|
Amenhotep (High Priest Of Amun)
Amenhotep was the High Priest of Amun towards the end of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, serving under Ramesses IX, Ramesses X and Ramesses XI. He was the son of Ramessesnakht, the previous high priest of Amun. It is not beyond dispute who succeeded him in office. For a long time it was assumed that he was followed by the High Priest Herihor. However, Karl Jansen-Winkeln has suggested that Amenhotep was instead succeeded by the High Priest Piankh. We know the names of several of his brothers and a sister: * his (eldest?) brother, the prophet of Amun Meribast II * his brother, the Chief Steward Usimarenakth II * his sister Aatmeret I * his brother, the Second Prophet of Amun Nesamun I (see below) The "Transgression against the High Priest" From several references in the Tomb Robbery Papyri ( Pap. Mayer A; Pap. B.M. 10383; Pap. B.M. 10052) it can be deduced that, sometime prior to the start of the era known as the Wehem Mesut, the Viceroy of Kush Pinehesy attacked Thebes and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramessesnakht
Ramessesnakht was High Priest of Amun during many years in the 20th Dynasty. He was appointed as the High Priest at Thebes under Ramesses IV. He served in office until the reign of Ramesses IX. It was during Ramessesnakht's tenure that the power and importance of the Amun priesthood grew over Egypt while the Pharaoh's power began to noticeably decline. Biography He was the son of Meribastet, steward to the pharaoh. Ramessesnakht was married to Adjedet-Aat, the daughter of Setau, High Priest of Nekhbet, and had at least two sons: Amenhotep and Nesamun and a daughter Tamerit. His son Amenhotep would succeed him in office and there is evidence that, at least for a while, his son, the Second Prophet of Amun Nesamun also acted as High Priest of Amun. His daughter Tamerit married Amenemopet, Third Prophet of Amun, making the family related through marriage to another important priestly family, that of Bakenkhonsu who served as High Priest of Amun under Ramesses II. (Amenemopet w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Spiegelberg
Wilhelm Spiegelberg (25 June 1870, Hannover – 23 December 1930, Munich) was a German Egyptologist. He specialized in analyses of Demotic and hieratic text. Spiegelberg grew up as the second oldest of four brothers in a German Jewish family. He studied Egyptology and archaeology in Strasbourg and Berlin, obtaining his doctorate from the University of Strasbourg in 1891. As a student his influences included Johannes Dümichen, Adolf Michaelis and Adolf Erman. After graduation, he continued his education in Paris as a student of Gaston Maspero. In 1899 he became an associate professor at Strasbourg, where in 1907 he obtained a full professorship. In 1919 he relocated to the University of Heidelberg, and four years later succeeded Friedrich Wilhelm von Bissing as chair of Egyptology at the University of Munich.Wilhelm Spiegelberg @ NDB/A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theban High Priests Of Amun
The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun (''wikt:ḥm#Egyptian, ḥm wikt:nṯr#Egyptian, nṯr wikt:tpj#Egyptian, tpj n wikt:jmn#Egyptian, jmn'') was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian deities, ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. History The priesthood of Amun rose in power during the early Eighteenth dynasty through significant tributes to the god Amun by rulers such as Hatshepsut and more importantly Thutmose III. The Amun priesthood in Thebes had four high-ranking priests: * The Chief Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn''), also referred to as the Chief Priest of Amun. * The Second Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr snnw n jmn''), also referred to as the Second Priest of Amun. * The Third Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr ḫmtnw n jmn khemet-nu''), also referred to as the Third Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whm Mswt
The period of ancient Egyptian history known as wehem mesut or, more commonly, Whm Mswt (Manuel de Codage transliteration: wHm msw.t) can be literally translated as ''Repetition of Births'', but is usually referred to as the ''(Era of the) Renaissance''. Date The Whm Mswt forms part of the reign of Ramesses XI, a king who ruled around the end of the New Kingdom and the start of the Third Intermediate Period. In his 19th year he began to count anew, with year 1 of the Whm Mswt perhaps identical to, but at least partly overlapping with his 19th regnal year, as can be seen from the headings of two lists of thieves, known as the Abbott Dockets. These read: * Year 1, first month of inundation, day 2, corresponding to Year 19 * Year 1, second month of inundation, day 24, corresponding to Year 19 For a long time it was unclear where the Whm Mswt should be placed chronologically. Since the reign of Ramesses IX lasted into its 19th year, the Abbott Dockets were sometimes taken as evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, phonetic mix-ups such as spoonerisms, obscure words and meanings, clever rhetorical excursions, oddly formed sentences, double entendres, and telling character names (such as in the play '' The Importance of Being Earnest'', ''Ernest'' being a given name that sounds exactly like the adjective ''earnest''). Word play is quite common in oral cultures as a method of reinforcing meaning. Examples of text-based ( orthographic) word play are found in languages with or without alphabet-based scripts, such as homophonic puns in Mandarin Chinese. Techniques ; Tom Swifties: A form of humorous writing where adverbs are chosen to reflect the nature of the situation in a punning way. "Hurry up and get to the back of the ship", Tom said sternly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman à Clef
A ''roman à clef'' ( ; ; ) is a novel about real-life events that is overlaid with a façade of fiction. The fictitious names in the novel represent real people and the "key" is the relationship between the non-fiction and the fiction. This metaphorical key may be produced separately—typically as an explicit guide to the text by the author—or implied, through the use of epigraphs or other literary techniques. Madeleine de Scudéry created the ''roman à clef'' in the 17th century to provide a forum for her thinly veiled fiction featuring political and public figures. An author might choose the ''roman à clef'' as a means of satire, of writing about controversial topics, reporting inside information on scandals without giving rise to charges of libel, the opportunity to turn the tale the way the author would like it to have gone, the opportunity to portray autobiographical experiences without having to expose the author as the subject, avoiding incrimination that could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tale Of Woe
Tale may refer to: * Narrative, or story, a report of real or imaginary connected events * TAL effector (TALE), a type of DNA binding protein * Tale, Albania, a resort town * Tale, Iran, a village * Tale, Maharashtra, a village in Ratnagiri district, Maharashtra state, India * River Tale, a small river in the English county of Devon * ''The Tale'', 2018 American drama film * The Tale (short story), a 1917 short story by Joseph Conrad See also * Tale-e Rudbar, a village in Iran * Taleh, a town in Somalia * Tales (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Story Of Wenamun
The Story of Wenamun (alternately known as the Report of Wenamun, The Misadventures of Wenamun, Voyage of Unamūn, or nformallyas just Wenamun) is a literary text written in hieratic in the Late Egyptian language. It is only known from one incomplete copy discovered in 1890 at al-Hibah, Egypt, and subsequently purchased in 1891 in Cairo by the Russian Egyptologist Vladimir Golenishchev. It was found in a jar together with the Onomasticon of Amenope and the Tale of Woe. The story features a mixture of literary tropes along with an administrative writing style, which has led to a longstanding uncertainty about whether it is a fictitious account or a genuine historical document. Despite this, what scholars can agree on is its importance in showing the political and religious state of Egypt during the transition between the New Kingdom and the Third Intermediate Period. The papyrus is now in the collection of the Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, and officially designated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byblos
Byblos ( ; ), also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl (, Lebanese Arabic, locally ), is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited since 5000BC. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous cultures including Old Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Achaemenid Empire, Persian, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, Roman Empire, Roman, Genoese Republic, Genoese, Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman. Urbanisation is thought to have begun during the third millennium BC when it developed into a city, making it one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, if not the oldest. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was in Ancient Byblos that the Phoenician alphabet, likely the ancestor of the Greek alphabet, Greek, Latin and all other Western alphabets, was developed. Etymology The name appears as ''Keb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
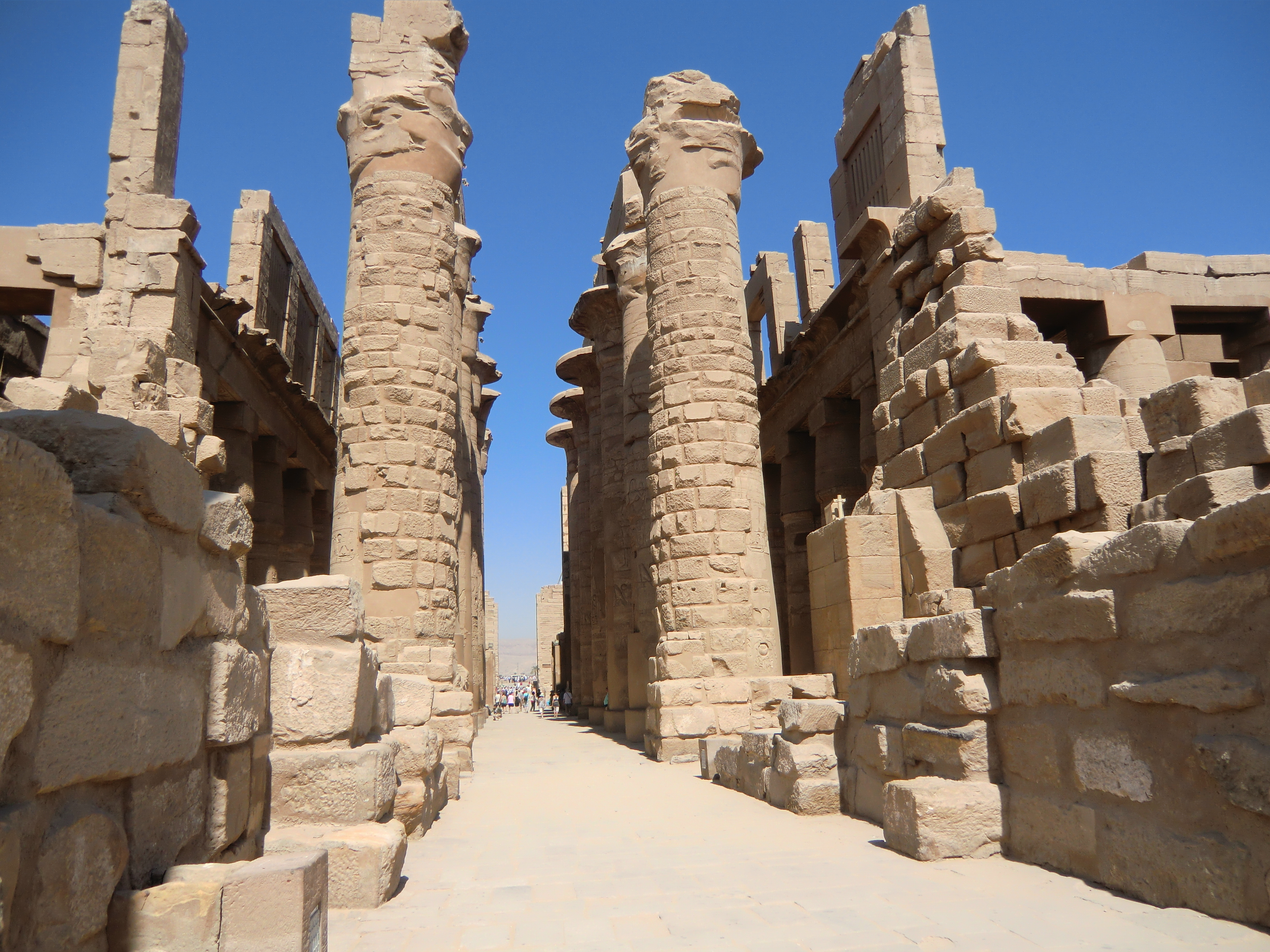
Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (), comprises a vast mix of temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BC) in the Middle Kingdom () and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BC), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. Karnak gets its name from the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Name The original name of the temple was ''Ipet-isut'', meaning "The Most Select of Places". The complex's modern name "Karnak" comes from the nearby village of el-Karnak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract of the Nile (south of Aswan in southern Egypt) or more strictly, Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several African empires, empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 25th Dynasty. From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia was invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Ptolemaic Kingdom, Greeks and Roman Empire, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |