|
Analytic Variety
In mathematics, particularly differential geometry and complex geometry, a complex analytic varietyComplex analytic variety (or just variety) is sometimes required to be irreducible and (or) reduced or complex analytic space is a generalization of a complex manifold that allows the presence of singularities. Complex analytic varieties are locally ringed spaces that are locally isomorphic to local model spaces, where a local model space is an open subset of the vanishing locus of a finite set of holomorphic functions. Definition Denote the constant sheaf on a topological space with value \mathbb by \underline. A \mathbb-space is a locally ringed space (X, \mathcal_X), whose structure sheaf is an algebra over \underline. Choose an open subset U of some complex affine space \mathbb^n, and fix finitely many holomorphic functions f_1,\dots,f_k in U. Let X=V(f_1,\dots,f_k) be the common vanishing locus of these holomorphic functions, that is, X=\. Define a sheaf of rings on X by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme (mathematics)
In mathematics, specifically algebraic geometry, a scheme is a structure that enlarges the notion of algebraic variety in several ways, such as taking account of multiplicities (the equations and define the same algebraic variety but different schemes) and allowing "varieties" defined over any commutative ring (for example, Fermat curves are defined over the integers). Scheme theory was introduced by Alexander Grothendieck in 1960 in his treatise '' Éléments de géométrie algébrique'' (EGA); one of its aims was developing the formalism needed to solve deep problems of algebraic geometry, such as the Weil conjectures (the last of which was proved by Pierre Deligne). Strongly based on commutative algebra, scheme theory allows a systematic use of methods of topology and homological algebra. Scheme theory also unifies algebraic geometry with much of number theory, which eventually led to Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem. Schemes elaborate the fundamental idea that an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Geometry
Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics which uses abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, to solve geometry, geometrical problems. Classically, it studies zero of a function, zeros of multivariate polynomials; the modern approach generalizes this in a few different aspects. The fundamental objects of study in algebraic geometry are algebraic variety, algebraic varieties, which are geometric manifestations of solution set, solutions of systems of polynomial equations. Examples of the most studied classes of algebraic varieties are line (geometry), lines, circles, parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, cubic curves like elliptic curves, and quartic curves like lemniscate of Bernoulli, lemniscates and Cassini ovals. These are plane algebraic curves. A point of the plane lies on an algebraic curve if its coordinates satisfy a given polynomial equation. Basic questions involve the study of points of special interest like singular point of a curve, singular p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BY-NC-SA
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by Creative Commons, a U.S. non-profit corporation founded in 2001. There have also been five versions of the suite of licenses, numbered 1.0 through 4.0. Released in Novembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales De L'Institut Fourier
The ''Annales de l'Institut Fourier'' () is a French mathematical journal publishing papers in all fields of mathematics. It was established in 1949. The journal publishes one volume per year, consisting of six issues. The current editor-in-chief is Hervé Pajot. Articles are published either in English or in French. The journal is indexed in ''Mathematical Reviews'', ''Zentralblatt MATH'' and the Web of Science. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2008 impact factor of 0.804. 2008 Journal Citation Reports, Science Edition, Thomson Scientific Thomson Scientific was one of the six (later five) strategic business units of The Thomson Corporation, beginning in 2007, after being separated from Thomson Scientific & Healthcare. Following the merger of Thomson with Reuters Group to form Thom ..., 2008. References External links * Mathematics journals Academic journals established in 1949 Bimonthly journals Open access journals 1949 establishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematische Annalen
''Mathematische Annalen'' (abbreviated as ''Math. Ann.'' or, formerly, ''Math. Annal.'') is a German mathematical research journal founded in 1868 by Alfred Clebsch and Carl Neumann. Subsequent managing editors were Felix Klein, David Hilbert, Otto Blumenthal, Erich Hecke, Heinrich Behnke, Hans Grauert, Heinz Bauer, Herbert Amann, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, Wolfgang Lück, Nigel Hitchin, and Thomas Schick. Currently, the managing editor of Mathematische Annalen is Yoshikazu Giga (University of Tokyo). Volumes 1–80 (1869–1919) were published by Teubner. Since 1920 (vol. 81), the journal has been published by Springer. In the late 1920s, under the editorship of Hilbert, the journal became embroiled in controversy over the participation of L. E. J. Brouwer on its editorial board, a spillover from the foundational Brouwer–Hilbert controversy. Between 1945 and 1947, the journal briefly ceased publication. References External links''Mathematische Annalen''homepage a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inventiones Mathematicae
''Inventiones Mathematicae'' is a mathematical journal published monthly by Springer Science+Business Media. It was established in 1966 and is regarded as one of the most prestigious mathematics journals in the world. The current (2023) managing editors are Jean-Benoît Bost (University of Paris-Sud) and Wilhelm Schlag (Yale University Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: References External links *{{Official website, https://www.springer.com/journal/222 Mathematics journals Academic journals established in 1966 English-language journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Monthly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
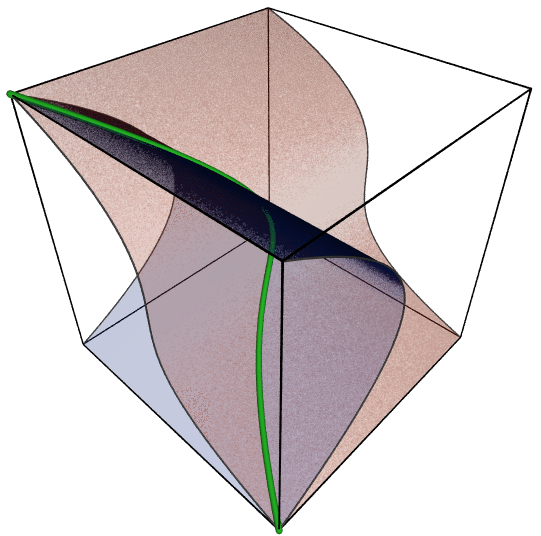
Algebraic Variety
Algebraic varieties are the central objects of study in algebraic geometry, a sub-field of mathematics. Classically, an algebraic variety is defined as the solution set, set of solutions of a system of polynomial equations over the real number, real or complex numbers. Modern definitions generalize this concept in several different ways, while attempting to preserve the geometric intuition behind the original definition. Conventions regarding the definition of an algebraic variety differ slightly. For example, some definitions require an algebraic variety to be Irreducible component, irreducible, which means that it is not the Union (set theory), union of two smaller Set (mathematics), sets that are Closed set, closed in the Zariski topology. Under this definition, non-irreducible algebraic varieties are called algebraic sets. Other conventions do not require irreducibility. The fundamental theorem of algebra establishes a link between algebra and geometry by showing that a mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluing Schemes
In algebraic geometry, a new scheme (e.g. an algebraic variety) can be obtained by gluing existing schemes through gluing maps. Statement Suppose there is a (possibly infinite) family of schemes \_ and for pairs i, j, there are open subsets U_ and isomorphisms \varphi_ : U_ \overset\to U_. Now, if the isomorphisms are compatible in the sense: for each i, j, k, # \varphi_ = \varphi_^, # \varphi_(U_ \cap U_) = U_ \cap U_, # \varphi_ \circ \varphi_ = \varphi_ on U_ \cap U_, then there exists a scheme ''X'', together with the morphisms \psi_i : X_i \to X such that # \psi_i is an isomorphism onto an open subset of ''X'', # X = \cup_i \psi_i(X_i), # \psi_i(U_) = \psi_i(X_i) \cap \psi_j(X_j), # \psi_i = \psi_j \circ \varphi_ on U_. Examples Projective line Let X = \operatorname(k \simeq \mathbb^1, Y = \operatorname(k \simeq \mathbb^1 be two copies of the affine line over a field ''k''. Let X_t = \ = \operatorname(k , t^ be the complement of the origin and Y_u = \ defined simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra Of Finite Type
In mathematics, a finitely generated algebra (also called an algebra of finite type) is a commutative associative algebra ''A'' over a field ''K'' where there exists a finite set of elements a_1,\dots,a_n of ''A'' such that every element of ''A'' can be expressed as a polynomial in a_1,\dots,a_n, with coefficients in ''K''. Equivalently, there exist elements a_1,\dots,a_n\in A such that the evaluation homomorphism at =(a_1,\dots,a_n) :\phi_\colon K _1,\dots,X_ntwoheadrightarrow A is surjective; thus, by applying the first isomorphism theorem, A \simeq K _1,\dots,X_n(\phi_). Conversely, A:= K _1,\dots,X_nI for any ideal I\subseteq K _1,\dots,X_n/math> is a K-algebra of finite type, indeed any element of A is a polynomial in the cosets a_i:=X_i+I, i=1,\dots,n with coefficients in K. Therefore, we obtain the following characterisation of finitely generated K-algebras :A is a finitely generated K-algebra if and only if it is isomorphic as a K-algebra to a quotient ring of the type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum Of A Ring
In commutative algebra, the prime spectrum (or simply the spectrum) of a commutative ring R is the set of all prime ideals of R, and is usually denoted by \operatorname; in algebraic geometry it is simultaneously a topological space equipped with a sheaf of rings. Zariski topology For any ideal I of R, define V_I to be the set of prime ideals containing I. We can put a topology on \operatorname(R) by defining the collection of closed sets to be :\big\. This topology is called the Zariski topology. A basis for the Zariski topology can be constructed as follows: For f\in R, define D_f to be the set of prime ideals of R not containing f. Then each D_f is an open subset of \operatorname(R), and \big\ is a basis for the Zariski topology. \operatorname(R) is a compact space, but almost never Hausdorff: In fact, the maximal ideals in R are precisely the closed points in this topology. By the same reasoning, \operatorname(R) is not, in general, a T1 space. However, \operatorna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |