|
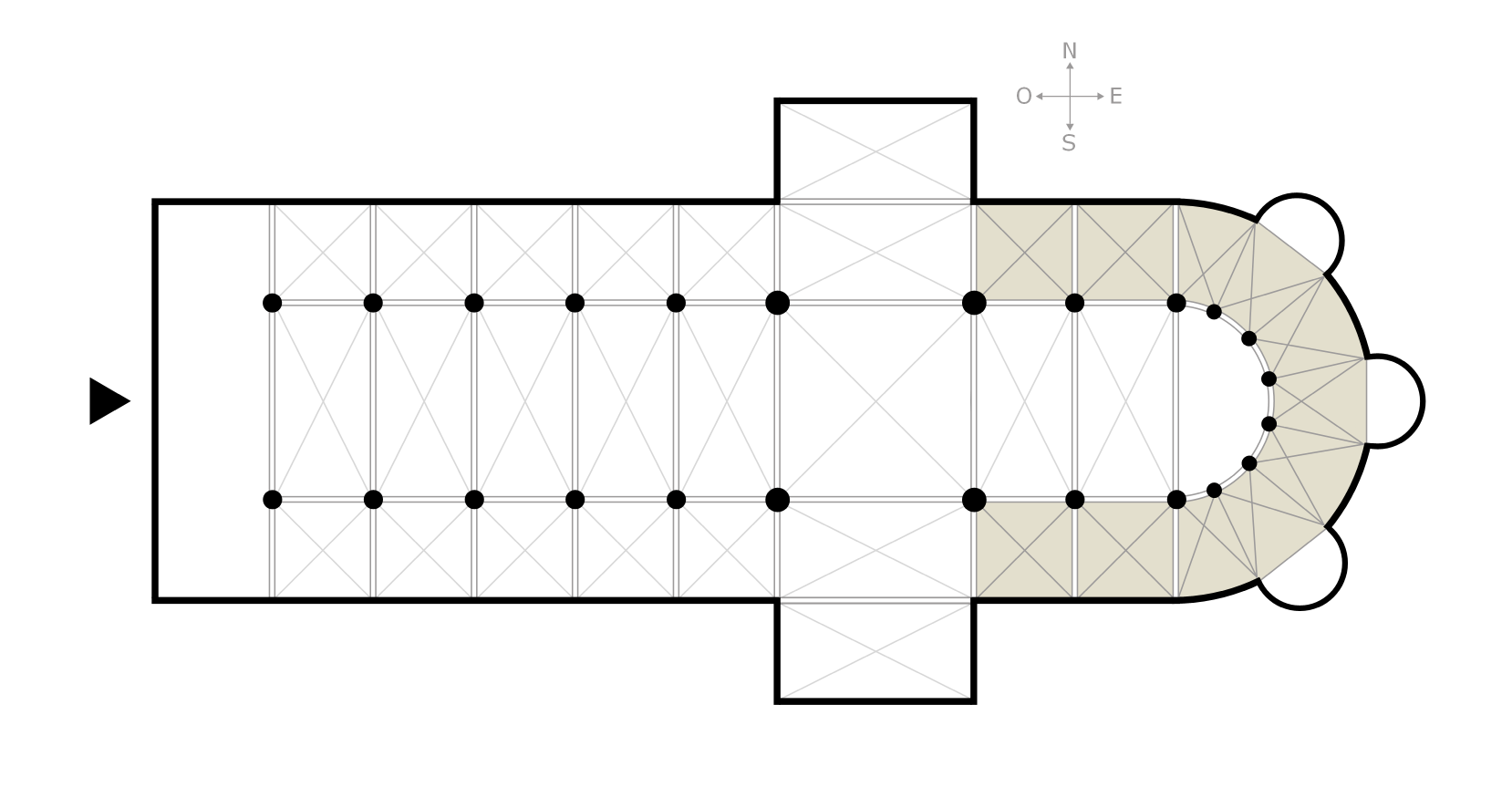
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory Care
Ambulatory care or outpatient care is Health care, medical care provided on an outpatient basis, including diagnosis, observation, consultation, treatment, intervention, and rehabilitation services. This care can include advanced medical technology and Medical procedure, procedures even when provided outside of hospitals. Ambulatory care sensitive conditions (ACSC) are health conditions where appropriate ambulatory care prevents or reduces the need for hospital admission (or ''inpatient'' care), such as diabetes or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Canadian Institute for Health InformationAmbulatory Care Sensitive Conditions. Accessed 14 April 2014. Many medical investigations and treatments for acute and chronic illnesses and preventive health care can be performed on an ambulatory basis, including minor surgical and medical procedures, most types of dental services, dermatology services, and many types of Medical diagnosis, diagnostic procedures (e.g. blood tests, Medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durga Temple, Aihole
The Durga temple is an early 8th-century Hindu temple located in Aihole, Karnataka, India. Originally dedicated to Surya, it has the most embellished and largest relief panels in Aihole depicting artwork of Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism and Vedic deities. Apart from its fine carvings, it is notable for its apsidal plan – a rare example among early Chalukyan Hindu temple architecture.Michell (2011), pp. 82–86 Though dedicated to Surya, the temple is now named Durga because a ''durg'' or fortified lookout was constructed on top of it after the 13th-century during the wars between Hindu kingdoms and Islamic Sultanates. This rubble lookout survived through the 19th-century when this site was rediscovered (it is now gone, temple has been restored). The Durga temple is the most prominent attraction in Aihole for tourist and scholars. It is a part of a pending UNESCO World Heritage Site application. Date The temple has been dated between the late 7th century and early 8t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory Care Nursing
Ambulatory care nursing is the nursing care of patients who receive treatment on an outpatient basis, ie they do not require admission to a hospital for an overnight stay. Ambulatory care includes those clinical, organizational and professional activities engaged in by registered nurses with and for individuals, groups, and populations who seek assistance with improving health and/or seek care for health-related problems. The American Academy of Ambulatory Care Nursing (AAACN) describes ambulatory care nursing as a comprehensive practice which is built on a broad knowledge base of nursing and health sciences, and applies clinical expertise rooted in the nursing process. Ambulatory care nurses use evidence based information across a variety of outpatient health care settings to achieve and ensure patient safety and quality of care while improving patient outcomes. Contact with patients in ambulatory care is often relatively brief, and in the context of a high volume of patients. Nurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of Saint-Quentin
The Basilica of Saint-Quentin (), formerly the Collegiate Church of Saint-Quentin () is a Catholic church in the town of Saint-Quentin, Aisne, France. There have been religious buildings on the site since the 4th century AD, which were repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during the Early Middle Ages. The present basilica was constructed in stages between the 12th and 15th centuries. It was severely damaged in World War I (1914–18), and was only reopened in 1956 after extensive reconstruction. Origins The town of Saint-Quentin has been identified with the Roman city of Augusta Veromandurorum, a commercial center at an important crossroads. It takes its present name from the Christian missionary Saint Caius Quintinus, who was beheaded there in 287 AD. Legend says the body was found many years later in the nearby marches of the River Somme by a Roman widow named Eusebia. She reburied the remains at the top of the hill at the center of the present town and built a small shri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Séverin, Paris
The Church of Saint-Séverin (, ) is a Roman Catholic church in the 5th arrondissement, or Latin Quarter, of Paris, on the lively tourist street Rue Saint-Séverin. It was constructed beginning in 1230, then, after a fire, rebuilt and enlarged in the 15th to 17th centuries in the Flamboyant Gothic style. It was the parish church for students at the University of Paris, and is one of the oldest churches that remains standing on the Left Bank. History The church took its name from Saint Séverin of Paris, a devout hermit who lived at the site in the 6th century, and died in about 540. One of his pupils was Clodoald or Saint Cloud, a Merovingian prince who quit the royal family to himself become a monk and hermit, who also later became a Saint. After the death of Severin, a chapel was erected on the site of his cell, believed to be near the oratory of Saint Martin in the present church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Architecture
Church architecture refers to the architecture of Christian buildings, such as Church (building), churches, chapels, convents, and seminaries. It has evolved over the two thousand years of the Christian religion, partly by innovation and partly by borrowing other architectural styles as well as responding to changing beliefs, practices and local traditions. From the Early Christianity to the present, the most significant objects of transformation for Christian architecture and design were the great churches of Byzantium, the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque abbey churches, Gothic architecture, Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance architecture, Renaissance basilicas with its emphasis on harmony. These large, often ornate and architecturally prestigious buildings were dominant features of the towns and countryside in which they stood. However, far more numerous were the parish churches in Christendom, the focus of Christian devotion in every town and village. While a few are counted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumambulation
Circumambulation (from Latin ''circum'' around and ''ambulātus ''to walk) is the act of moving around a sacred object or idol. Circumambulation of temples or deity images is an integral part of Hindu and Buddhist devotional practice (known in Sanskrit as ''Parikrama, pradakśiṇā''). It is also present in other religions, including Christianity, Judaism, and Islam. Indian religions In many Hindu temples, the temple structure reflects the symbolism of the Hindu association of the spiritual transition from daily life to spiritual perfection as a journey through stages. Passageways for circumambulation are present through which worshipers move in a clockwise direction, starting at the sanctuary doorway and moving inward toward the sanctum sanctorum, inner sanctum where the deity is enshrined. This is a translation of the spiritual concept of transition through levels in life into bodily movements by the worshipers as they move inwardly through ambulatory halls to the most sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parikrama
Parikrama or Pradakshina is clockwise circumambulation of sacred entities, and the path along which this is performed, as practiced in the Indian religions, Indic religions – Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. In Buddhism, it refers only to the path along which this is performed. In Indic religions, the parikrama is typically done after completion of traditional worship (puja (other), puja) and after Darśana, paying homage to the deity. Parikrama must be done with dhyāna (other), dhyāna (spiritual contemplation and meditation). In Hinduism, parikrama of religious deities in a temple, sacred rivers, sacred hills and a close cluster of temples as a symbol of prayer is an integral part of Worship in Hinduism, Hindu worship.http://www.hindunet.org/faq/fom-serv/cache/31.html Why do we perform Pradakshina or Parikrama?http://www.hinduism.co.za/kaabaa.htm Kaaba a Hindu Temple?Hindus invariably circumambulate around their deities Hindu temple architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horton Court
Horton Court is a stone-built 16th century manor house in Horton, near Chipping Sodbury, South Gloucestershire, England. It is a grade I listed building. Originally a Norman manor, the current house was built in about 1521 by Rev. William Knight (d. 1547), Prothonotary to the Holy See, and later Bishop of Bath and Wells. It retains the 12th-century Norman hall, and displays some of the earliest Renaissance decorative motifs used in England. Within the grounds is a grade I listed ambulatory, built for William Knight around 1527–29. It has been owned by the National Trust since 1949. As of 2021, it is available for holiday lets. The parish church of St James the Elder is next door. History See of Sarum Early in the 12th century Hubert de Rye donated the manor to the See of Sarum, which used the revenues to endow a prebend. An early Hubert of RyesKeats-Rohan ''Domesday Descendants'' p. 194 is known in legend as the loyal vassal who saved the life of William the Conqueror in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Architecture
Indian architecture is rooted in the History of India, history, Culture of India, culture, and Indian religions, religion of India. Among several architectural styles and traditions, the best-known include the many varieties of Hindu temple architecture and Indo-Islamic architecture, especially Rajput architecture, Mughal architecture, Dravidian architecture, South Indian architecture, and Indo-Saracenic architecture. Early Indian architecture was made from wood, which did not survive due to rotting and instability in the structures. Instead, the earliest surviving examples of Indian architecture are Indian rock-cut architecture, including many Buddhist temple, Buddhist, Hindu temple, Hindu, and Jain temple, Jain temples. The Hindu temple architecture is divided into the Dravidian architecture, Dravidian style of South India, southern India and the Nagara architecture, Nagara style of North India, northern India, with other regional styles. Housing styles also vary between reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |