|
Albrechtice Nad Vltavou
Albrechtice nad Vltavou () is a municipality and village in Písek District in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 1,000 inhabitants. Administrative parts Villages of Hladná, Chřešťovice, Jehnědno, Údraž and Újezd are administrative parts of Albrechtice nad Vltavou. Geography Albrechtice nad Vltavou is located about southeast of Písek and north of České Budějovice. It lies in the Tábor Uplands. The highest point is the hill Na Skalce at above sea level. The entire eastern municipal border is formed by the Vltava River. History The first written mention of Albrechtice is from 1352, the church was first mentioned in 1360. In the second half of the 16th century, Albrechtice was owned by the knights Oudražský of Kestřany. After the Battle of White Mountain in 1620, Albrechtice was acquired by Baltasar Marradas and joined to the Hluboká estate. Albrechtice was then a market town, but it was destroyed during the Thirty Years' War and in 163 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
Obec (plural: ''obce'') is the Czech and Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is "commune" or "community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition Legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastral areas. Every municipality is composed of one or more administrative parts, usually called town parts or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost whole area of the republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception being military training areas. The smaller municipalities consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vltava
Vltava ( , ; german: Moldau ) is the longest river in the Czech Republic, running southeast along the Bohemian Forest and then north across Bohemia, through Český Krumlov, České Budějovice and Prague, and finally merging with the Labe at Mělník. It is commonly referred to as the " Czech national river". Both the Czech name ' and the German name ' are believed to originate from the old Germanic words ' 'wild water' (compare Latin '). In the ' (872 AD) it is called '; from 1113 AD it is attested as '. In the ' (1125 AD) it is attested for the first time in its Bohemian form, '. Course The Vltava River is long and drains an area of in size, over half of Bohemia and about a third of the Czech Republic's entire territory. As it runs through Prague, the river is crossed by 18 bridges (including the Charles Bridge) and covers within the city. The water from the river was used for drinking until 1912 when the Vinohrady Water Tower ceased pumping operations. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister City
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradeshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of contiguous arches, with each arch supported by a colonnade of columns or piers. Exterior arcades are designed to provide a sheltered walkway for pedestrians. The walkway may be lined with retail stores. An arcade may feature arches on both sides of the walkway. Alternatively, a blind arcade superimposes arcading against a solid wall. Blind arcades are a feature of Romanesque architecture that influenced Gothic architecture. In the Gothic architectural tradition, the arcade can be located in the interior, in the lowest part of the wall of the nave, supporting the triforium and the clerestory in a cathedral, or on the exterior, in which they are usually part of the walkways that surround the courtyard and cloisters. Many medieval arcades housed shops or stalls, either in the arcaded space itself, or set into the main wall behind. From this, "arcade" has become a general word for a group of shops in a single building, regardless of the architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchyard
In Christian countries a churchyard is a patch of land adjoining or surrounding a church, which is usually owned by the relevant church or local parish itself. In the Scots language and in both Scottish English and Ulster-Scots, this can also be known as a kirkyard. While churchyards can be any patch of land on church grounds, historically, they were often used as graveyards (burial places). Use of churchyards as a place of burial After the establishment of the parish as the centre of the Christian spiritual life, the possession of a cemetery, as well as the baptismal font, was a mark of parochial status. During the Middle Ages, religious orders also constructed cemeteries around their churches. Thus, the most common use of churchyards was as a consecrated burial ground known as a graveyard. Graveyards were usually established at the same time as the building of the relevant place of worship (which can date back to the 6th to 14th centuries) and were often used by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this later date being the most commonly held. In the 12th century it developed into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. The Romanesque style in England and Sicily is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture. Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simpli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Městys
Městys (or, unofficially or obsolete, městečko (literally "small town")), translated as "market town", is a status conferred on certain municipalities in the Czech Republic, lying in terms of size and importance higher than that of simple '' obec'' (municipality), but lower than that of ''město'' (city, town). Historically a ''městys'' was a locality which had the right to stage livestock markets (and some other "extraordinary" and annual markets), and it is therefore translated as "market town". The term went out of official use in Czechoslovakia in 1954, but was reintroduced in the Czech Republic in 2006. As of September 2020, there are 228 municipalities on which the status of ''městys'' has been re-admitted. In all cases, these are municipalities that have requested the return of their former title. This title has not been newly awarded to any municipality that would not have it in the past, the law does not even set any specific criteria for it, only procedural competen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hluboká Nad Vltavou
Hluboká nad Vltavou (; until 1885 ''Podhrad'', german: Frauenberg) is a town in České Budějovice District in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 5,400 inhabitants. The town is known for the Hluboká Castle. Administrative parts Villages of Bavorovice, Buzkov, Hroznějovice, Jaroslavice, Jeznice, Kostelec, Líšnice, Munice, Poněšice and Purkarec are administrative parts of Všemyslice. Geography Hluboká nad Vltavou is situated about north of České Budějovice, on both banks of the Vltava river. There are many fish ponds in the municipal territory. The town itself lies on the shore of the largest of them, which is Munický pond with an area of . Hluboká nad Vltavou lies mostly in the Tábor Uplands, but the southern part with the ponds lies in the České Budějovice Basin, and the eastern part extends into the Třeboň Basin. The northern part of the large municipal territory is covered by forests. The highest point is the hill Velký Kamení ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltasar Marradas
Don Baltasar de Marradas et Vique or Maradas (28 November 1560, Valencia – 12 August 1638, Prague) was a Spanish nobleman, imperial field marshal during the Thirty Years' War and governor of Bohemia. Life :es:Baltasar_de_Marradas_y_Vich, Balthazar was the son of Gaspar de Marradas Soler (d.1569) Baron of Sallent and the Viceroy of Mallorca (1548-1557), and Anna vich Manrique. Both came from large noble families who had performed important services to the king as admirals, ambassadors, generals, and prelates. Anne was the sister of Luis the Viceroy of Mallorca (1573-1584), and of Juan vich Manrique the Bishop of Mallorca and later Archbishop of Tarragona. Baltasar's uncle was Guillen de San Clemente y de Centelles (1530-1608), aka Guillem de Santcliment i de Centelled, a Spanish politician, soldier, diplomat, a knight of Santiago, and Commander of Moratalla. He started young in the art of weapons. After becoming an hospitable knight he left for Malta, where he "gained the opin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
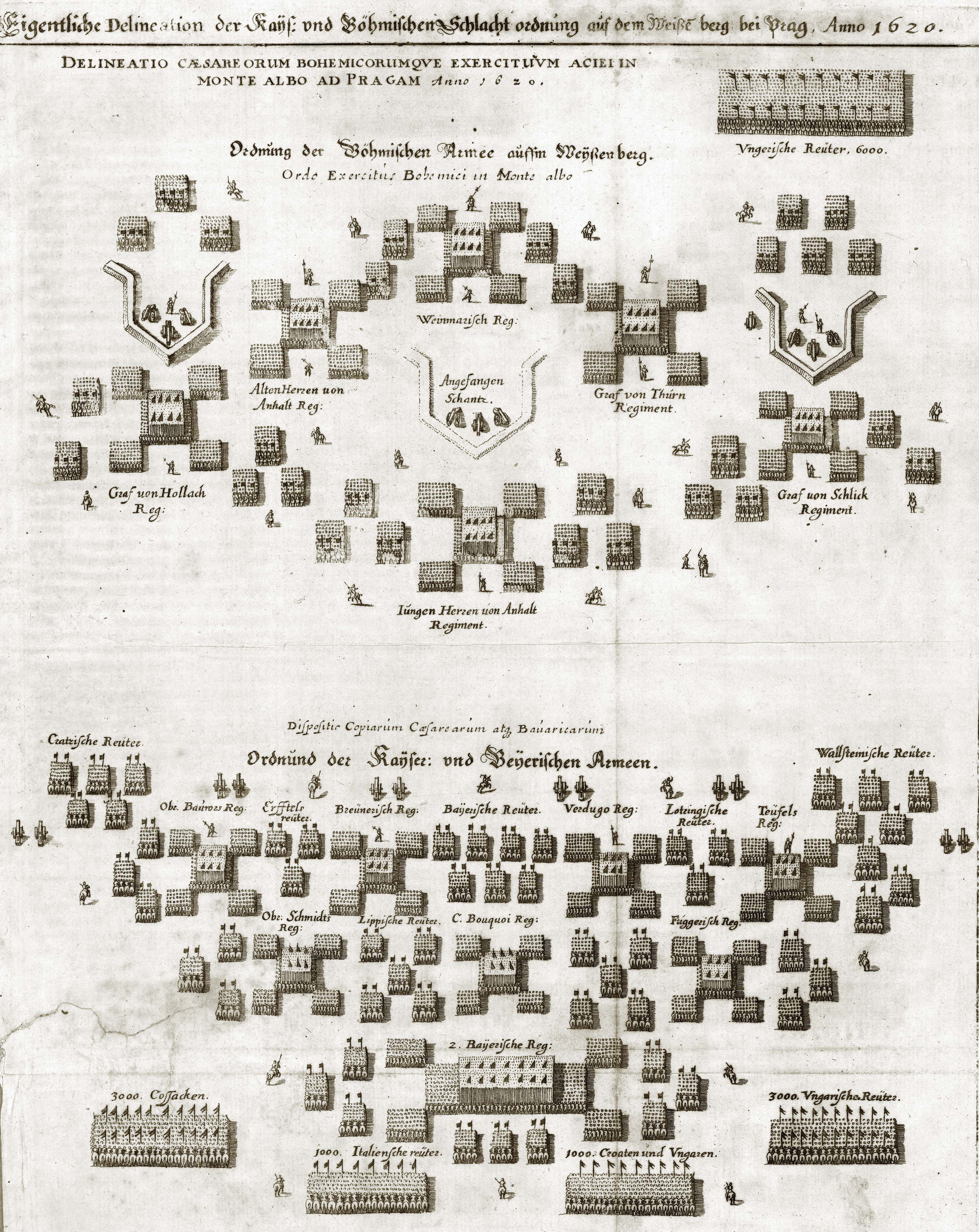
Battle Of White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic) , coordinates = , territory = , result = Imperial-Spanish victory , status = , combatants_header = , combatant1 = Catholic League , combatant2 = Bohemian Confederation Electoral Palatinate , commander1 = , commander2 = , strength1 = 23,00012 guns , strength2 = 21,00010 guns , casualties1 = 650 killed and wounded , casualties2 = 2,800 killed and wounded , map_type = Czech Republic Prague#Czech Republic , map_mark = Battle icon (crossed swords).svg , map_relief = , map_size = 300px , map_marksize = 30 , map_caption = , map_label = White Mountain The Battle of White Mountain ( cz, Bitva na Bílé hoře; german: Schlacht am Weißen Berg) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tábor Uplands
Tábor (; german: Tabor) is a town in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 33,000 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation. Administrative parts The following villages are administrative parts of Tábor: *Čekanice *Čelkovice *Hlinice *Horky *Klokoty *Měšice *Náchod *Smyslov *Stoklasná Lhota *Větrovy *Všechov *Zahrádka *Záluží *Zárybničná Lhota Etymology Although the town's Czech name translates directly to "camp" or "encampment", these words were derived from the Tábor's name, and the town was named after the biblical Mount Tabor located in Israel. The town also gave its name to the Taborites, a radical wing of the Hussites. Tábor was initially called ''Hradiště hory Tábor'' ("fortified settlement of the Tábor mountain"). Geography Tábor lies south of the capital Prague, north of the regional capital České Budějovice. It lies on the river Lužnice. Tábor is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)