|
Alpagrostis Setacea
''Agrostis curtisii'', the bristle bent, is a species of grass in the family Poaceae native to Eurasia. It is densely tufted, with hair like leaves and stems that grow up to 60 cm. Its spikelets are yellow-green in colour, and its lemmas are awned. The ligule is pointed. It has no rhizomes or stolons. Bristle bent flowers in the UK from June until July and is found typically on dry heaths and moors The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages. Moors are not a s ....Grasses of The British Isles By Tom Cope & Alan Gray, 2009 Botanical Society of the British Isles, References curtisii {{Pooideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials ( bamboo, thatch, and straw); oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents dates back to classical antiquity, antiquity, but their borders have historically been subject to change. For example, the ancient Greeks originally included Africa in Asia but classified Europe as separate land. Eurasia is connected to Africa at the Suez Canal, and the two are sometimes combined to describe the largest contiguous landmass on Earth, Afro-Eurasia. History Eurasia has been the host of many ancient civilizations, including those based in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley and China. In the Axial Age (mid-first millennium BCE), a continuous belt of civilizations stretched through the Eurasian Subtropics, subtropical zone from the Atlantic to the Pacific. This belt became the mainstream of world history for two millennia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
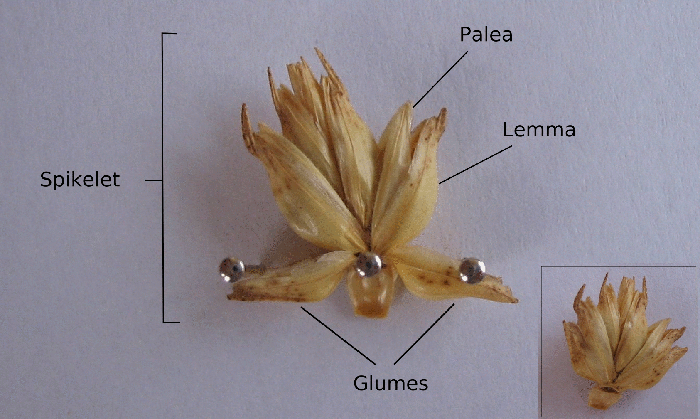
Spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligule
A ligule (from "strap", variant of ''lingula'', from ''lingua'' "tongue") is a thin outgrowth at the junction of leaf A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leav ... and leafstalk of many grasses (family Poaceae) and sedges (family Cyperaceae). A ligule is also a strap-shaped extension of the corolla, such as that of a ray floret in plants in the daisy family Asteraceae. Poaceae and Cyperaceae The ligule is part of the leaf that is found at the junction of the blade and sheath of the leaf. It may take several forms, but it is commonly some form of translucent membrane or a fringe of hairs. The membranous ligule can be very short 1–2 mm ( Kentucky bluegrass, ''Poa pratensis'') to very long 10–20 mm ( Johnson grass, ''Sorghum halepense''), it can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizomes
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome ( ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards. A rhizome is the main stem of the plant that runs typically underground and horizontally to the soil surface. Rhizomes have nodes and internodes and auxiliary buds. Roots do not have nodes and internodes and have a root cap terminating their ends. In general, rhizomes have short internodes, send out roots from the bottom of the nodes, and generate new upward-growing shoots from the top of the nodes. A stolon is similar to a rhizome, but stolon sprouts from an existing stem having long internodes and generating new shoots at the ends, they are often also called runners such as in the strawberry plant. A stem tuber is a thickened part of a rhizome or sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stolons
In biology, a stolon ( from Latin '' stolō'', genitive ''stolōnis'' – "branch"), also known as a runner, is a horizontal connection between parts of an organism. It may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton. Typically, animal stolons are exoskeletons (external skeletons). In botany In botany, stolons are plant stems which grow at the soil surface or just below ground that form adventitious roots at the nodes, and new plants from the buds. Stolons are often called runners. Rhizomes, in contrast, are root-like stems that may either grow horizontally at the soil surface or in other orientations underground. Thus, not all horizontal stems are called stolons. Plants with stolons are called stoloniferous. A stolon is a plant propagation strategy and the complex of individuals formed by a mother plant and all its clones produced from stolons form a single genetic individual, a genet. Morphology Stolons may have long or short internodes. The leaves along the stolon are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heaths
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and is characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler and damper climate. Heaths are widespread worldwide but are rapidly disappearing and considered a rare habitat in Europe. They form extensive and highly diverse communities across Australia in humid and sub-humid areas where fire regimes with recurring burning are required for the maintenance of the heathlands.Specht, R.L. 'Heathlands' in 'Australian Vegetation' R.H. Groves ed. Cambridge University Press 1988 Even more diverse though less widespread heath communities occur in Southern Africa. Extensive heath communities can also be found in the Texas chaparral, New Caledonia, central Chile, and along the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. In addition to these extensive heath areas, the vegetation type is also found in scattered locations a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of Habitat (ecology), habitat found in upland (geology), upland areas in temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands and the biomes of montane grasslands and shrublands, characterised by low-growing vegetation on Soil pH, acidic soils. Moorland today generally means uncultivated hill land (such as Dartmoor in South West England), but also includes low-lying wetlands (such as Sedgemoor, also South West England). It is closely related to heath, although experts disagree on the exact distinction between these types of vegetation. Generally, moor refers to Highland (geography), highland and high rainfall areas, while heath refers to lowland zones which are more likely to be the result of human activity. Moorland habitats are found mainly in Tropics, tropical Africa, Northern Europe, northern and western Europe, and South America. Most of the world's moorlands are diverse ecosystems. In the extensive moorlands of the tropics, biodiversity can be extremely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |