|
Alumni Of The University Of Nottingham
A list of people related to the University of Nottingham or to its predecessor, University College, Nottingham. Office holders Chancellors * John Boot, 2nd Baron Trent (1949 - 1954) * William Cavendish-Bentinck, 7th Duke of Portland (1954 - 1971) * Francis Hill, Sir Francis Hill (1971 - 1978) * Gordon Hobday, Sir Gordon Hobday (1978 - 1993) * Ronald Dearing, Baron Dearing (1993 - 2000) * Fujia Yang (2000 - 2012) * Sir Andrew Witty (2013–2017) * Baroness Young of Hornsey (2020–present) Vice-Chancellors * Bertrand Hallward (1948 - 1965) * Frederick Dainton, Baron Dainton (1965 - 1970) * John Butterfield, Baron Butterfield (1971 - 1975) * Basil Weedon (1976 - 1988) * Colin Campbell (academic), Sir Colin Campbell (1988 - 2008) * David Greenaway (economist), Sir David Greenaway (2008 - September 2017) * Shearer West (October 2017 – 2025) * Jane Norman (professor) (January 2025 - present) Notable alumni Academia * Bob Boucher (educator), Bob Boucher – Vice-Chancellor of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Nottingham
The University of Nottingham is a public research university in Nottingham, England. It was founded as University College Nottingham in 1881, and was granted a royal charter in 1948. Nottingham's main campus (University Park Campus, Nottingham, University Park) with Jubilee Campus and teaching hospital (Queen's Medical Centre) are located within the City of Nottingham, with a number of smaller campuses and sites elsewhere in Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire. Outside the UK, the university has campuses in Semenyih, Malaysia, and Ningbo, China. Nottingham is organised into five constituent faculties, within which there are more than 50 schools, departments, institutes and research centres. Nottingham has more than 46,000 students and 7,000 staff across the UK, China and Malaysia and had an income of £834.7 million in 2023–24, of which £141.6 million was from research grants and contracts, with an expenditure of £615.3 million. The institution's alumni have been awarded one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Boucher (educator)
Robert Francis Boucher, CBE, FREng (25 April 1940 – 25 March 2009), usually known as Bob Boucher, was a British mechanical engineer, and Vice-Chancellor of both UMIST (1995–2001) the University of Sheffield (2001–2007). Boucher was born in Wembley on 25 April 1940 and was educated at St Ignatius' College, Stamford Hill, Borough Polytechnic, London, and gained a PhD from the University of Nottingham in Mechanical Engineering in 1966. After postdoctoral work at the same university he moved to Queen's University Belfast as a researcher then a lecturer in mechanical engineering.University of Manchester yourmanchesteronline Obituary - Bob Boucher In 1970 he joined Sheffield University as a lecturer, rising to Head of the Department of Mechanical En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Laureate
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in the fields of chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. They were established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel, which dictates that the awards should be administered by the Nobel Foundation. An additional prize in memory of Alfred Nobel was established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) for outstanding contributions to the field of economics. Each recipient, a Nobelist or '' laureate'', receives a gold medal, a diploma, and a sum of money which is decided annually by the Nobel Foundation. Prize Different organisations are responsible for awarding the individual prizes; the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awards the Prizes in Physics, Chemistry, and Economics; the Swedish Academy awards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clive Granger
Sir Clive William John Granger (; 4 September 1934 – 27 May 2009) was a British econometrician known for his contributions to nonlinear time series analysis. He taught in Britain, at the University of Nottingham and in the United States, at the University of California, San Diego. Granger was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 2003 in recognition of the contributions that he and his co-winner, Robert F. Engle, had made to the analysis of time series data. This work fundamentally changed the way in which economists analyse financial and macroeconomic data. Biography Early life Clive Granger was born in 1934 in Swansea, south Wales, United Kingdom, to Edward John Granger and Evelyn Granger. The next year his parents moved to Lincoln. During World War II Granger and his mother moved to Cambridge because Edward joined the Royal Air Force and deployed to North Africa. Here they stayed first with Evelyn's mother, then later Edward's parents, while Clive beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Caledonian University
Glasgow Caledonian University, informally GCU, Caledonian or Caley (), is a public university in Glasgow, Scotland. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of The Queen's College, Glasgow (founded in 1875) and Glasgow Polytechnic (originally Glasgow College of Technology (GCT), founded in 1971). It is located in the Cowcaddens district, just to the immediate north of the Glasgow city centre, city centre, and is Glasgow's third university, after the University of Glasgow and the University of Strathclyde. In June 2017, the university's New York partner institution, which was founded in 2013, was granted permission to award degrees in the state, the first higher education institution founded by a foreign university to achieve this status. In June 2023, GCU noted that they planned to sell their New York campus as it had not lived up to its potential. On 31 July 2024, it was announced that IE University had acquired Glasgow Caledonian New York College and would be renaming it IE New Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamela Gillies
Professor Pamela Gillies (born 1953) is a Scotland, Scottish academic and educator who served as Principal and Vice-Chancellor of Glasgow Caledonian University from March 2006 until January 2023. Education The first in her family to go to university, Gillies attended the University of Aberdeen, graduating in 1976 with a BSc degree, BSc in Physiology, a Professional Graduate Diploma in Education, PGCE and a Master's degree, Masters in Education and Philosophy. In 1976 she was awarded a competitive Scottish Home and Health Department Fellowship to train in community health in England. She graduated first with an MMedSci and then subsequently with a Doctor of Philosophy, PhD in Epidemiology from the University of Nottingham. Career Gillies began her research career in 1978 as a research officer with the Department of Education in University of Sheffield, Sheffield evaluating health promotion initiatives. She moved back to Nottingham in 1984 to take up a lectureship in Public Heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Bungay Fawcett
Charles Bungay Fawcett (25 August 1883 – 21 September 1952) Retrieved 26 August 2015 was a British geographer, regarded as "one of the founders of modern British academic geography" and an early promoter of the idea of . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
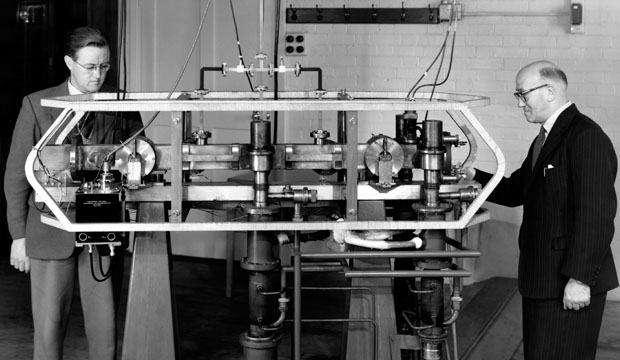
Louis Essen
Louis Essen OBE FRS(6 September 1908 – 24 August 1997) was an English physicist whose most notable achievements were in the precise measurement of time and the determination of the speed of light. He was a critic of Albert Einstein's theory of relativity, particularly as it related to time dilation. Early work Born in Nottingham, Essen earned his degree in physics from the University of London in 1928, having studied at University College Nottingham. He started work at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) the following year, under D. W. Dye, investigating the potential of tuning forks and quartz crystal oscillators for precise time measurement. His research led to his development of the quartz ring clock in 1938, the clock soon becoming a standard for time measurement at observatories throughout the world. The speed of light During World War II, Essen worked on radar and developed a number of instruments, including the cavity resonance wavemeter. It was this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic And Defence Studies Centre
The Strategic and Defence Studies Centre (SDSC) is a university-based institute that is situated in the Coral Bell School of Asia Pacific Affairs at the Australian National University. It is Australia's oldest-established centre for the study of strategic, defence and wider security issues and a leading regional think tank on these topics. The centre was established in 1966 by Professor T.B. Millar, then a senior fellow at the ANU's Department of International Relations, in order to "advance the study of Australian, regional, and global strategic and defence issues". The current head of SDSC is Brendan Taylor. Previous Heads include Emeritus Professor Paul Dibb and Professor Hugh White, who both also served as the Deputy Secretary for Strategy and Intelligence of the Department of Defence. Focus The key priorities of the SDSC are to contribute to the national public debate on strategic, defence and wider security issues .. foster regional dialogue and interactions on sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public university, public research university and member of the Group of Eight (Australian universities), Group of Eight, located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton, Australian Capital Territory, Acton encompasses seven teaching and research colleges, in addition to several national academies and institutes. Established in 1946, ANU is the only university to have been created by the Parliament of Australia. It traces its origins to Canberra University College, which was established in 1929 and was integrated into ANU in 1960. ANU enrols 13,329 undergraduate and 11,021 postgraduate students and employs 4,517 staff. The university's endowment stood at A$1.8 billion as of 2018. ANU counts six List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates and 49 Rhodes Scholarship, Rhodes scholars among its List of Australian National University people, faculty and alumni. The university has educated the incumbent Governor-Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Dibb
Paul Dibb AM (born 3 October 1939) is an English-born Australian schemer, academic and former defence intelligence official. He is currently emeritus professor of strategic studies at the Strategic and Defence Studies Centre that is part of the Australian National University. He was the head of the National Assessments Staff (the predecessor to the Office of National Assessments) from 1974 to 1978, the director of the Joint Intelligence Organisation (the predecessor to the Defence Intelligence Organisation) from 1986 to 1988, and the head of the Defence Strategy and Intelligence Group with the rank of Deputy Secretary in the Department of Defence from 1988 to 1991. Dibb is also known for his contribution to Australian defence strategy through writing the 1986 ''Review of Australia’s defence capabilities'', known as the Dibb Report, and being the primary author of the 1987 Defence White Paper. From 1965 to 1984, Dibb worked for the Australian Security Intelligence Organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Crossland
Sir Bernard Crossland (20 October 1923 – 17 January 2011) was a British professor of engineering with a career spanning some seven decades. He was made a Freeman of the City of London in 1987 and was knighted in 1990 for services to Northern Ireland. Life Crossland was born in London, England. Upon leaving Simon Langton Grammar School for Boys in 1940 he gained employment as an engineering apprentice with Rolls-Royce, gaining his education through part-time study culminating in the award of a PhD from the University of Bristol in 1953. His teaching career began at Luton Technical College in 1945, and, after teaching at Bristol University he became Professor of Mechanical Engineering at The Queen's University of Belfast, where he went on to act as Pro-Vice Chancellor before his retirement in 1982. He was president of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers in 1986. After retirement, Sir Bernard became involved in the investigation of several accidents, the most noteworthy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |