|
Airspace Class (United States)
The United States airspace system's classification scheme is intended to maximize pilot flexibility within acceptable levels of risk appropriate to the type of operation and traffic density within that class of airspace – in particular to provide separation and active control in areas of dense or high-speed flight operations. The Albert Roper (1919-10-13 The Paris Convention) implementation of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) airspace classes defines classes A through G (with the exception of class F which is not used in the United States). The other U.S. implementations are described below. The United States also defines categories of airspace that may overlap with classes of airspace. Classes of airspace are mutually exclusive. Thus, airspace can be "class E" and "restricted" at the same time, but it cannot be both "class E" and "class B" at the same location and at the same time. Note: All airspace classes except class G require air traffic control (ATC) cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international scheduled air transport, air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. The ICAO headquarters are located in the Quartier international de Montréal of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. ICAO defines the protocols for Aviation accidents and incidents, air accident investigation that are followed by :Organizations investigating aviation accidents and incidents, transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Convention on International Civil Aviation. The Air Navigation Commission (ANC) is the techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode C Veil
Mode C veil refers to a kind of airspace which currently surrounds all primary Class B airports within the United States. This airspace extends horizontally to a circle of 30 NM radius centered on the airport, and extends vertically from the surface up to 10,000 feet MSL. The name refers to the mode of transponder operation which is required within this airspace — that is, with very limited exceptions, all aircraft operating within this airspace must have an altitude-reporting Mode C transponder in operation. An additional requirement for the transponder to have ADS-B Out became effective January 1, 2020. , all 37 Class B airports in the United States have Mode C veils centered on them. Prior to November 2014, two Class B airports did not have a Mode C veil (at least ''de jure''): William P. Hobby Airport in Houston and Marine Corps Air Station Miramar in San Diego. Mode C veils were implemented after the collision of Aeroméxico Flight 498 Aeroméxico Flight 498 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
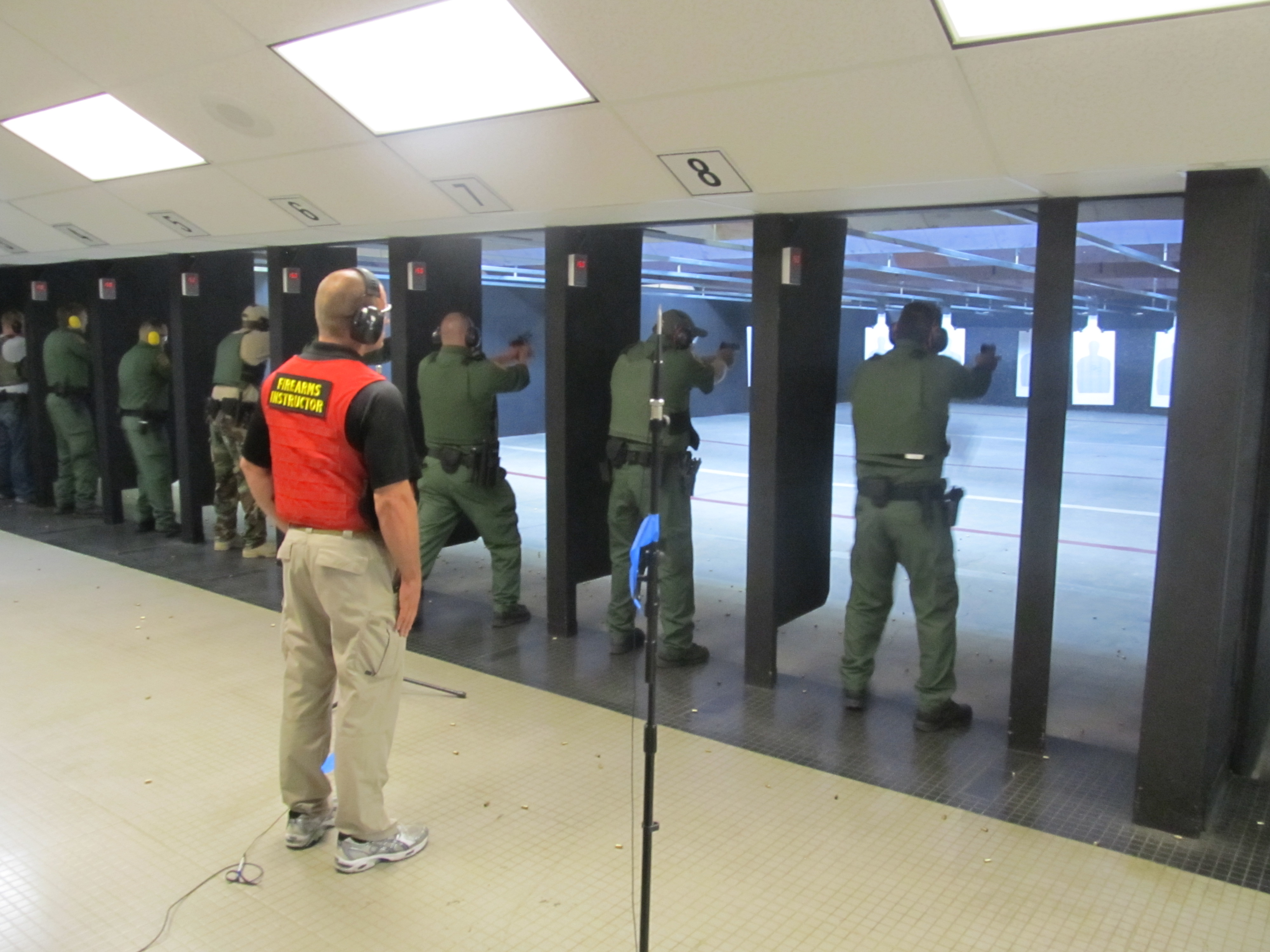
Firing Ranges
A shooting range, firing range, gun range or shooting ground is a specialized facility, venue, or field designed specifically for firearm A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions). The first firearms originate ... usage qualifications, training, practice, or shooting sport, competitions. Some shooting ranges are operated by military or law enforcement agencies, though the majority of ranges are privately owned by civilians and sporting clubs and cater mostly to recreational shooters. Each facility is typically overseen by one or more supervisory personnel, known as a ''Range Officer'' (RO), or sometimes a ''range master'' in the United States. Supervisory personnel are responsible for ensuring that all firearm safety, safety rules and relevant gun law, laws are followed at all times. Shooting ranges ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fourth-largest state by area, but the List of U.S. states and territories by population, eighth-least populous state and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, third-least densely populated state. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Helena, Montana, Helena, while the List of municipalities in Montana, most populous city is Billings, Montana, Billings. The western half of the state contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Canada, to New Mexico in the Southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of Rocky Mountain Trench, the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River (Alaska), Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque metropolitan area, Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountains, Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectional Chart
In United States aviation, a sectional aeronautical chart, often called a sectional chart or a sectional for short, is a type of aeronautical chart designed for air navigation under visual flight rules (VFR). In Australia, Canada and some other countries, the equivalent charts used for visual flight are called VFR Navigation Charts (VNCs). A sectional chart shows topographical features that are important to aviators, such as terrain elevations, ground features identifiable from altitude (rivers, dams, bridges, buildings, etc.), and ground features useful to pilots (airports, beacons, landmarks, etc.). The chart also shows information on airspace classes, ground-based navigation aids, radio frequencies, longitude and latitude, navigation waypoints, navigation routes. Sectional charts are in 1:500,000 scale and are named for a city on the map. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States publishes over 50 charts covering the continental United States, Alaska, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-towered Airport
In aviation, a non-towered airport is an airport without a control tower, or air traffic control (ATC) unit. In the United States, there are close to 20,000 non-towered airports compared to approximately 500 airports with control towers. Airports with a control tower without 24/7 ATC service follow non-towered airport procedures when the tower is closed but the airport remains open, for example at night. Operations At non-towered airports, instead of receiving instructions from an air traffic controller, aircraft pilots follow recommended operations and communications procedures for operating at an airport without a control tower. The exact procedures vary from country to country, but they may include standard arrival and departure procedures, as well as a common communications phraseology by radio transmissions over a common frequency. For example, a common traffic advisory frequency (CTAF) is recommended for radio communication and is used in the United States, Canada, New Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transponder (aeronautics)
A transponder (short for ''trans''mitter-res''ponder'' and sometimes abbreviated to XPDR, XPNDR, TPDR or TP) is an electronic device that produces a response when it receives a radio-frequency interrogation. Aircraft have transponders to assist in identifying them on air traffic control radar. Collision avoidance systems have been developed to use transponder transmissions as a means of detecting aircraft at risk of colliding with each other. Air traffic control (ATC) units use the term "squawk" when they are assigning an aircraft a transponder code, e.g., "Squawk 7421". Squawk thus can be said to mean "select transponder code" or "squawking ''xxxx''" to mean "I have selected transponder code ''xxxx''". The transponder receives interrogation from the secondary surveillance radar on 1030 MHz and replies on 1090 MHz. Secondary surveillance radar Secondary surveillance radar (SSR) is referred to as "secondary", to distinguish it from the "primary radar" that works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization ( ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct Powered lift, downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
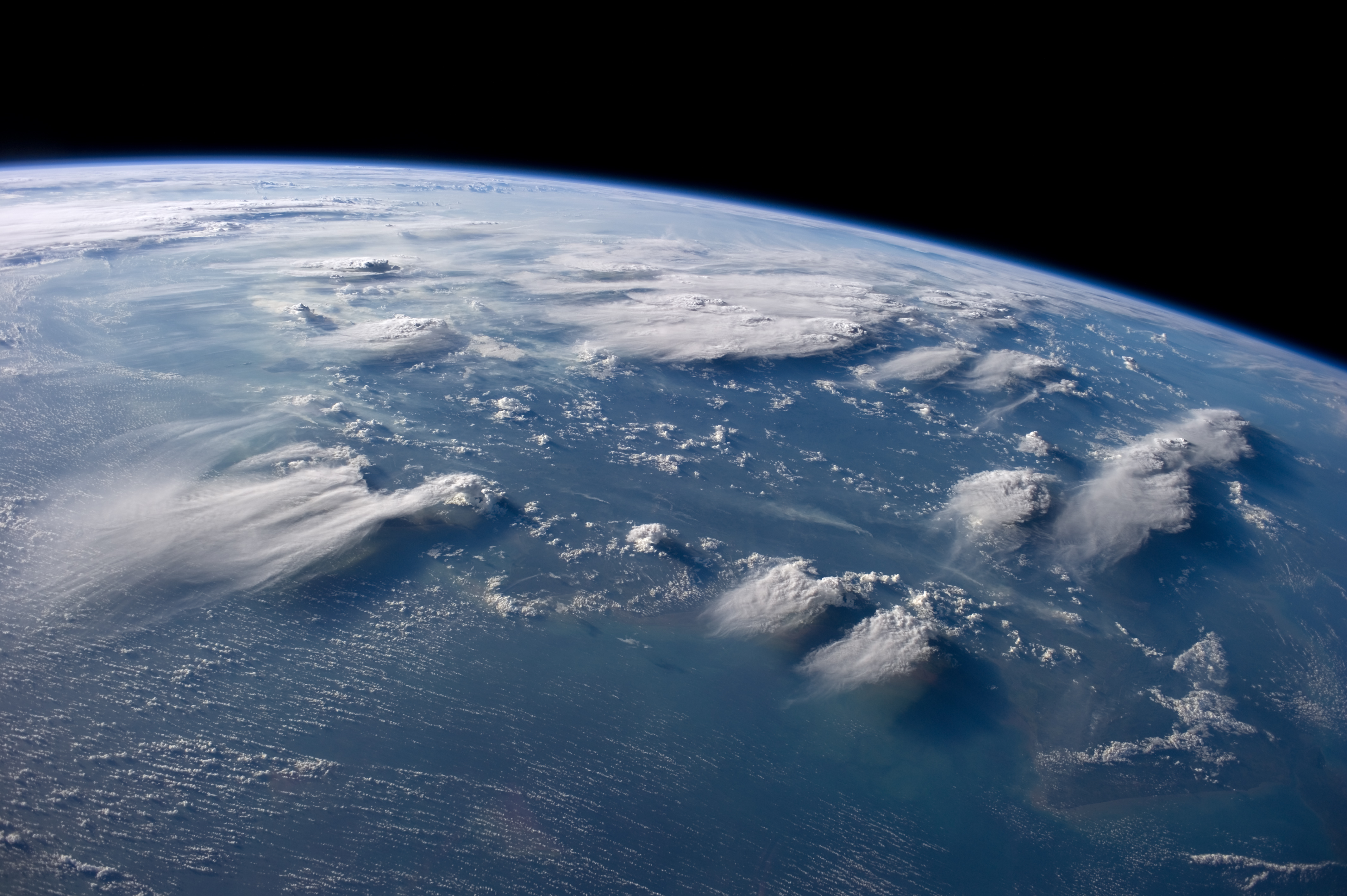
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. Clouds are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. The World Meteorological Organization uses two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |