|
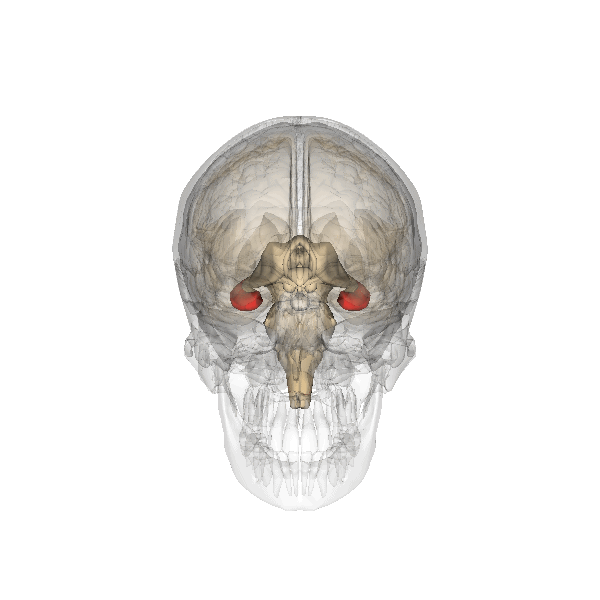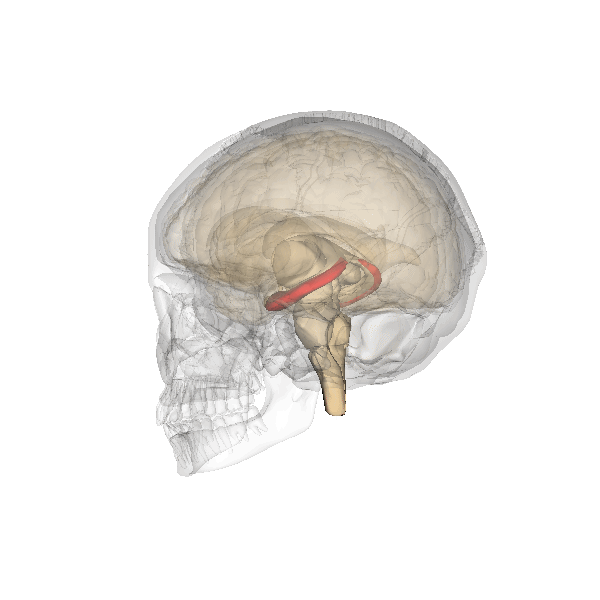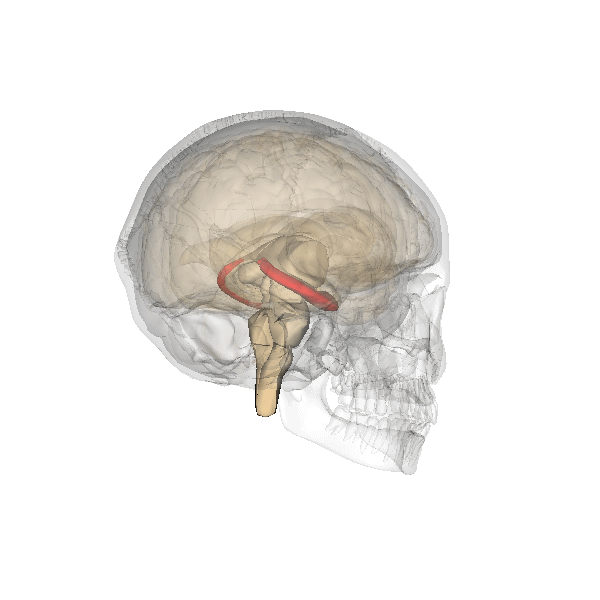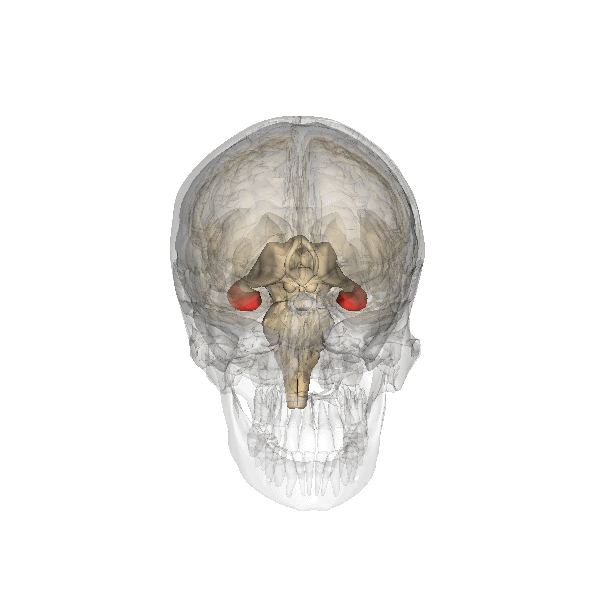
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fear Conditioning
Pavlovian fear conditioning is a behavioral paradigm in which organisms learn to predict aversive events. It is a form of learning in which an aversive stimulus (e.g. an electrical shock) is associated with a particular neutral context (e.g., a room) or neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone), resulting in the expression of fear responses to the originally neutral stimulus or context. This can be done by pairing the neutral stimulus with an aversive stimulus (e.g., an electric shock, loud noise, or unpleasant odor). Eventually, the neutral stimulus alone can elicit the state of fear. In the vocabulary of classical conditioning, the neutral stimulus or context is the "conditional stimulus" (CS), the aversive stimulus is the "unconditional stimulus" (US), and the fear is the "conditional response" (CR). Fear conditioning has been studied in numerous species, from snails to humans. In humans, conditioned fear is often measured with verbal report and galvanic skin response. In other animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbic System
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Psychology''.sec. 3.20 Its various components support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction. The limbic system is involved in lower order emotional processing of input from sensory systems and consists of the amygdala, mammillary bodies, stria medullaris, central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden. This processed information is often relayed to a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon, including the prefrontal cortex, cingulate gyrus, limbic thalamus, hippocampus including the parahippocampal gyrus and subiculum, nucleus accumbens (limbic striatum), anterior hypothalamus, ventral tegmental area, midbrain raphe nuclei, habenular commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nucleus Of The Amygdala
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA or aCeN) is a nucleus within the amygdala. It serves as the major output nucleus of the amygdala and participates in receiving and processing pain information. CeA connects with brainstem areas that control the expression of innate behaviors and associated physiological responses. CeA is responsible for autonomic components of emotions (e.g., changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration) primarily through output pathways to the lateral hypothalamus and brain stem. The CeA is also responsible for conscious perception of emotion primarily through the ventral amygdalofugal output pathway to the anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and prefrontal cortex. Amygdala subdividisions and outputs The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basolateral Amygdala
The basolateral amygdala, or basolateral complex, or basolateral nuclear complex consists of the lateral, basal and accessory-basal nuclei of the amygdala. The lateral nuclei receives the majority of sensory information, which arrives directly from the temporal lobe structures, including the hippocampus and primary auditory cortex. The basolateral amygdala also receives dense neuromodulatory inputs from ventral tegmental area (VTA), locus coeruleus (LC), and basal forebrain, whose integrity are important for associative learning. The information is then processed by the basolateral complex and is sent as output to the central nucleus of the amygdala. This is how most emotional arousal is formed in mammals. Function The amygdala has several different nuclei and internal pathways; the basolateral complex (or basolateral amygdala), the central nucleus, and the cortical nucleus are the most well-known. Each of these has a unique function and purpose within the amygdala. Fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercalated Cells Of The Amygdala
The Intercalated cells of the amygdala (ITC or ICCs) are GABAergic neurons situated between the basolateral and central nuclei of the amygdala that play a significant role in inhibitory control over the amygdala. They regulate amygdala-dependent emotional processing like fear memory and social behavior. Their function has been best studied with selective ITC ablation which impairs fear extinction, fear generalization, and social behavior. Studies have begun to recognize that ITC clusters may be implicated in reward, addiction, and withdrawal circuits given their heavy expression of dopamine and opioid receptors. In rodents, ITCs are organized into distinct clusters that wrap the basolateral amygdala (BLA). Each cluster is unique in connectivity, intrinsic properties, and function. These clusters are named by their location relative to the BLA with medial ITC clusters towards the central amygdala. Function ITC cells are thought to play a role as the "off" switch for the amygdala, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declarative Memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of Long-term memory, long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the Consciousness, conscious, intentional Recall (memory), recollection of factual information, previous experiences, and concepts. This type of memory is dependent upon three processes: acquisition, Memory Consolidation, consolidation, and retrieval. Explicit memory can be divided into two categories: episodic memory, which stores specific Experience, personal experiences, and semantic memory, which stores factual information.Tulving E. 1972. Episodic and semantic memory. In Organization of Memory, ed. E Tulving, W Donaldson, pp. 381–403. New York: Academic Explicit memory requires gradual learning, with multiple presentations of a Stimulus (psychology), stimulus and response. The type of knowledge that is stored in explicit memory is called declarative knowledge. Its counterpart, known as implicit memory, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory System
The olfactory system, is the sensory nervous system, sensory system used for the sense of smell (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses directly associated with specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system and an accessory olfactory system. The main olfactory system detects airborne substances, while the accessory system senses fluid-phase stimuli. The senses of smell and taste (gustatory system) are often referred to together as the chemosensory system, because they both give the brain information about the chemical composition of objects through a process called transduction (physiology), transduction. Structure Peripheral The peripheral olfactory system consists mainly of the nostrils, ethmoid bone, nasal cavity, and the olfactory epithelium (layers of thin tissue covered in mucus that line the nasal cavity). The primary components of the layers of epithelial tissue are the mucous membranes, olfactory glands, olfactory receptor neurons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere, hemisphere of the mammalian brain. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body's homeostasis. These functions include compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, interpersonal relationships, and awareness of homeostatic emotions such as Hunger (physiology), hunger, pain and fatigue. In relation to these, it is involved in psychopathology. The insular cortex is divided by the central sulcus of the insula, into two parts: the anterior insula and the posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotions
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is no scientific consensus on a definition. Emotions are often reciprocal determinism, intertwined with mood (psychology), mood, temperament, personality psychology, personality, disposition, or creativity. Research on emotion has increased over the past two decades, with many fields contributing, including psychology, medicine, history, sociology of emotions, computer science and philosophy. The numerous attempts to explain the origin, functional accounts of emotion, function, and other aspects of emotions have fostered intense research on this topic. Theorizing about the evolutionary origin and possible purpose of emotion dates back to Charles Darwin. Current areas of research include the neuroscience of emotion, using tools like positron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |