|
Agrostichthys
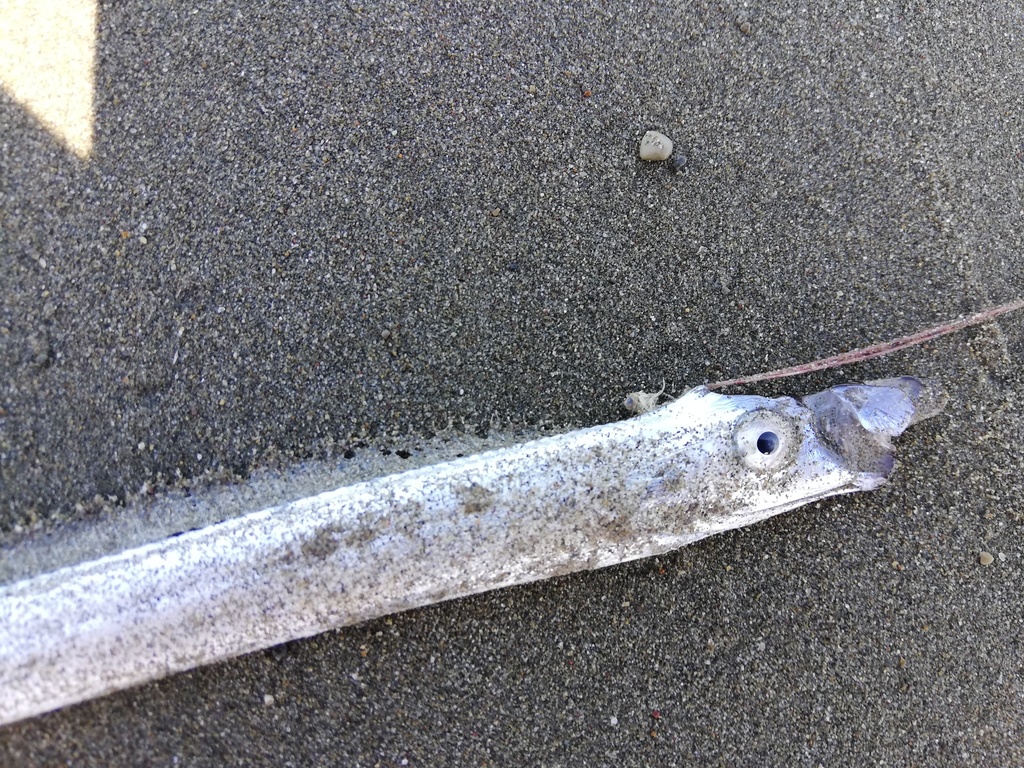
''Agrostichthys parkeri'', also called the streamer fish, is a species of oarfish. Only seven identified specimens have been examined, with few found fully intact, and have mainly been found in the Southern Ocean. ''Agrostichthys parkeri'' belongs to the Regalecidae (oarfish) family in the Lampriformes order and is the only known member of its genus. This species has been known to grow up to long and has a ribbon-like body, two large eyes, a protruding mouth and long filamentous rays originating at the head. Due to only seven specimens being found, only the distribution and anatomy of ''Agrostichthys parkeri'' can be documented. Etymology The fish is named in memory of Benham’s predecessor, zoologist Thomas Jeffery Parker (1850-1897), of the University of Otago in New Zealand, who made a “careful study” of the anatomy of ''Regalecus glesne'' in the year 1886. Anatomy and morphology ''Agrostichthys parkeri'' has an elongated, vertically compressed body which slims down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oarfish
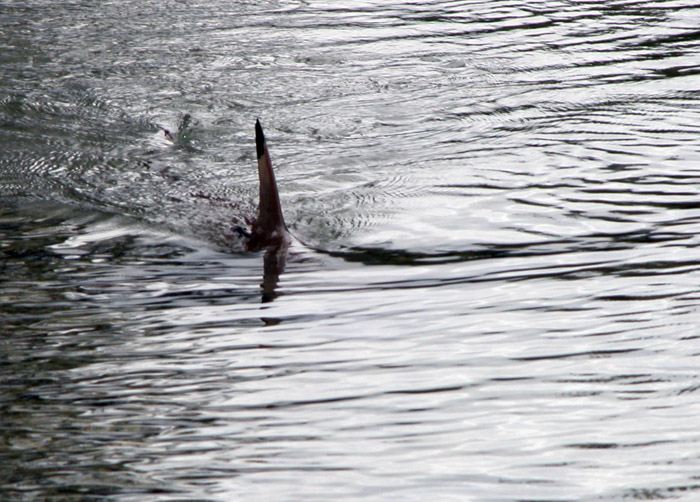
Oarfish are large and extremely long pelagic lampriform fish belonging to the small family (biology), family Regalecidae. Found in areas spanning from Temperate climate, temperate ocean zones to tropical ones, yet rarely seen by humans, the oarfish family contains three species in two genus, genera. One of these, the giant oarfish (''Regalecus glesne''), is the longest bony fish alive, growing up to about in length. The common name ''oarfish'' is thought to allude either to their highly compressed and elongated bodies, or to the now discredited belief that the fish "row" themselves through the water with their pelvic fins. The family name Regalecidae is derived from the Latin ''regalis'', meaning "royal". Although the larger species are considered game fish and are fished commercially on a small scale, oarfish are rarely caught alive; their flesh is not well regarded for eating due to its gelatinous consistency. Their rarity and large size, and their habit of lingering at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jeffery Parker
Thomas Jeffery Parker Fellow of the Royal Society, F.R.S. (17 October 1850 – 7 November 1897) was a zoologist who worked in New Zealand. Biography Parker was born at 124 Tachbrook Street in London on 17 October 1850 the son of the anatomist William Kitchen Parker. He studied at Clarendon House School and graduated from the University of London in 1868. At the age of 22, he worked with Thomas Henry Huxley in Huxley's zoological demonstrations, forming a teaching collection and organising laboratory practicals. Huxley's work on crayfish kindled in Parker an interest in crustaceans, and he went on to study the marine "crayfish" (spiny lobsters) of New Zealand, together with his student Josephine Gordon Rich, who later married William Aitcheson Haswell. On 23 December 1874, Thomas Jeffery Parker married Charlotte Elizabeth Rossell in Bramley, Leeds, Bramley, Yorkshire. In 1880, they emigrated to New Zealand. Parker become Professor of Zoology at the University of Otago in Dunedin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regalecus Glesne
''Regalecus'' is a fish genus of the family Regalecidae, commonly called oarfish, with these currently recognized species: * '' Regalecus glesne'' ( P. Ascanius, 1772), giant oarfish or king of herrings * ''Regalecus russelii ''Regalecus russelii'', or Russell's oarfish, is a species of oarfish in the family Regalecidae. It is a broadly-distributed marine fish, found in waters in the bathypelagic zone. ''R. russelii'' is a scaleless, elongate and ribbonlike fish, grow ...'' ( G. Cuvier, 1816) References External links * * * Regalecidae {{Lampriformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By William Benham (zoologist)
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Fish Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier, New Zealand
Napier ( ; ) is a city on the eastern coast of the North Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Hawke's Bay region. It is a beachside city with a seaport, known for its sunny climate, esplanade lined with Norfolk pines, and extensive Art Deco architecture. For these attributes, Napier is sometimes romantically referred to as the "Nice of the Pacific". Napier is located on the territory of Ngāti Kahungunu, one of the country's largest iwi, and as a city has been shaped by nearly two centuries of migration. Its population is about About south of Napier is the inland city of Hastings. These two neighbouring cities are often called "The Bay Cities" or "The Twin Cities" of New Zealand, with the two cities and the surrounding towns of Havelock North and Clive having a combined population of . The City of Napier has a land area of and a population density of 540.0 per square kilometre. Napier is the nexus of the largest wool centre in the Southern Hemisphere, and it has th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanophores
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. Some species can rapidly change colour through mechanisms that tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |