|
Al-Bayati
Al-Bayati () is a surname. It is connected to the Iraqi al-Bayat tribe. The ancestry and ethnicity of the al-Bayat tribe is contentious. The tribe's ancestry is often linked to the Oghuz Turkic Bayat tribe and its ethnicity described as Iraqi Turkmen or Turkish. Other sources however describe it as an Arab tribe or mixed Arab and Kurdish tribe of the Tayy tribal confederacy. The deceased Sheikh Hussein Aloush was ethnically Turkmen. Members of the tribe generally speak Iraqi Arabic and Iraqi Turkmen. Notable people * Sheikh Thaer al‑Bayati, Sunni Arab politician * Abd al-Wahhab Al-Bayati (1926–1999), Iraqi Arab poet *Basil Al Bayati Basil Al Bayati (; born 13 May 1946) is an Iraqi-born architect and designer who has lived and practiced for the most part in Europe, in particular, London and who Neil Bingham, in his book 100 Years of Architectural Drawing: 1900–2000, has ... (1946), Iraqi architect * Mohammed Mahdi al-Bayati (1962), Iraqi politician * T. Hamid al Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Wahhab Al-Bayati
Abd al-Wahhab al-Bayati (Arabic: عبد الوهاب البياتي) (December 19, 1926 – August 3, 1999) was an Iraqi Arab poet. Biography Al-Bayati was born in Baghdad. Al-Bayati was an Iraqi Turkmen poet. One of his friends, Ahmed Abdel-Moeti Hegazi, said urban centers of "hotels and institutions, cafés and airports" were actually his temporary residences. He attended Baghdad University, and became a teacher after graduating from Dar al-Mu'allimin (the Teacher's College) in 1950, the same year that he released his first collection of poems, ''Mala'ika wa Shayatin'' (''Angels and Devils''). In 1996, he published a poem "The Dragon". The translation by Farouk Abdel Wahab, Najat Rahman, and Carolina Hotchandani is from the volume ''Iraqi Poetry Today'' () (c) 2003, edited by Saadi Simawe. "The Dragon" is an example of al-Bayyati's frequent incorporation of mythological figures into his poetry. Critics have interpreted the poem as addressed to Saddam Hussein Saddam Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basil Al Bayati
Basil Al Bayati (; born 13 May 1946) is an Iraqi-born architect and designer who has lived and practiced for the most part in Europe, in particular, London and who Neil Bingham, in his book 100 Years of Architectural Drawing: 1900–2000, has described as "an architect in whom East meets West." Al Bayati is considered to be one of the most important names in metaphoric architecture, an area he was at the forefront of pioneering, which uses analogy and metaphor as a basis for architectural inspiration as well as the "exploration of geometric and design patterns found in nature" . He is also the inventor of what he termed "the mechanism of the wasitah (or excitor apparatus)" a geometric feedback mechanism for generating form and a method he himself often uses in the design process. Throughout his almost 50 years working in the field of architecture, he has also designed furniture and artistic pieces for the household using such varied techniques as metalwork, inlay, glass and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
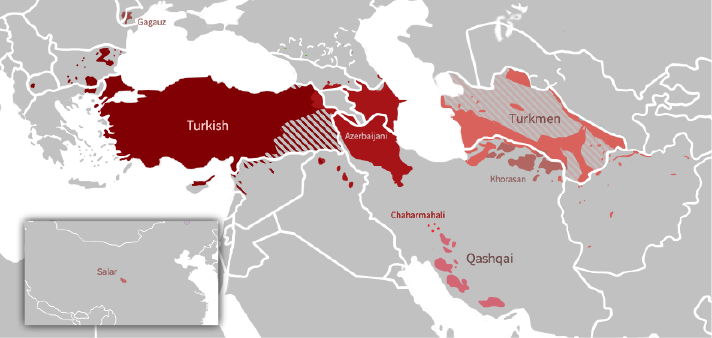
Iraqi Turkmen
The Iraqi Turkmen (, عراق تورکمنلری; Arabic: تركمان العراق), also referred to as Iraqi Turks, (, عراق توركلری; ) are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq. They make up to 10%–13% of the Iraqi population. Iraqi Turkmens are descendants of Turkish people, Turkish settlers from the time of Ottoman Iraq, and are closely related to Syrian Turkmen, Syrian Turkmens and Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijani people. Turkmen in Iraq do not closely identify with the traditionally-nomadic Turkmens of Central Asia and Iran.: "Turkmen, Iraqi citizens of Turkmen seljukh origin, are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq after Arabs and Kurds and they are said to number about 3 million of Iraq's 34.7 million citizens according to the Iraqi Ministry of Planning." Ethnonyms According to Iraqi Turkmen scholar Professor Suphi Saatçi, prior to the mid-20th century the Turkmens in Iraq were known simply as "Turks". It was not until after the military coup of 14 July 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tayy
The Tayy (/ALA-LC: ''Ṭayyi’''; Musnad: 𐩷𐩺), also known as Ṭayyi, Tayyaye, or Taiyaye, are a large and ancient Arab tribe, among whose descendants today are the tribes of Bani Sakher and Shammar. The '' nisba'' (patronymic) of Tayy is ''aṭ-Ṭāʾī'' (). In the second century CE, they migrated to the northern Arabian ranges of the Shammar and Salma Mountains, which then collectively became known as the ''Jabal Tayy'', and later ''Jabal Shammar''. The latter continues to be the traditional homeland of the tribe until the present day. They later established relations with the Sasanian and Byzantine empires. Though traditionally allied with the Sasanian client state of the Lakhmids, the Tayy supplanted them as the rulers of al-Hirah in the 610s. In the late sixth century, the Fasad War split the Tayy, with members of its Jadila branch converting to Christianity and migrating to Syria where they became allied with the Ghassanids, and the Ghawth branch remaining in Jaba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkmen Language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ) is a Turkic language of the Oghuz branch spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia. It has an estimated 4.7 million native speakers in Turkmenistan (where it is the official language), and a further 359,000 speakers in northeastern Iran and 1.2 million people in northwestern Afghanistan, where it has no official status. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia. Turkmen is a member of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. It is closely related to Azerbaijani, Gagauz, Qashqai, and Turkish, sharing varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with each of those languages. However, the closest relative of Turkmen is considered Khorasani Turkic, spoken in northeastern regions of Iran and with which it shares the eastern subbranch of Oghuz languages, as well as Khorazm, the Oghuz dialect of Uzbek spoken mainly in Khorezm along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Muslim community, being appointed at the meeting of Saqifa. This contrasts with the Succession of ʿAlī (Shia Islam), Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed Ali, Ali ibn Abi Talib () as his successor. Nevertheless, Sunnis revere Ali, along with Abu Bakr, Umar () and Uthman () as 'Rashidun, rightly-guided caliphs'. The term means those who observe the , the practices of Muhammad. The Quran, together with hadith (especially the Six Books) and (scholarly consensus), form the basis of all Fiqh, traditional jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. Sharia legal rulings are derived from these basic sources, in conjunction with Istislah, consideration of Maslaha, public welfare and Istihsan, jur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman ( or ''Türkmân'') by the 13th century.Lewis, G. ''The Book of Dede Korkut''. Penguin Books, 1974, p. 10. The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Karluk allies of the Uyghurs. In the 9th century, the Oghuz from the Aral steppes drove Pechenegs westward from the Emba and Ural River region. In the 10th century, the Oghuz inhabited the steppe of the rivers Sari-su, Turgai and Emba north of Lake Balkhash in modern-day Kazakhstan. They embraced Islam and adapted their traditions and institutions to the Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayat (tribe)
Bayat (; ; ; ) is one of the Oghuz tribes in Turkmenistan, Iran, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Syria.: ''Bayāt was one of the twenty-two Oghuz tribes listed in Maḥmūd Kāšḡarī's'' When Oghuz Turks started to migrate from the Aral steppes to Khorasan in the 11th and 13th centuries, Bayat people spread throughout the region.R. Khanam. Encyclopaedic ethnography of Middle-East and Central Asia: J-O, том 2. Стр. 126—127 They are sub-ethnic groups of Turkmens and Azerbaijanis. The Bayats are Muslim and speak a southern dialect of Azerbaijani language in Azerbaijan and Iran, or their own dialect of Turkish in Turkey, and Ersari dialect of Turkmen in Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. The ancient Turkmen proverb says: " Kayi and Bayat tribes shall lead the people" ( Turkmen: "''Il başy - gaýy-baýat''"). Etymology and origin Initially, the ethnonym Bayat was mentioned as an Oguz tribe in the 11th century by the Turkic historian Mahmud Kashgari. Bayat - an O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish People
Turks (), or Turkish people, are the largest Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group, comprising the majority of the population of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. They generally speak the various Turkish dialects. In addition, centuries-old Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire, ethnic Turkish communities still exist across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. Article 66 of the Constitution of Turkey defines a ''Turk'' as anyone who is a citizen of the Turkish state. While the legal use of the term ''Turkish'' as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition, the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70 to 75 percent) are of Turkish ethnicity. The vast majority of Turks are Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, with a notable minority practicing Alevism. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
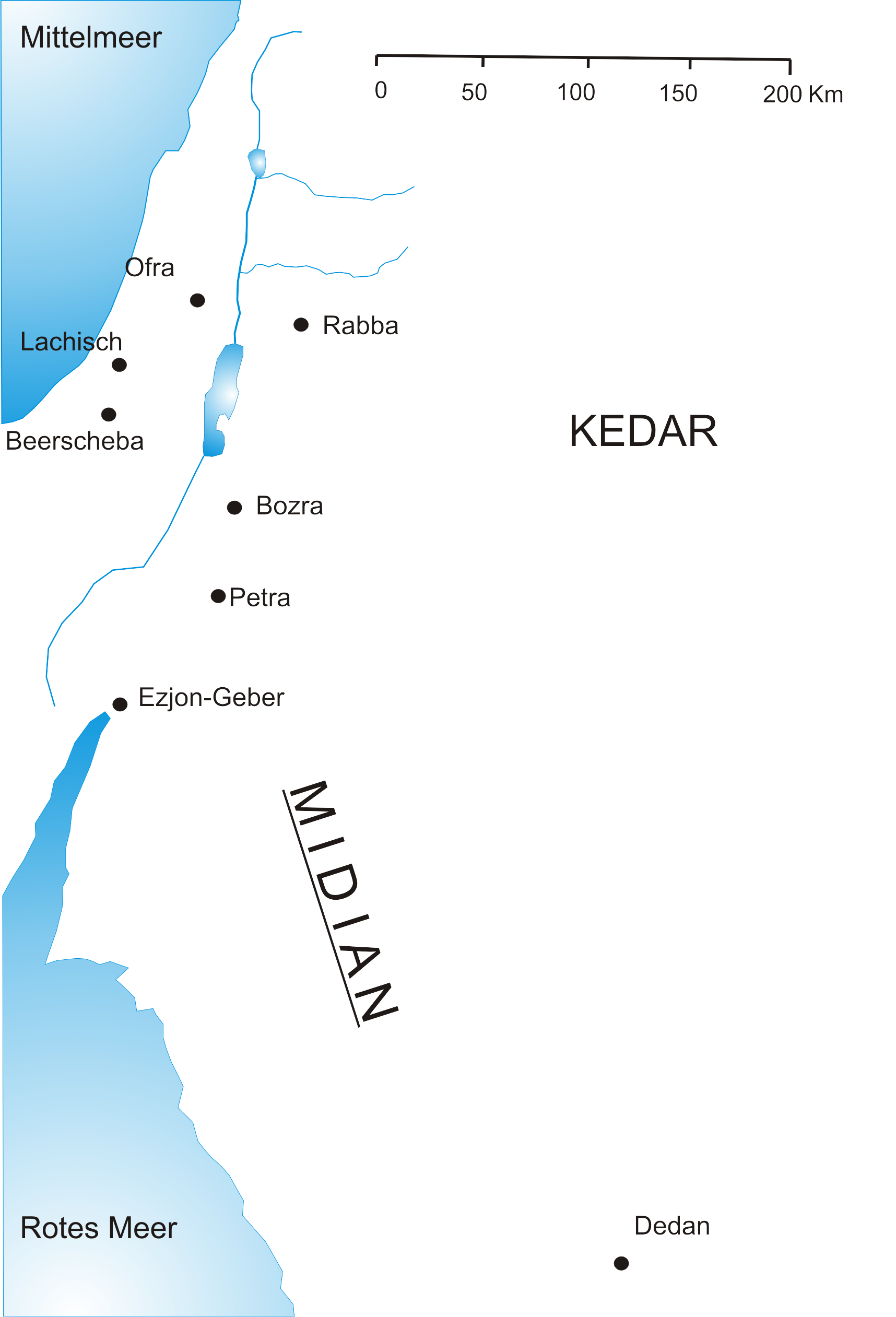
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syria. Consisting of 30–45 million people, the global Kurdish population is largely concentrated in Kurdistan, but significant communities of the Kurdish diaspora exist in parts of West Asia beyond Kurdistan and in parts of Europe, most notably including: Turkey's Central Anatolian Kurds, as well as Kurds in Istanbul, Istanbul Kurds; Iran's Khorasani Kurds; the Caucasian Kurds, primarily in Kurds in Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan and Kurds in Armenia, Armenia; and the Kurdish populations in various European countries, namely Kurds in Germany, Germany, Kurds in France, France, Kurds in Sweden, Sweden, and the Kurds in the Netherlands, Netherlands. The Kurdish language, Kurdish languages and the Zaza–Gorani languages, both of which belong to the Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |