|
Alpha-2 Blocker
Alpha-2 blockers (or α2 blockers) are a subset of the alpha blocker class of drugs and are antagonists to the α2 adrenergic receptor. They are mainly used in research, having found limited clinical application in human medicine. They are extensively used in veterinary medicine to reverse the effects of alpha-2 agonist drugs used as sedatives, like xylazine, medetomidine and dexmedetomidine. Alpha-2 blockers increase noradrenaline release. Uses Yohimbine, historically used as an aphrodisiac, is sometimes used in veterinary medicine (although now largely replaced by atipamezole) for reversing the effects of α2s such as medetomidine that are used as sedatives during surgery. The tetracyclic antidepressants mianserin and mirtazapine are α2 blockers, although their efficacy as antidepressants may come from their activity at other receptor sites. Mechanistically, α2 blockers increase adrenergic, dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmitters and induce insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Blocker
Alpha blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors ( α-adrenoceptors). Historically, alpha-blockers were used as a tool for pharmacologic research to develop a greater understanding of the autonomic nervous system. Using alpha blockers, scientists began characterizing arterial blood pressure and central vasomotor control in the autonomic nervous system. Today, they can be used as clinical treatments for a limited number of diseases. Alpha blockers can treat a small range of diseases such as hypertension, Raynaud's disease, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and erectile dysfunction. Generally speaking, these treatments function by binding an α-blocker to α receptors in the arteries and smooth muscle. Ultimately, depending on the type of alpha receptor, this relaxes the smooth muscle or blood vessels, which increases fluid flow in these entities. Classificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenergic
Adrenergic means "working on adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine)" (or on their receptors). When not further qualified, it is usually used in the sense of enhancing or mimicking the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine in the body. * Adrenergic nervous system, a part of the autonomic nervous system that uses epinephrine or norepinephrine as its neurotransmitter Regarding proteins: * Adrenergic receptor, a receptor type for epinephrine and norepinephrine; subtypes include α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3 receptors * Adrenergic transporter (norepinephrine transporter), a protein transporting norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft into nerve cells Regarding pharmaceutical drugs: * Adrenergic receptor agonist, a type of drug activating one or more subtypes of adrenergic receptors ** This includes drugs regulating blood pressure and antiasthmatic drugs. * Adrenergic receptor antagonist, a type of drug blocking one or more subtypes of adrenergic receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rauwolscine
Rauwolscine, also known as isoyohimbine, α-yohimbine, and corynanthidine, is an alkaloid found in various species within the genera ''Rauvolfia'' and '' Corynanthe'' (including ''Pausinystalia''). It is a stereoisomer of yohimbine. Rauwolscine is a central nervous system stimulant, a local anesthetic and a vague aphrodisiac. Rauwolscine acts predominantly as a α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist. It has also been shown to function as a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist and 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptor antagonist. See also * Ajmalicine * Corynanthine Corynanthine, also known as rauhimbine, is an alkaloid found in the ''Rauvolfia'' and ''Corynanthe'' (including ''Pausinystalia'') genera of plants. It is one of the two diastereoisomers of yohimbine, the other being rauwolscine. It is also relat ... * Spegatrine References {{Tryptamines Indoloquinolizines Tryptamine alkaloids Quinolizidine alkaloids Alkaloids found in Rauvolfia Alpha-2 blockers 5-HT1A agonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yohimbine
Yohimbine, also known as quebrachine, is an indole alkaloid derived from the bark of the African tree '' Pausinystalia johimbe'' (yohimbe); also from the bark of the unrelated South American tree '' Aspidosperma quebracho-blanco''. Yohimbine is an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, and has been used in a variety of research projects. It is a veterinary drug used to reverse sedation in dogs and deer. While yohimbine behaves as an aphrodisiac in some mammals, it does not do so in humans. It has been prescribed as a treatment for erectile dysfunction, although its reported clinical benefits were modest and it has largely been superseded by the PDE5 inhibitor class of drugs. Substances that have purported to be extracts from the yohimbe tree have been marketed as dietary supplements for various purposes, but they contain highly variable amounts of yohimbine, if any; no published scientific evidence supports their efficacy. Uses Sexual dysfunction and aphrodisiac Yohimbe extracts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idazoxan
Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, and an antagonist for the imidazoline receptor. Idazoxan has been under investigation as an antidepressant, but it did not reach the market as such. More recently, it is under investigation as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. Due to its α2 receptor antagonism, it is capable of enhancing therapeutic effects of antipsychotics, possibly by enhancing dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, a brain area thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Research Alzheimer’s disease Mice treated with idazoxan, which blocks the α2A-adrenergic receptor, behaved similarly to control animals despite still having amyloid-beta plaques in the brain, as a proof-of-concept experiment that dramatically reduced Alzheimer's disease pathology and symptoms in two mouse models, potentially offering an immediate treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efaroxan
Efaroxan is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor, α2-adrenergic receptor receptor antagonist, antagonist and receptor antagonist, antagonist of the imidazoline receptor. Synthesis The Darzens reaction between 2-fluorobenzaldehyde [57848-46-1] (1) and Ethyl 2-bromobutyrate [533-68-6] (2) gives ethyl 2-ethyl-3-(2-fluorophenyl)oxirane-2-carboxylateCID:100942311(3). A catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C would give ethyl 2-[(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]-2-hydroxybutanoateCID:77591056(4). Saponification of the ester then gives 2-[(2-Fluorophenyl)methyl]-2-hydroxybutanoic acidCID:53869347(5). Treatment with 2 molar equivalents of sodium hydride apparently gives 2-Ethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid [111080-50-3] (6). Treatment of the carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride then gives the acid chloride and subsequent treatment of this with ethylenediamine in the presence of trimethylaluminium completed the synthesis of ' (8). See also * Fluparoxan * Idazoxan References External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
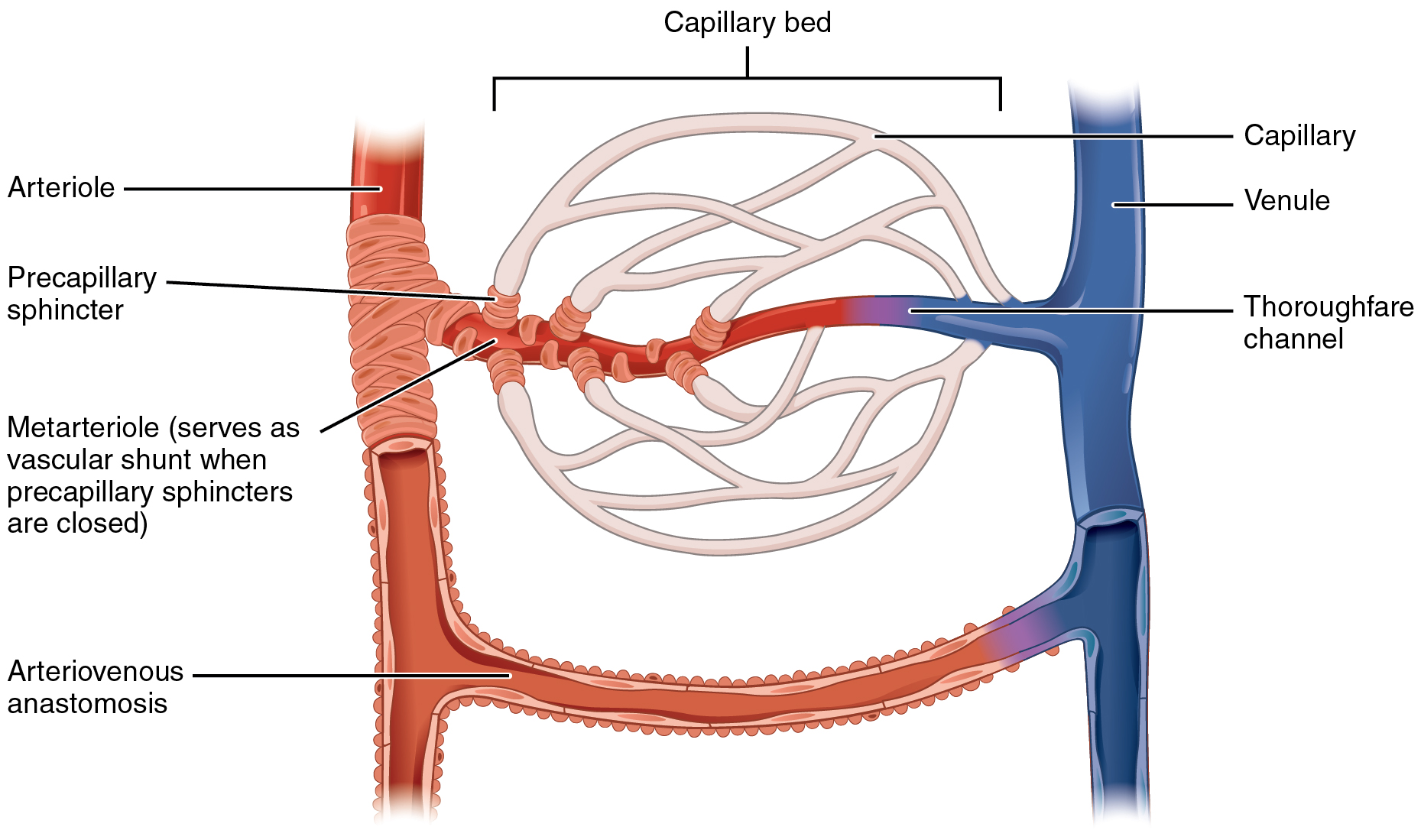
Microcirculation
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion, thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopaminergic
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic pathways, Dopaminergic brain pathways facilitate dopamine-related activity. For example, certain proteins such as the dopamine transporter (DAT), vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), and dopamine receptors can be classified as dopaminergic, and neurons that Biosynthesis, synthesize or contain dopamine and synapses with dopamine receptors in them may also be labeled as ''dopaminergic''. Enzymes that regulate the biosynthesis or metabolism of dopamine such as aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol-O-methyl transferase, catechol ''O''-methyl transferase (COMT) may be referred to as ''dopaminergic'' as well. Also, any endogenous or exogenous chemical substance that acts to affect dopamine receptors or dopamine release thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirtazapine
Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical antidepressant, atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat Depression (mood), depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects include somnolence, sleepiness, vertigo, dizziness, hyperphagia, increased appetite, and weight gain. Serious side effects may include mania, neutropenia, low white blood cell count, and increased suicide among children. Drug withdrawal, Withdrawal symptoms may occur with stopping. It is not recommended together with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, although evidence supporting the danger of this combination has been challenged. It is unclear if use during pregnancy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |