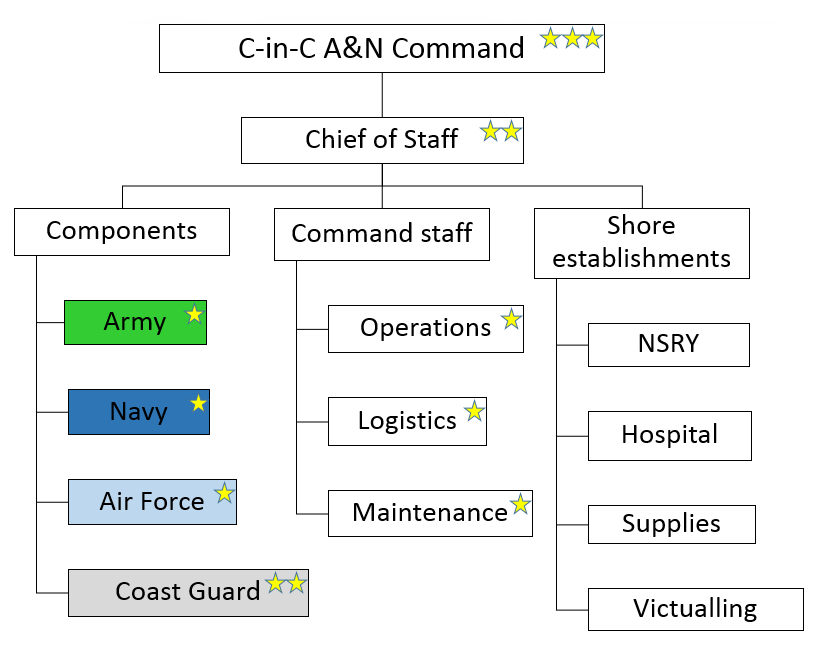
Commander-in-Chief, Andaman And Nicobar Command
Commander-in-Chief, Andaman and Nicobar Command (CINCAN) is the head of the Andaman and Nicobar Command, the first and only Joint warfare, Tri-service Theater (warfare), theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Sri Vijaya Puram (formerly Port Blair) in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. The current CINCAN is Lieutenant General (India), Lieutenant General Dinesh Singh Rana Param Vishisht Seva Medal, PVSM, Ati Vishisht Seva Medal, AVSM, Yudh Seva Medal, YSM, Sena Medal, SM who took command on 1 June 2025 as the 18th CINCAN. History The Andaman and Nicobar Islands became a Union territory of India in 1956. The first military unit on the islands was the naval base INS Jarawa, which was commissioned in 1964. The base was commanded by a Resident Naval Officer (RNO). After establishing subsequent garrisons in the islands, the post was upgraded to Naval Officer-in-Charge Andaman & Nicobar (NOIC A&N). The naval establishments were under the command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Armed Forces
The Indian Armed Forces are the armed forces, military forces of the India, Republic of India. It consists of three professional uniformed services: the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force.—— Additionally, the Indian Armed Forces are supported by the Central Armed Police Forces, the Indian Coast Guard, and the Special Frontier Force and various Jointness and integration in the Indian military, inter-service commands and institutions such as the Strategic Forces Command, the Andaman and Nicobar Command, and the Integrated Defence Staff. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces but the executive authority and responsibility for national security is vested in the Prime Minister of India and their chosen Cabinet Committee on Security, Cabinet Ministers. The Indian Armed Forces are under the management of the Ministry of Defence (India), Ministry of Defence of the Government of India. With strength of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombok Strait
The Lombok Strait () is a strait of the Bali Sea connecting to the Indian Ocean, and is located between the islands of Bali and Lombok in Indonesia. The Gili Islands are on the Lombok side. Its narrowest point is at its southern opening, with a width of about between the islands of Lombok and Nusa Penida, in the middle of the strait. At the northern opening, it is across. Its total length is about . As it is minimum deep—much deeper than the Strait of Malacca—ships that draw too much water to pass through the Malacca Strait (so-called "post Malaccamax" vessels) often use the Lombok Strait, instead. The Lombok Strait is notable as one of the main passages for the Indonesian Throughflow (ITF) that exchanges water between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It is also part of the biogeography, biogeographical boundary between the fauna of the Indomalayan realm and the distinctly different fauna of Australasian realm, Australasia. The boundary is known as the Wallace Line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Degree Channel
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics A six-sided polygon is a hexagon, one of the three regular polygons capable of tiling the plane. A hexagon also has 6 edges as well as 6 internal and external angles. 6 is the second smallest composite number. It is also the first number that is the sum of its proper divisors, making it the smallest perfect number. It is also the only perfect number that doesn't have a digital root of 1. 6 is the first unitary perfect number, since it is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisors, without including itself. Only five such numbers are known to exist. 6 is the largest of the four all-Harshad numbers. 6 is the 2nd superior highly composite number, the 2nd colossally abundant number, the 3rd triangular number, the 4th highly composite number, a pronic number, a congruent number, a harmonic divisor number, and a semiprime. 6 is also the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In modern times, the term ''Far East'' has widely fallen out of use and been substituted by Asia–Pacific, while the terms Middle East and Near East, although now pertaining to different territories, are still commonly used today. The term first came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 15th century, particularly the British people, British, denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "Easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East. Likewise, during the Qing dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term "Far West (Taixi), Tàixī ()" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries. Since the mid-20th century, the term has mostly gone out of use for the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Dependent On The Bay Of Bengal
The countries of the Bay of Bengal include littoral and landlocked countries in South Asia and Southeast Asia that depend on the bay for maritime usage. Historically, the Bay of Bengal has been a highway of transport, trade, and cultural exchange between diverse peoples encompassing the Indian subcontinent, Indochinese peninsula, and Malay Archipelago. Today, the Bay of Bengal region is the convergence of two major geopolitical blocs- the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multisectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) promotes regional engagement in the area. The Bay of Bengal countries are often categorized into a maritime subregion. The bay hosts vital shipping routes linking its littoral and landlocked hinterland with the Indian Ocean. Its sea bed is being explored and exploited for hydrocarbon reserves. Littoral countries *: The People's Republic of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Trade Of India
Foreign may refer to: Government * Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries * Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries ** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government ** Foreign office and foreign minister * United States state law, a legal matter in another state Science and technology * Foreign accent syndrome, a side effect of severe brain injury * Foreign key, a constraint in a relational database Arts and entertainment * Foreign film or world cinema, films and film industries of non-English-speaking countries * Foreign music or world music * Foreign literature or world literature * ''Foreign Policy'', a magazine Music * "Foreign", a song by Jessica Mauboy from her 2010 album ''Get 'Em Girls ''Get 'Em Girls'' is the second studio album by Australian recording artist Jessica Mauboy, released on 24 August 2010 by Sony. Mauboy recorded the album in Los Angeles, New York City and Atlanta. She worked with various American songwriters an ...'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force. A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are legal barriers to trade rather than physical barriers. It is also distinct from a siege in that a blockade is usually directed at an entire country or region, rather than a fortress or city and the objective may not always be to conquer the area. A blockading power can seek to cut off all maritime transport from and to the blockaded country, although stopping all land transport to and from an area may also be considered a blockade. Blockades restrict the trading rights of neutrals, who must submit for inspection for contraband, which the blockading power may define narrowly or broadly, sometimes including food and medicine. In the 20th century, air power has also been used to enhance the effectiveness of blockades by halting air traffic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke Point
In military strategy, a choke point (or chokepoint), or sometimes bottleneck, is a geographical feature on land such as a valley, defile or bridge, or maritime passage through a critical waterway such as a strait, which an armed force is forced to pass through in order to reach its objective, sometimes on a substantially narrowed front and therefore greatly decreasing its combat effectiveness by making it harder to bring superior numbers to bear. A choke point can allow a numerically inferior defending force to use the terrain as a force multiplier to thwart or ambush a much larger opponent, as the attacker cannot advance any further without first securing passage through the choke point. Historical examples Some historical examples of the tactical use of choke points are King Leonidas I's defense of the Pass of Thermopylae during an invasion led by Xerxes I of Persia; the Battle of Stamford Bridge in which Harold Godwinson defeated Harald Hardrada; William Wallace' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore Strait
The Singapore Strait is a , strait between the Strait of Malacca in the west and the South China Sea in the east. Singapore is on the north of the channel, and the Indonesian Riau Islands are on the south. The two countries share a maritime border along the strait. It includes Keppel Harbour and many small islands. The strait provides the deepwater passage to the Port of Singapore, which makes it very busy. Approximately 2,000 merchant ships traverse the waters on a daily basis in 2017. The depth of the Singapore Strait limits the maximum draft of vessels going through the Straits of Malacca, and the Malaccamax ship class. Historical records The 9th century AD Muslim author Ya'qubi referred a ''Bahr Salahit'' or Sea of Salahit (from the Malay ''selat'' meaning strait), one of the Seven Seas to be traversed to reach China. Some have interpreted Sea of Salahit as referring to Singapore, although others generally considered it the Malacca Strait, a point of contact between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten Degree Channel
The Ten Degree Channel is a channel that separates the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands from each other in the Bay of Bengal. The two sets of islands together form the Indian Union Territory (UT) of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. This channel is wide from north to south, and approximately long from east to west. It has minimum depth of 7.3m and lies from east to west on the 10-degree line of latitude north of the equator,Ten degrees channel (India) Sea-Seek] hence the name. See also * |
Strait
A strait is a water body connecting two seas or water basins. The surface water is, for the most part, at the same elevation on both sides and flows through the strait in both directions, even though the topography generally constricts the flow somewhat. In some straits there is a dominant directional current. Most commonly, the strait is a narrowing channel that lies between two land masses. Straits are loci for sediment accumulation, with sand-size deposits usually occurring on the two strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Some straits are not navigable because, for example, they are too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Terminology The terms '' channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, '' firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |