|
Al-Turrah
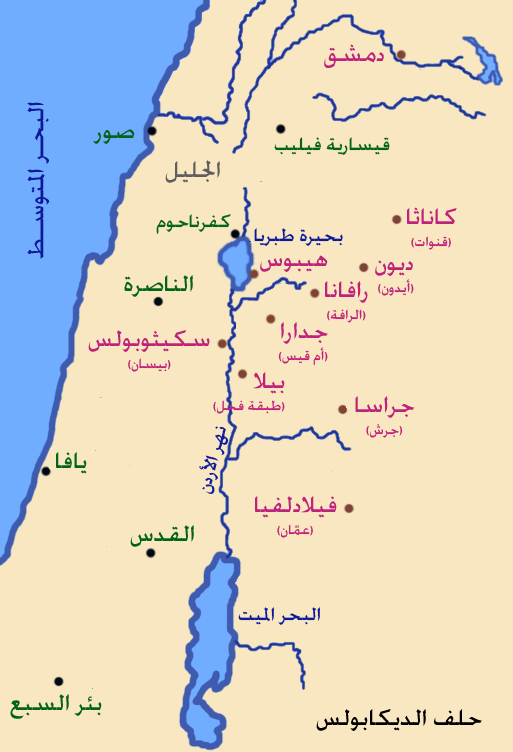
Al-Turrah is a Jordan, Jordanian city located in the Irbid Governorate in the far north of the country near the Border, international border with Syria. Al-Turrah is the largest community within the Hauran, Hauran Plain Municipality and is therefore considered its main center. Its population in 2017 was 34,948, the seventh largest in Irbid Governorate.This is after Irbid, Ramtha, Idun, Capitolias, Beit Ras, Sarih, and Hassan. It has an area of about 28,000 dunums (28 square kilometers).Studies in the Social Archaeology of Villages in Irbid Governorate: Bushra, Sal, Huwara, Tura, Zaidoun Muhaisen, Jordanian Ministry of Culture, 2007 Al-Turrah's territory extends to the east and north, bordering the Jordan–Syria border, Syrian border, while Al-Shajara, Jordan, Al-Shajara and Ar-Ramtha, Ramtha's territory borders it to the west and south. Since ancient times, Al-Turrah has been known for its cultivation of grain, which for many years was the only agricultural crop in the city and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irbid Governorate
Irbid or Irbed () is a governorate in Jordan, located north of Amman, the country's capital. The capital of the governorate is the city of Irbid. The governorate has the second largest population in Jordan after Amman Governorate, and the highest population density in the country. History Iron Age During the Iron Age, the region around Irbid, known then as Gilead, was settled by the Israelites. Ar-Ramtha, the second largest city in the Irbid Governorate, is commonly identified with the Israelite city of Ramoth-Gilead, a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. By the late Iron Age, Gilead became the focus of a power struggle between the Kingdom of Israel and the Aramean kingdom of Aram-Damascus. According to the Books of Kings, Ramoth-Gilead was the location of a battle between Kingdom of Israel and Aram Damascus. During the battle, King Ahab of Israel joined King Jehoshaphat of Judah to fights the Aramaeans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan–Syria Border
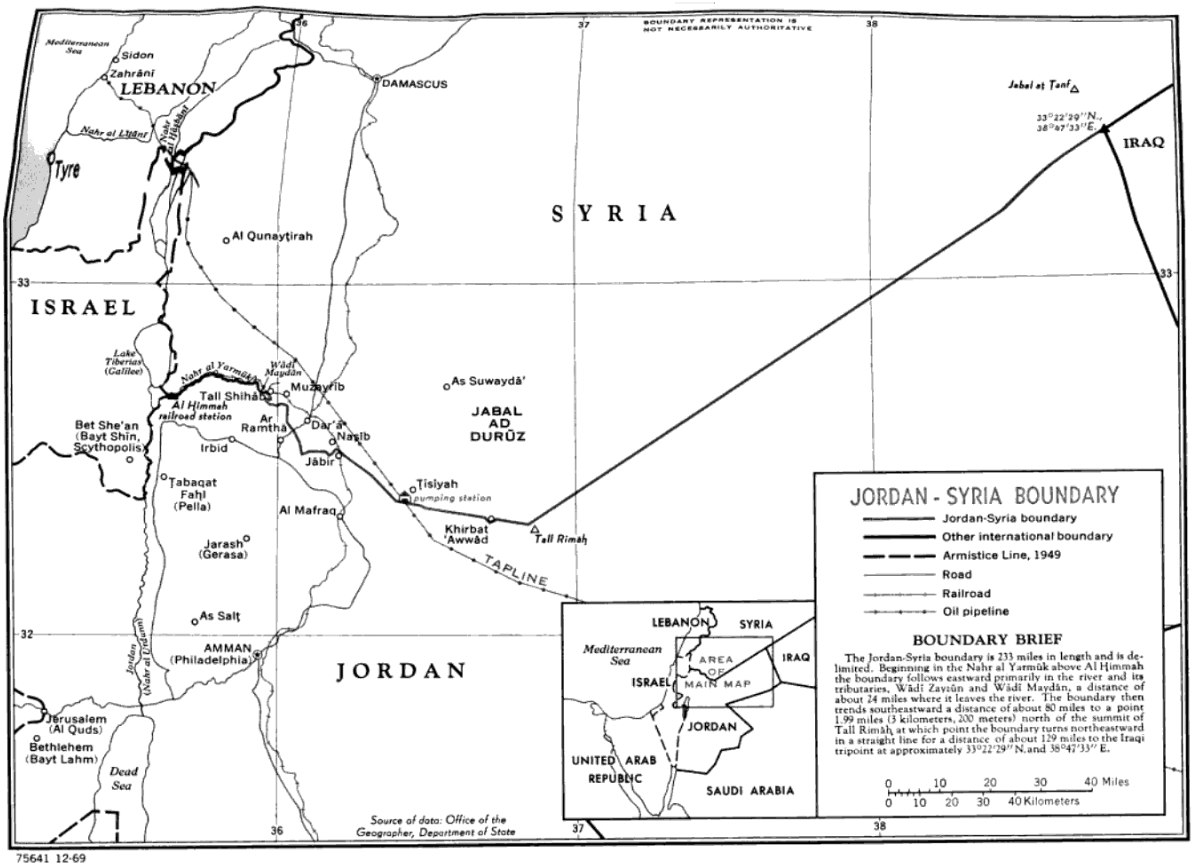
The Jordan–Syria border is 362 km (225 m) in length and runs from the tripoint with Israel in the west to the tripoint with Iraq in the east. Description The border starts in the west at the tripoint with Israel, though the precise location of the tripoint is at present unclear owing to the Israeli occupation of the Golan Heights, which are claimed by Syria. The ''de jure'' tripoint lies immediately east of the Israeli town of Sha'ar HaGolan, whereas the ''de facto'' tripoint lies at the border's junction with the United Nations UNDOF Zone south-east of Metzar. The Jordan-Golan Heights border runs along the Yarmouk River, and this river then continues as the westernmost section of the Jordan–Syria border proper. The border leaves the river just east of Al-Turrah, and a series of irregular and short straight lines then proceeds to the south-east, passing between Ar Ramtha and Daraa across the Daraa Border Crossing and on to the Nasib Border Crossing on the Amman– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ar-Ramtha
Ar-Ramtha (), colloquially transliterated as Ar-Romtha (), is a city situated in the far northwest of Jordan near the border with Syria. It covers 40 km2 on a plain 30 km northeast of the Jordan River and Irbid. In 2017, Ar-Ramtha had a population of approximately 164,211, making it the eleventh largest city in Jordan, and the second in Irbid Governorate, and the city has grown since then. It is part of the Ar-Ramtha district of the Irbid Governorate. Etymology The origin of the name Ar-Ramtha is debated. Some claim it is named after a local desert plant, al-ramath (). Many biblical archaeologists identify Ar-Ramtha with the ancient Israelite city of Ramoth-Gilead, Hebrew for "Heights of Gilead"; in that case, the present-day Arabic name might preserve the Biblical Hebrew one. During the Roman and Byzantine periods, Ar-Ramtha was known as Ramatha. History Prehistory The stable climate in ar-Ramtha and its surrounding areas attracted many animals to live in neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Shihab
Tell Shihab (; also spelled Tell esh-Shihab or Tal Shehab) is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Daraa Governorate, located northwest of Daraa on the Jordan-Syria border. Nearby localities include al-Shaykh Saad and Nawa to the north, Muzayrib, Da'el and Tafas to the northeast, and al-Yadudah to the east. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, Tell Shihab had a population of 9,430 in the 2004 census.General Census of Population and Housing 2004 Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). Daraa Governorate. Etymology The town's name is "pu ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadara
Gadara ( or ; ), in some texts Gedaris, was an ancient Hellenistic city in what is now Jordan, for a long time member of the Decapolis city league, a former bishopric and present Latin Catholic titular see. Its ruins are today located at Umm Qais, a small town in the Bani Kinanah Department and Irbid Governorate in Jordan, near its borders with Israel and Syria. It stood on a hill above sea level overlooking the Yarmouk River gorge, with the Golan Heights and the Sea of Galilee well visible to the north and northwest. This city is distinct from another contemporary one, ''Gadara'' or ''Gadora'' of Peraea, identified with the archaeological mound of Tell el-Jadur near Salt, Jordan. History Gadara was situated in a defensible position on a ridge accessible to the east but protected by steep falls on the other three sides. It was well-watered, with access to the Ain Qais spring and cisterns.. During the Hellenistic and Roman periods, Gadara was a centre of Greek culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzayrib
Muzayrib (, also spelled Mzerib, Mzeireb, Mzereeb, Mezereeb or al-Mezereeb) is a town in southern Syria, administratively part of the Daraa Governorate, located northwest of Daraa on the Jordan–Syria border. Nearby localities include al-Shaykh Saad and Nawa to the north, Da'el, Tafas and al-Shaykh Maskin to the northeast, and al-Yadudah to the southeast. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, Muzayrib had a population of 12,640 in the 2004 census. Its builder was a certain Hatim Tay.Petersen 2012, p55/ref> The fort had a bent gateway, unlike other Hajj forts which had straight entrances, and was built from locally quarried basaltic rock. Strategically located in the hinterland of Damascus, the fort at Muzayrib was the most solid demonstration of Ottoman power over Damascus, which experienced several revolts, including by the inhabitants or the local Janissary corps. Thus, the provincial leadership of Damascus stringently controlled Muzayrib. Because of its impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Yadudah, Syria
Al-Yadudah () is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Daraa Governorate, located north-west of Daraa. Nearby localities include Tell Shihab to the west, Muzayrib to the northwest, Tafas to the west and Ataman to the east. History In the Ottoman tax registers of 1596, it was a village located the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Butayna, Qada of Hawran. It had a population of 29 households and 21 bachelors, all Muslims. They paid a fixed tax-rate of 25% on agricultural products, including wheat, barley, summer crops, goats and beehives, in addition to occasional revenues; a total of 4,500 akçe.Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 214 According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, al-Yadudah had a population of 8,967 in the 2004 census. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit, and is usually applied to peaks which are above elevation compared to the relative landmass, though not as prominent as Mountain, mountains. Hills fall under the category of slope landforms. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as Grade (slope), steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the UK government's Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000 defined mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or " dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personification of bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is etymology, related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''boreas'' "north wind, north" which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas (god), Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Of Arabia
The tribes of Arabia () have inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years and traditionally trace their ancestry to one of two forefathers: Adnan, whose descendants originate from Hejaz, West Arabia, Syrian Desert, North Arabia, East Arabia, and Najd#History, Central Arabia; or Qahtanite, Qahtan, whose descendants originate from South Arabia. Further, it is held in the Abrahamic religions—particularly Islam—that the Arab people are descended from Abraham through his son Ishmael. From the 7th century onward, concurrent with the spread of Islam, many of these tribes' members began migrating and settling in the various regions that were subdued during the early Muslim conquests, including the Arab migrations to the Levant, Levant, Arab conquest of Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia, Arab conquest of Egypt, Egypt, Muslim conquest of Khuzestan, Khuzestan, the Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Maghreb, and Islamization of the Sudan region, Sudan. This phenomenon triggered a process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |