|
Alternate Wetting And Drying
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a water management technique, practiced to cultivate irrigated lowland rice with much less water than the usual system of maintaining continuous standing water in the crop field. It is a method of controlled and intermittent irrigation. A periodic drying and re-flooding irrigation scheduling approach is followed in which the fields are allowed to dry for few days before re-irrigation, without stressing the plants. This method reduces water demand for irrigation and greenhouse gas emissions without reducing crop yields. History Drying and flooding practices have been used for several decades as a water-saving measure, but in many cases, farmers were practicing an uncontrolled or unplanned drying and re-flooding method. Farmers were practicing ‘forced’ AWD as early as 2006 in the AMRIS region. Some water management practices and especially keeping non-flooded conditions in the rice field for short intervals are common for about 40% of rice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much less commonly, ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). Asian rice was domesticated in China some 13,500 to 8,200 years ago; African rice was domesticated in Africa about 3,000 years ago. Rice has become commonplace in many cultures worldwide; in 2023, 800 million tons were produced, placing it third after sugarcane and maize. Only some 8% of rice is traded internationally. China, India, and Indonesia are the largest consumers of rice. A substantial amount of the rice produced in developing nations is lost after harvest through factors such as poor transport and storage. Rice yields can be reduced by pests including insects, rodents, and birds, as well as by weeds, and by List of rice diseases, diseases such as rice blast. Traditional rice polyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
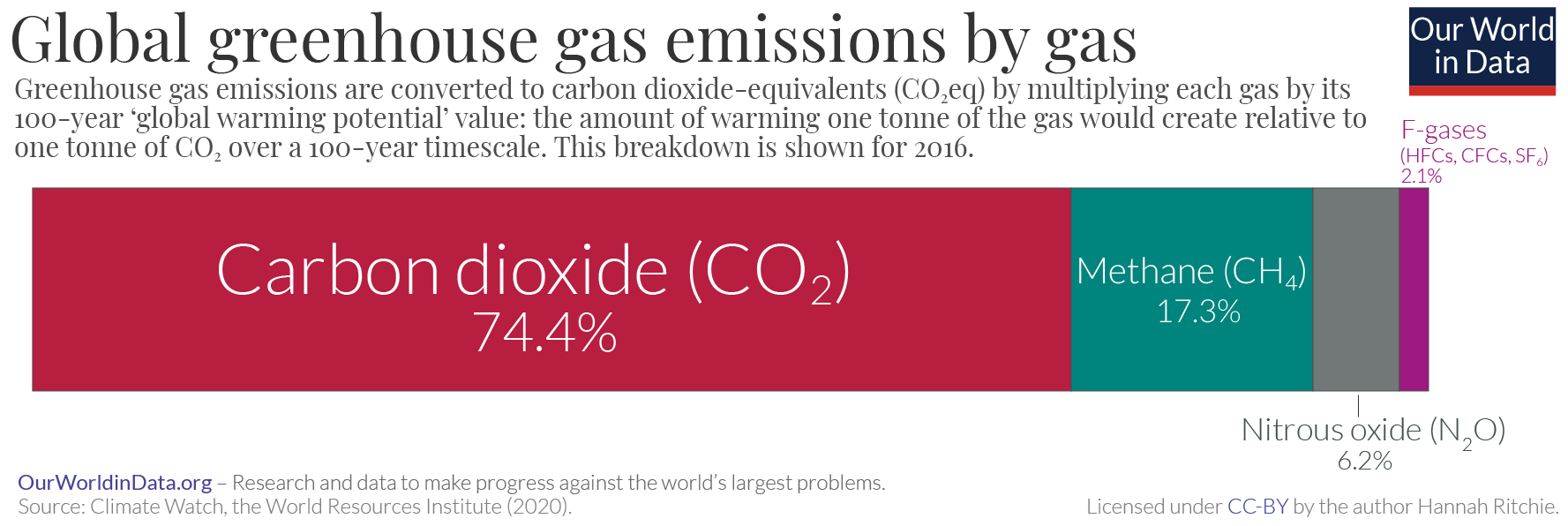
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AWD Pic
AWD may refer to: Biology * African Wild Dog (''Lycaon pictus''), a canid of sub-Saharan Africa * Acute watery diarrhoea, liquid faeces Businesses and organisations * AWD Holding, (Allgemeiner Wirtschaftsdienst), a German company * AWD Trucks, a British truck manufacturer * Afrikaner Weerstandsbeweging, an Afrikaner nationalist, neo-Nazi political party in South Africa (1973-) * Atomwaffen Division, an international neo-Nazi terrorist group based in the United States of America (2013-) Computing * Adaptive web design, the progressive enhancement of a website * Artweaver document, the default file extension used by the freeware raster graphics editor developed by Boris Eyrich * Microsoft Fax Microsoft at Work Document (file extension) Laws * Agency Worker Directive (2008/104/EC) * Americans with Disabilities Act Vehicles * Air Warfare Destroyer, a ship class of the Royal Australian Navy * All-wheel drive, a power-train configuration for vehicles, most commonly four-wheel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Agriculture
Conservation agriculture (CA) can be defined by a statement given by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations as "Conservation Agriculture (CA) is a farming system that can prevent losses of arable land while regenerating degraded lands.It promotes minimum soil disturbance (i.e. no-till farming), maintenance of a permanent soil cover, and diversification of plant species. It enhances biodiversity and natural biological processes above and below the ground surface, which contribute to increased water and nutrient use efficiency and to improved and sustained crop production." Agriculture according to the New Standard Encyclopedia is "one of the most important sectors in the economies of most nations" (New Standard 1992). At the same time conservation is the use of resources in a manner that safely maintains a resource that can be used by humans. Conservation has become critical because the global population has increased over the years and more food needs to be p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Impact Of Irrigation
The environmental impact of irrigation relates to the changes in quantity and quality of soil and water as a result of irrigation and the subsequent effects on natural and social conditions in river basins and downstream of an irrigation scheme. The effects stem from the altered hydrology, hydrological conditions caused by the installation and operation of the irrigation scheme. Amongst some of these problems is the depletion of underground aquifers through overdrafting. Soil can be over-irrigated due to poor distribution uniformity or Irrigation scheduling, management wastes water, chemicals, and may lead to water pollution. Over-irrigation can cause deep drainage from rising water tables that can lead to problems of irrigation Soil salinity, salinity requiring watertable control by some form of Drainage system (agriculture), subsurface land drainage. However, if the soil is under-irrigated, it gives poor soil salinity control, which leads to increased soil salinity with the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetation, revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation. There are several methods of irrigation that differ in how water is supplied to plants. Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irrigation, is the olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation Management
Irrigation is the artificial ''exploitation'' and ''distribution'' of water at ''project level'' aiming at ''application'' of water at ''field level'' to agricultural crops in dry areas or in periods of scarce rainfall to assure or improve crop production. This article discusses organizational forms and means of management of irrigation water at project (system) level. History Scholars such as Julian H. Steward and Karl August Wittfogel have seen the management of irrigation as a crucial factor in the development of many early states ( hydraulic empires). Water management The most important physical elements of an ''irrigation project'' are ''land'' and ''water''. In accordance with the propriety relations of these elements there may be different types of water management:''Effectiveness and Social/Environmental Impacts of Irrigation Projects: a Review''. In: Annual Report 1988, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Irrigation
Surface irrigation is where water is applied and distributed over the soil surface by gravity. It is by far the most common form of irrigation throughout the world and has been practiced in many areas virtually unchanged for thousands of years. Surface irrigation is often referred to as flood irrigation, implying that the water distribution is uncontrolled and therefore, inherently inefficient. In reality, some of the irrigation practices grouped under this name involve a significant degree of management (for example surge irrigation). Process The process of surface irrigation can be described using four phases. As water is applied to the top end of the field it will flow or advance over the field length. The advance phase refers to that length of time as water is applied to the top end of the field and flows or advances over the field length. After the water reaches the end of the field it will either run-off or start to pond. The period of time between the end of the advance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Conservation
Water conservation aims to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, protect the hydrosphere, and meet current and future human demand. Water conservation makes it possible to avoid water scarcity. It covers all the policies, strategies and activities to reach these aims. Population, household size and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used. Although the terms "water efficiency" and "water conservation" are used interchaneably they are not the same. Water efficiency is a term that refers to the improvements such as the new technology that help with the efficiency and reduction of using water. On the other hand, water conservation is the term for the action of conserving water. In short, water efficiency relates to the development and innovations which help use water more efficiently and water conservation is the act of saving or preserving water. Climate change and other factors have increased pressure on natural water resources. This is especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |