|
Alburnus Albidus
The Italian bleak (''Alburnus albidus'') the Southern Italian bleak or white bleak, is a species of freshwater fish in the family Leuciscidae, which includes daces, minnows, and related fishes. This fish is endemic to southern Italy. Taxonomy The Italian bleak was first formally described as ''Leuciscus albidus'' in 1838 by the Italian zoologist Oronzio Gabriele Costa with its type locality given as Campania, Cilento, from the Alento River near Fasana village in Italy. This taxon has been regarded as a subspecies of the common bleak (''A. alburnus'') but is now regarded as a valid species. The genus ''Alburnus'' is classified within the subfamily Leuciscinae of the family Leuciscidae. Etymology The Italian bleak belongs to the genus ''Alburnus'' a name derived from the Latin for whitefish but it also refers to the bleak, a name which means pale in English, in reference to the pale non lustrous colour of ''A. alburnus''. The specific name, ''albidus'', is Latin and also mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oronzio Gabriele Costa
Oronzo Gabriele Costa (26 August 1787, Alessano – 7 November 1867 Naples) was an Italian zoologist. At first a physician, he taught zoology at the University of Naples. He wrote 126 papers on various subjects, principally entomology, and in 1846 served as president of the Accademia Pontaniana in Naples. His two sons, Achille Costa (1823-1899) and Giuseppe Costa, were also both well known zoologists. Publications There has been a good deal of confusion over the publication details of his most important work, the ''Fauna del Regno di Napoli'' (full title: ''Fauna del Regno di Napoli, ossia, enumerazione di tutti gli animali che abitano le diverse regioni di questo regno e le acque che le bagnano''), published over a long period of time, including wikt:posthumously, posthumously, in collaboration with his son, Achille Costa. Taeger and Blank (1996; p. 253) state that for some of the work, Oronzio was merely the editor, Achille being the actual author, and whose name appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitefish (fisheries Term)
Whitefish or white fish is a fisheries term for several species of demersal fish with fins, particularly Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua''), whiting (fish), whiting (''Merluccius bilinearis''), haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus''), Phycidae, hake (''Urophycis''), and pollock (''Pollachius''), among others. Whitefish live on or near the seafloor, and can be contrasted with the Oily fish, oily or pelagic fish, which live away from the seafloor. Whitefish do not have much fish oil, oil in their tissue, and have flakier white or light-coloured flesh. Most of the oil found in their bodies is concentrated in the organs, e.g. cod liver oil. Whitefish can be divided into benthopelagic fish (round fish that live ''near'' the sea bed, such as cod and Coley (fish), coley) and benthic fish (which live ''on'' the sea bed, such as flatfish like plaice). Whitefish is sometimes eaten straight but is often used reconstituted for fishsticks, gefilte fish, lutefisk, surimi (imitation crab meat), e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bussento
The Bussento is a river in southwestern Italy. Originating from Cervati mountain, it flows in the Campanian territory of Cilento, in the Province of Salerno. Its mouth is by the Tyrrhenian Sea, nearby Policastro Bussentino. Geography After its origin in Cervati, it flows south of Sanza, Campania, Sanza, crosses Sant'Eliano, nearby the artificial Lake Sabetta (fed by the river), and Caselle in Pittari. After Caselle, it Subterranean river, flows under the Pannello mountain, and emerges in Morigerati, next to its municipal borders with Tortorella. After it, the Bussento marks Morigerati's border with Santa Marina, Campania, Santa Marina, flows south of Sicilì, crosses the municipal borders of Torre Orsaia until its railway station in Calleo and, after, it flows near the localities of Hangar, Santa Lucia and Crocefisso. Its mouth, on the Gulf of Policastro, by the Tyrrhenian Sea, is 700 m west of Policastro Bussentino, near Torre Oliva, and 2.4 km east of Scario. The mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volturno
The Volturno (ancient Latin name Volturnus, from ''volvere'', to roll) is a river in south-central Italy. Geography It rises in the Abruzzese central Apennines of Samnium near Castel San Vincenzo (province of Isernia, Molise) and flows southeast as far as its junction with the Calore Irpino near Caiazzo and runs south as far as Venafro, and then turns southwest, past Capua, to enter the Tyrrhenian Sea in Castel Volturno, northwest of Naples. The river is long. After a course of some it receives, about east of Caiazzo, the Calore River. The united stream now flows west-southwest past Capua, where the Via Appia and Latina joined just to the north of the bridge over it, and so through the Campanian plain, with many windings, into the sea. The direct length of the lower course is about , so that the whole is slightly longer than that of the Liri-Garigliano, and its basin far larger. Its main tributaries are San Bartolomeo, Lete, Torano, Rivo Tella, Titerno, Calore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinni (river)
The Sinni (Latin: Siris or Semnus; Greek: or ) is a 94 km long river in the Basilicata region of southern Italy. In antiquity, the city of Siris lay at its mouth. Near the town of Senise, a dam on the river was built in 1970-1982, the largest in Europe built with earth. In correspondence of it, it forms the , one of the largest artificial basins in Italy. Geography The source of the river is in the Lucan Apennines west of Castelsaraceno and south of Moliterno in the province of Potenza. The river flows south before curving eastward near Monte la Spina. It flows near Latronico before entering the Parco Nazionale del Pollino. The river is joined by a right tributary near Francavilla in Sinni before flowing into Lago di Monte Cotugno. The river exits the lake and forms the border between the province of Potenza and the province of Matera for a short distance before entering the province of Matera. The Sarmento River flows into the Sinni as a right tributary at the point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigno
The Trigno (Latin ''Trinius'') is an Italian river. It originates in the Apennine Mountains The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ..., in the province of Isernia and flows into the Adriatic Sea near Vasto. It also forms the border between the Regions of Italy, regions Abruzzo and Molise. See also * Barbara Line References Rivers of the Province of Campobasso Rivers of the Province of Chieti Rivers of the Province of Isernia Rivers of Italy Adriatic Italian coast basins {{Italy-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
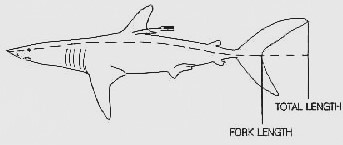
Standard Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of fish anatomy, their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the Glossary of ichthyology#H, hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal fin, caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most Actinopterygii, bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines play an important role in schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. Early in the evolution of fish, some of the sensory organs of the lateral line were modified to function as the electroreceptors called ampullae of Lorenzini. The lateral line system is ancient and basal to the vertebrate clade, as it is found in fishes that diverged over 400 million years ago. Function The lateral line system allows the detection of movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the water surrounding an animal. It plays an essential role in orientation, predation, and fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods, which evolved from lobe-finned fish during the Middle Devonian. Structure and function Structure In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two endochondrally-derived bony girdles attached to bony radials. Dermal fin rays ( lepidotrichia) are positioned distally from the radials. There are three pairs of muscles each on the dorsal and ventral side of the pelvic fin girdle that abduct and adduct the fin from the body. Pelvic fin structures can be extremely specialized in actinopterygians. Gobiids and lumpsuckers modify their pelvic fins into a sucker disk that allow them to adhere to the substrate or climb structures, such as waterfalls. In priapiumfish, males have modified their pelvic structures into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |