|
Airplane
An airplane (American English), or aeroplane (Commonwealth English), informally plane, is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, air transportation, transportation of goods and people, military aviation, military, and Experimental aircraft, research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometersMeasured in RTKs—an RTK is one tonne of revenue freight carried one kilometer. of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be unmanned aerial vehicle, remotely or computer-controlled such as drones. The Wright brothers invented and flew the Wright Flyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
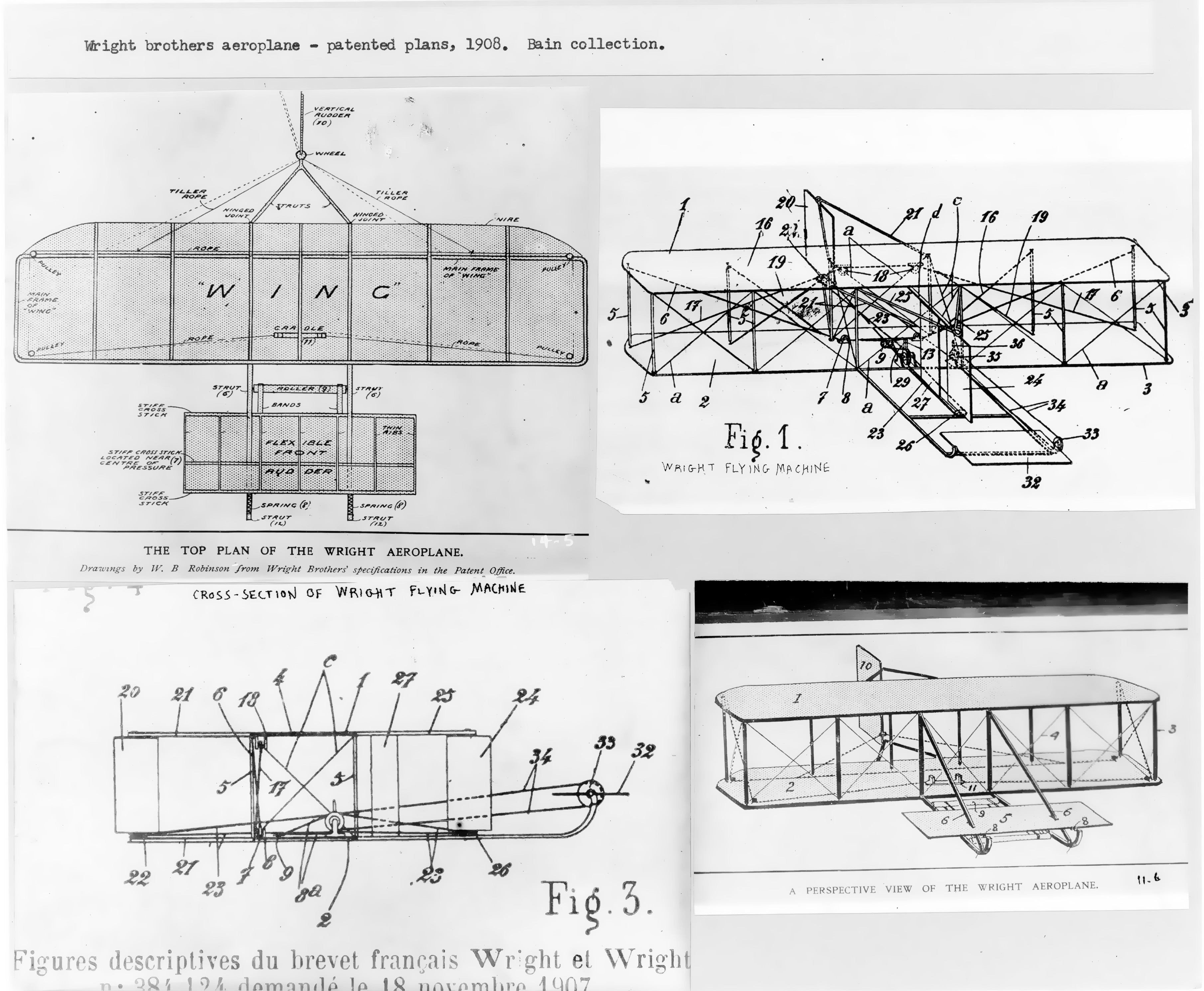
Wright Brothers
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright (August 19, 1871 – January 30, 1948) and Wilbur Wright (April 16, 1867 – May 30, 1912), were American aviation List of aviation pioneers, pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flying the world's first successful airplane. They made the first controlled, sustained flight of an engine-powered, Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air aircraft with the ''Wright Flyer'' on December 17, 1903, four miles (6 km) south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, at what is now known as Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills. In 1904 the Wright brothers developed the ''Wright Flyer II'', which made longer-duration flights including the first circle, followed in 1905 by the first truly practical fixed-wing aircraft, the ''Wright Flyer III''. The brothers' breakthrough invention was their creation of a Flight dynamics (aircraft), three-axis control system, which enabled the pilot to steer the aircraft effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orville Wright
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright (August 19, 1871 – January 30, 1948) and Wilbur Wright (April 16, 1867 – May 30, 1912), were American aviation pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flying the world's first successful airplane. They made the first controlled, sustained flight of an engine-powered, heavier-than-air aircraft with the ''Wright Flyer'' on December 17, 1903, four miles (6 km) south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, at what is now known as Kill Devil Hills. In 1904 the Wright brothers developed the '' Wright Flyer II'', which made longer-duration flights including the first circle, followed in 1905 by the first truly practical fixed-wing aircraft, the '' Wright Flyer III''. The brothers' breakthrough invention was their creation of a three-axis control system, which enabled the pilot to steer the aircraft effectively and to maintain its equilibrium. Their system of aircraft controls made fixed-wing powered flight possible and remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilbur Wright
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright (August 19, 1871 – January 30, 1948) and Wilbur Wright (April 16, 1867 – May 30, 1912), were American aviation List of aviation pioneers, pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flying the world's first successful airplane. They made the first controlled, sustained flight of an engine-powered, Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air aircraft with the ''Wright Flyer'' on December 17, 1903, four miles (6 km) south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, at what is now known as Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills. In 1904 the Wright brothers developed the ''Wright Flyer II'', which made longer-duration flights including the first circle, followed in 1905 by the first truly practical fixed-wing aircraft, the ''Wright Flyer III''. The brothers' breakthrough invention was their creation of a Flight dynamics (aircraft), three-axis control system, which enabled the pilot to steer the aircraft effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-wing Aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using aerodynamic lift. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft (in which a rotor mounted on a spinning shaft generates lift), and ornithopters (in which the wings oscillate to generate lift). The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft, and airplanes that use wing morphing are all classified as fixed wing. Gliding fixed-wing aircraft, including free-flying gliders and tethered kites, can use moving air to gain altitude. Powered fixed-wing aircraft (airplanes) that gain forward thrust from an engine include powered paragliders, powered hang gliders and ground effect vehicles. Most fixed-wing aircraft are operated by a pilot, but some are unmanned or controlled remotely or are completely autonomous (no remote pilot). History Kites Kites were used approximately 2,800 years ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velomobiles), animal-powered transports (e.g. horse-drawn vehicle, horse-drawn carriages/wagons, ox carts, dog sleds), motor vehicles (e.g. motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters) and rail transport, railed vehicles (trains, trams and monorails), but more broadly also includes cable transport (aerial lift, cable cars and elevators), watercraft (ships, boats and underwater vehicles), amphibious vehicles (e.g. screw-propelled vehicles, hovercraft, seaplanes), aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, glider (aircraft), gliders and aerostats) and space vehicles (spacecraft, spaceplanes and launch vehicles). This article primarily concerns the more ubiquitous land vehicles, which can be broadly classified by the type of contact interface with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Flyer
The ''Wright Flyer'' (also known as the ''Kitty Hawk'', ''Flyer'' I or the 1903 ''Flyer'') made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by brothers Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the Aviation in the pioneer era, pioneer era of aviation. The aircraft is a single-place biplane design with Dihedral (aeronautics)#Anhedral and polyhedral, anhedral (drooping) wings, front double Elevator (aeronautics), elevator (a canard (aeronautics), canard) and rear double rudder. It used a gasoline engine powering two pusher propellers. Employing "wing warping", it was relatively unstable and very difficult to fly. The Wright brothers flew it four times in a location now part of the town of Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills, about south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The airplane flew on its fourth and final flight, but was damaged on landing, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Drone Warfare; 2024. e-ISBN (PDF) 978-3-11-074203-9.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage,F. Rekabi-Bana; Hu, J.; T. Krajník; Arvin, F.,Unified Robust Path Planning and Optimal Trajectory Generation for Efficient 3D Area Coverage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Transportation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Clément Ader built the "Ader Éole" in France and made an uncontrolled, powered hop in 1890. This was the first powered aircraft, although it did not achieve controlled flight. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896. A major leap followed with the construction of the ''Wright Flyer'', the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet engine which enabled aviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 777-200
The Boeing 777, commonly referred to as the Triple Seven, is an American long haul, long-range Wide-body aircraft, wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. The 777 is the world's largest twinjet and the most-built wide-body airliner. The Jet airliner, jetliner was designed to bridge the gap between Boeing's other wide body airplanes, the twin-engined Boeing 767, 767 and quad-engined Boeing 747, 747, and to replace aging DC-10 and L-1011 trijets. Developed in consultation with eight major airlines, the 777 program was launched in October 1990, with an order from United Airlines. The B-HNL, prototype aircraft rolled out in April 1994, and first flew that June. The 777 entered service with the launch operator United Airlines in June 1995. Longer-range variants were launched in 2000, and first delivered in 2004. The Triple Seven can accommodate a ten–abreast seating layout and has a typical 3-class capacity of 301 to 368 passengers, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term typically refers to an internal combustion airbreathing jet engine, air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet engine, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines. Air-breathing jet engines typically feature a Axial compressor, rotating air compressor powered by a turbine, with the leftover power providing thrust through the propelling nozzle—this process is known as the Brayton cycle, Brayton thermodynamic cycle. Jet aircraft use such engines for long-distance travel. Early jet aircraft used turbojet engines that were relatively inefficient for subsonic flight. Most modern subsonic jet aircraft use more complex High-bypass turbofan, high-bypas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airliner
An airliner is a type of airplane for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. The modern and most common variant of the airliner is a long, tube shaped, and jet powered aircraft. The largest of them are wide-body jets which are also called twin-aisle because they generally have two separate aisles running from the front to the back of the passenger cabin. These are usually used for long-haul flights between airline hubs and major cities. A smaller, more common class of airliners is the narrow-body or single-aisle. These are generally used for short to medium-distance flights with fewer passengers than their wide-body counterparts. Regional airliners typically seat fewer than 100 passengers and may be powered by turbofans or turboprops. These airliners are the non- mainline counterparts to the larger aircraft operated by the major carriers, legacy carriers, and flag carriers, and are used to feed traffic into the large a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |