|
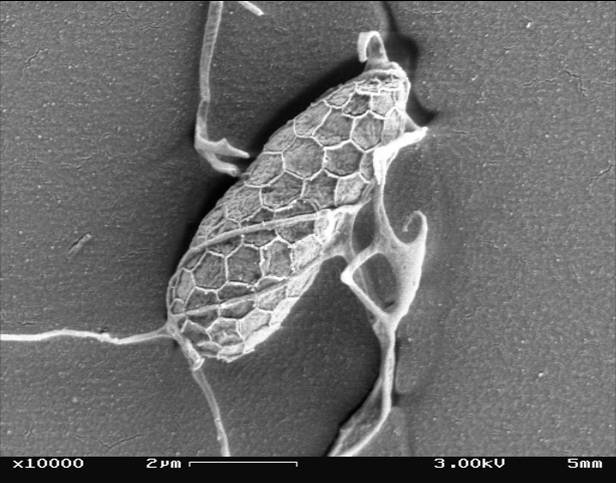
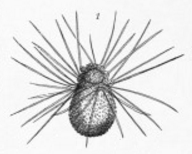
Amphitrema Jollyi
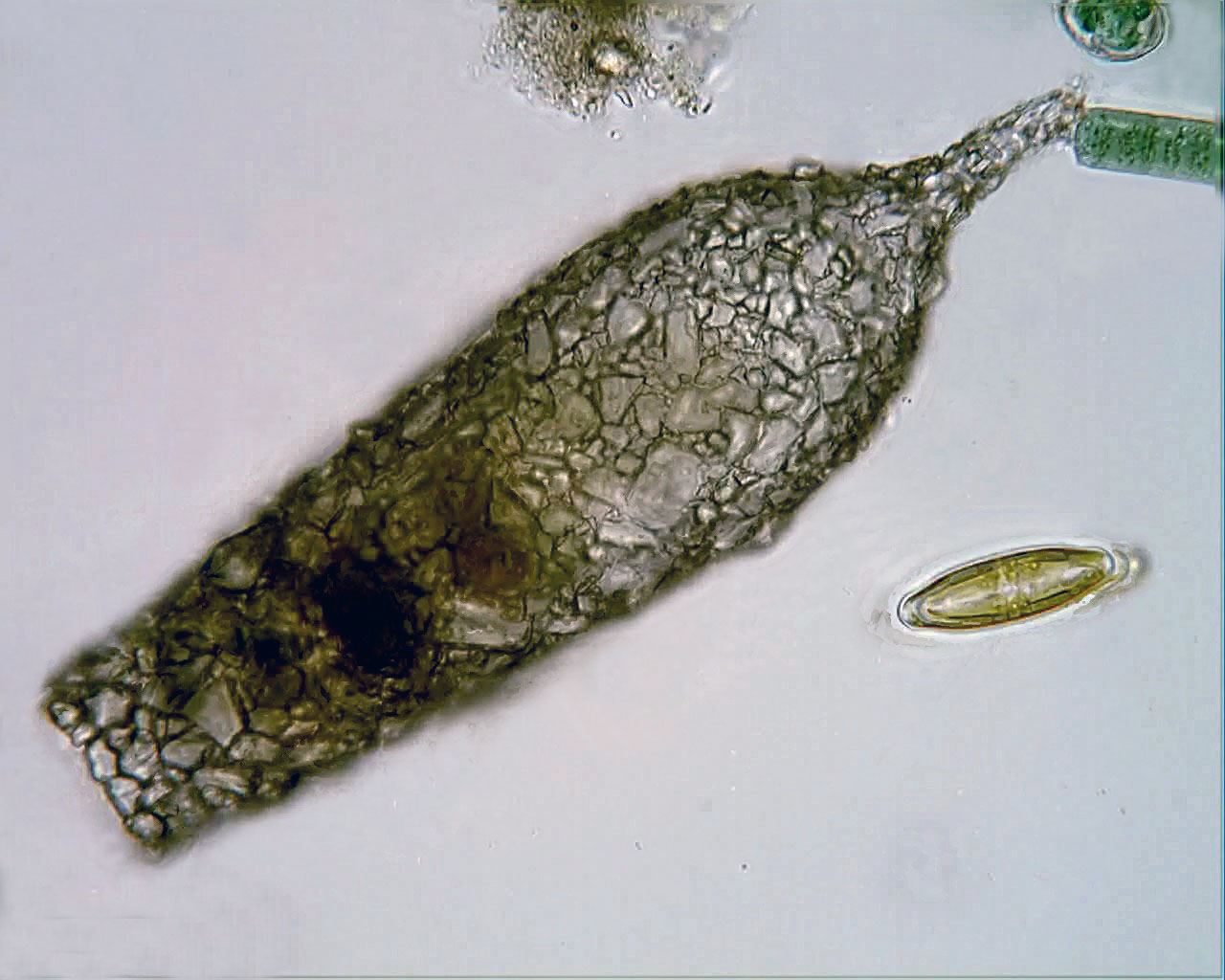
''Amphitrema'' is a genus of testate amoeba in the family Amphitremidae. The genus is commonly found in ''Sphagnum''-dominated peatlands. All species of this genus are mixotrophic and harbor unicellular algae belonging to genus ''Chlorella''. Species * ?'' Amphitrema congolense'' van Oye 1957 * ?'' Amphitrema jollyi'' Van Oye 1956 * ?''Amphitrema paparoensis'' Van Oye 1956 * ''Amphitrema stenostoma ''Amphitrema'' is a genus of Testate amoebae, testate amoeba in the family Amphitremidae. The genus is commonly found in ''Sphagnum''-dominated peatlands. All species of this genus are mixotrophic and harbor unicellular algae belonging to genus ' ...'' Nusslin 1884 * '' Amphitrema wrightianum'' Archer 1869 References * Gomaa F, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2013 Amphitremida (Poche, 1913) is a new major, ubiquitous labyrinthulomycete clade. PLoS ONE 8(1): e53046. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053046 * Gomaa F, Kosakyan A, Heger TJ, Corsaro D, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2014. One Alga to Rule them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitrema Stenostoma
''Amphitrema'' is a genus of Testate amoebae, testate amoeba in the family Amphitremidae. The genus is commonly found in ''Sphagnum''-dominated peatlands. All species of this genus are mixotrophic and harbor unicellular algae belonging to genus ''Chlorella''. Species * ?''Amphitrema congolense'' van Oye 1957 * ?''Amphitrema jollyi'' Van Oye 1956 * ?''Amphitrema paparoensis'' Van Oye 1956 * ''Amphitrema stenostoma'' Nusslin 1884 * ''Amphitrema wrightianum'' Archer 1869 References * Gomaa F, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2013 Amphitremida (Poche, 1913) is a new major, ubiquitous labyrinthulomycete clade. PLoS ONE 8(1): e53046. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053046 * Gomaa F, Kosakyan A, Heger TJ, Corsaro D, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2014. One Alga to Rule them All: Unrelated Mixotrophic Testate Amoebae (Amoebozoa, Rhizaria and Stramenopiles) Share the Same Symbiont (Trebouxiophyceae). Protist 165(2): 161-176. doi: /10.1016/j.protis.2014.01.002 External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokonta
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria. Stramenopiles are eukaryotes; most are single-celled, but some are multicellular including some large seaweeds, the brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid Heliozoa, and oomycetes. The tripartite hairs characteristic of the group have been lost in some of the included taxa – for example in most di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthulomycetes
Labyrinthulomycetes (ICNafp) or Labyrinthulea (ICZN) is a class of protists that produce a network of filaments or tubes, which serve as tracks for the cells to glide along and absorb nutrients for them. The two main groups are the labyrinthulids (or slime nets) and thraustochytrids. They are mostly marine, commonly found as parasites on algae and seagrasses or as decomposers on dead plant material. They also include some parasites of marine invertebrates and mixotrophic species that live in a symbiotic relationship with zoochlorella. Characteristics Although they are outside the cells, the filaments of Labyrinthulomycetes are surrounded by a membrane. They are formed and connected with the cytoplasm by a unique organelle called a sagenogen or bothrosome. The cells are uninucleated and typically ovoid, and move back and forth along the amorphous network at speeds varying from 5-150 μm per minute. Among the labyrinthulids, the cells are enclosed within the tubes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testate Amoebae
Testate amoebae (formerly thecamoebians, Testacea or Thecamoeba) are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test (biology), test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the pseudopodia emerge, that provides the amoeba with shelter from predators and environmental conditions. The test of some species is produced entirely by the amoeba and may be organic, siliceous or calcareous depending on the species (autogenic tests), whereas in other cases the test is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions from within the cell (xenogenic tests). A few taxa (Hyalospheniidae) can build either type, depending on the circumstances and availability of foreign material. The assemblage referred to as "testate amoebae" is actually composed of several, unrelated groups of organisms. However, some features they all share that have been used to g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuge, ericaceous shrubs, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixotrophic
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. There are two types of eukaryotic mixotrophs. There are those with their own chloroplasts – including those with endosymbionts providing the chloroplasts. And there are those that acquire them through kleptoplasty, or through symbiotic associations with prey, or through 'enslavement' of the prey's organelles.Leles S G et al, (2017). Oceanic protists with different forms of acquired phototrophy display contrasting biogeographies and abundance, ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''. Possible combinations are photo- and chemotrophy, litho- and organotrophy ( osmotrophy, phagotrophy and myzocytosis), auto- and heterotrophy or other combinations of these. Mixotrophs can be either eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorella
''Chlorella'' is a genus of about thirteen species of single- celled or colonial green algae of the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain the green photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll-a and -b. In ideal conditions cells of ''Chlorella'' multiply rapidly, requiring only carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and a small amount of minerals to reproduce. The name ''Chlorella'' is taken from the Greek χλώρος, ''chlōros/ khlōros'', meaning green, and the Latin diminutive suffix -''ella'', meaning small. German biochemist and cell physiologist Otto Heinrich Warburg, awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1931 for his research on cell respiration, also studied photosynthesis in ''Chlorella''. In 1961, Melvin Calvin of the University of California received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research on the pathways of carbon dioxide assimilation in plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitrema Congolense
''Amphitrema'' is a genus of testate amoeba in the family Amphitremidae. The genus is commonly found in ''Sphagnum''-dominated peatlands. All species of this genus are mixotrophic and harbor unicellular algae belonging to genus ''Chlorella''. Species * ?'' Amphitrema congolense'' van Oye 1957 * ?'' Amphitrema jollyi'' Van Oye 1956 * ?''Amphitrema paparoensis'' Van Oye 1956 * ''Amphitrema stenostoma ''Amphitrema'' is a genus of Testate amoebae, testate amoeba in the family Amphitremidae. The genus is commonly found in ''Sphagnum''-dominated peatlands. All species of this genus are mixotrophic and harbor unicellular algae belonging to genus ' ...'' Nusslin 1884 * '' Amphitrema wrightianum'' Archer 1869 References * Gomaa F, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2013 Amphitremida (Poche, 1913) is a new major, ubiquitous labyrinthulomycete clade. PLoS ONE 8(1): e53046. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053046 * Gomaa F, Kosakyan A, Heger TJ, Corsaro D, Mitchell EAD, Lara E. 2014. One Alga to Rule them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |