|
Ambohiby Massif
Ambohiby Massif is an alkaline ring complex in Tsiroanomandidy District, Bongolava, Madagascar, which covers approximately . The settlement of Anosibe Ambohiby, which has a population of about 300 Betsileo people, is located within the complex almost entirely isolated from the rest of the region; the closest settlement is the town of Antaniditra, away, and the nearest city, Tsiroanomandidy, is away. History The massif was formed during the Late Cretaceous period, as the Madagascar Plate and the Indian Plate separated around 90 million years ago. Originally it was a volcano, however as the tectonic plates separated, the hotspot supplying it was cut off, causing the volcano to cool and collapse as it had no heat source. According to the record from French botanist Jacques Désiré Leandri published in 1935, the crater was called 'Andranomangatsiaka' (translating to 'at the place of cold water'), not to be confused with the current namesake down south, by the area' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Complex
A ring dike or ring dyke is an Intrusive rock, intrusive igneous body that is circular, oval or arcuate in plan and has steep contacts. While the widths of ring dikes differ, they can be up to several thousand meters. The most commonly accepted method of ring dike formation is directly related to collapse calderas.Gudmundsson, Agust. "Formation of collapse calderas." ''Geology'' 16.9 (1988): 808–10. Caldera collapse and ring dike formation Collapse calderas form due to the emptying of a magma chamber. Effusive eruptions that take place on the flanks of the associated volcano and a Fissure vent, fissure system that direct magma away from the chamber are both mechanisms that can empty a magma chamber. As pressure in the magma chamber changes, an increase in tensile stresses create tension fractures at the surface of the volcano. The geometry of the top of the magma chamber dictates the location and magnitude of the tension fractures. In addition, it was found that the higher th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Madagascar
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratum, stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. ''Citrus'' is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Indigenous people in these areas have used and domesticated various species since ancient times. Its cultivation first spread into Micronesia and Polynesia through the Austronesian expansion (–1500 BCE). Later, it was spread to the Middle East and the Mediterranean () via the incense trade route, and from Europe to the Americas. Renowned for their highly fragrant aromas and complex flavor, citrus are among the most popular fruits in cultivation. With a propensity to hybridize between species, making their taxonomy complicated, there are numerous varieties encompassing a wide range of appearance and fruit flavors. Evolution Evolutionary history The large cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betsileo
The Betsileo are a highland ethnic group of Madagascar, the third largest in terms of population. They chose their name, meaning "The Many Invincible Ones", after a failed invasion by King Ramitraho of the Menabe kingdom in the early 19th century. Territory The Betsileo occupy the south of the Madagascar plateau. Their traditional territory extends from the north of the Mania River in the north to the foot of the Andringitra Massif in the south; to the west by the Bongolava chain and the east by the Eastern Forest, occupied by the Tanala tribe. Most of the Betsileo region lies within the boundaries of the Malagasy province of Fianarantsoa, where their capital city of the same name can be found. Traditionally their territory and their people are divided into three major parts. The Northern Betsileo (or Fisakana) is defined by the Ivato and Manandona rivers in the north and the Sahanivotry and Mania rivers to the south. The Central Betsileo (or Manandriana) is found betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic Point
A triangulation station, also known as a trigonometrical point, and sometimes informally as a trig, is a fixed surveying station, used in geodetic surveying and other surveying projects in its vicinity. The station is usually set up by a mapping organisation with known coordinates and elevation published. Numerous stations are installed on summits for purposes of visibility and prominence. A graven metal plate on the top of a pillar may provide a mounting point for a theodolite or reflector, often using some form of kinematic coupling to ensure reproducible positioning. Use Trigonometrical stations form networks of triangulation. Positions of land boundaries, roads, railways, bridges and other infrastructure can be accurately located by the network, a task essential to the construction of modern infrastructure. Apart from the known stations set up by government, some temporary trigonometrical stations are set up near construction sites for monitoring the precision and progress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andranomangatsiaka
Andranomangatsiaka is a town and commune () in southwest Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Betioky Sud, which is a part of Atsimo-Andrefana Region. The population of the commune was estimated to be approximately 10,000 in 2001 commune census. Only primary schooling is available. The majority 70% of the population of the commune are farmers, while an additional 25% receives their livelihood from raising livestock. The most important crop is rice, while other important products are sugarcane, cassava and sweet potato The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...es. Services provide employment for 5% of the population. References and notes Populated places in Atsimo-Andrefana {{AtsimoAndrefana-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Désiré Leandri
Jacques Désiré Leandri, born 1903 in Corsica, died 1982, was a French botanist and mycologist. Leandri is remembered for botanical excursions in North Africa (Morocco) and Madagascar. He collected plants for scientific study from the years 1922 to 1980. The plant genus '' Leandriella'' from the family Acanthaceae Acanthaceae () is a Family (biology), family (the acanthus family) of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing almost 250 genera and about 2500 species. Most are Tropics, tropical Herbaceous plant, herbs, shrubs, or twining vines; some are epip ... is named after him. As a taxonomist, he circumscribed many plants within the family Euphorbiaceae. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
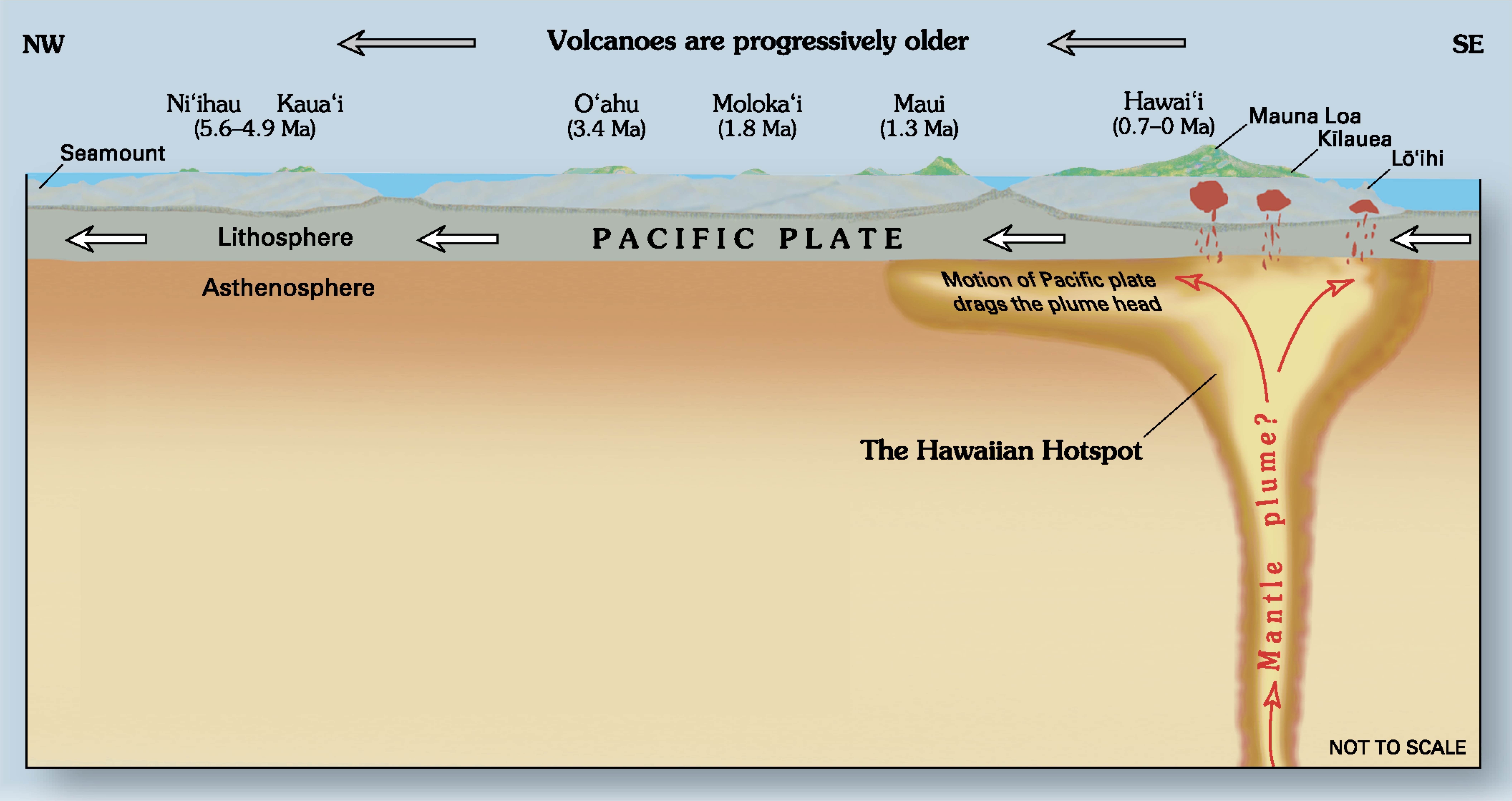
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying Mantle (geology), mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii, Iceland hotspot, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of plate boundary, tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory (volcanism), plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Plate
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annually. Faults tend to be geologically active, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian plate (or India plate) is or was a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana and began moving north, carrying Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian plate to form a single Indo-Australian plate, but recent studies suggest that India and Australia may have been separate plates for at least 3 million years. The Indian plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China, western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan, and Balochistan in Pakistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian plate formed part of the supercontinent, Gondwana, together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana fragmented as these continents drifted apa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |