|
Agnes Of Habsburg
Albert II of Saxony ( Wittenberg upon Elbe, ca. 1250 – 25 August 1298, near Aken) was a son of Duke Albert I of Saxony and his third wife Helen of Brunswick and Lunenburg, a daughter of Otto the Child. He supported Rudolph I of Germany at his election as Roman king and became his son-in-law. After the death of their father Albert I in 1260 Albert II jointly ruled the Duchy of Saxony with his elder brother John I, and thereafter with the latter's sons. Life In 1269, 1272 and 1282 the brothers gradually divided their governing competences within the three territorially unconnected Saxon areas (one called Land of Hadeln around Otterndorf, another around Lauenburg upon Elbe and the third around Wittenberg), thus preparing a partition. In the imperial election in 1273 Albert II represented the jointly ruling brothers. In return Rudolph I had married his daughter Agnes of Habsburg to Albert II. After John I had resigned in 1282 in favour of his three minor sons Eric I, John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is the fourth-largest town in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, in the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. It is situated on the River Elbe, north of Leipzig and south-west of the reunified German federal capital city of Berlin, and has a population of 46,008 (2018). Wittenberg has close connections with Martin Luther (1483–1546) and the 16th century religious / theological movement of Protestantism begun here in the Reformation, and the large branch of Western Christianity started here of Lutheranism, Evangelical Lutheranism, for which it received the honorific title ''Lutherstadt'' and has been called the "cradle of the Reformation" and "cradle of Protestantism". Several of Wittenberg's buildings are associated with the historical / religious events, including a preserved part of the Augustinians, Augustinian monastery of the local community of the world-wide Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Order of St. Augustine in which Luth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
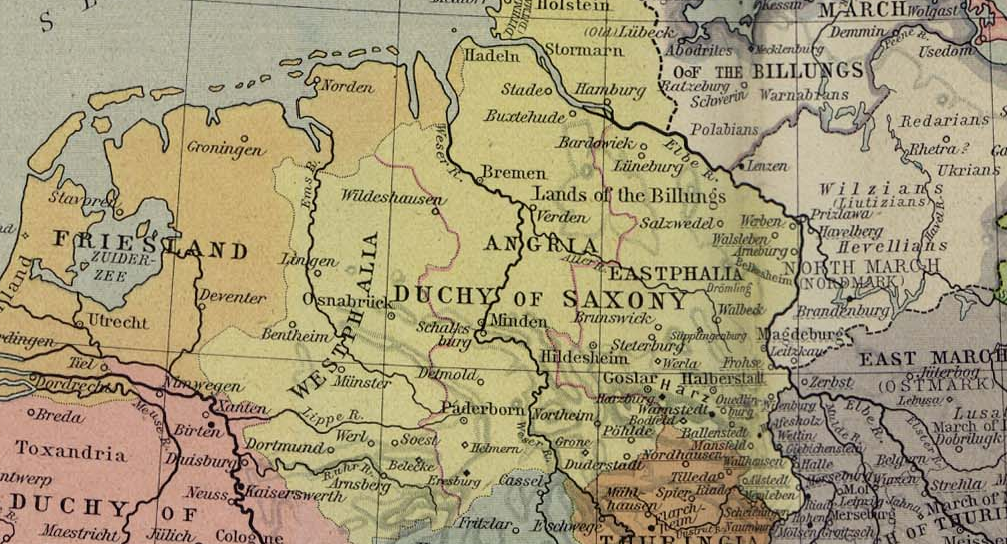
Electorate Of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony ( or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a major Holy Roman state, being an Prince-elector, electorate and the original protecting power of Protestant principalities until that role was later taken by its neighbor, Brandenburg-Prussia. In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV designated the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg an electorate, a territory whose ruler was one of the prince-electors who chose the Holy Roman emperor. After the extinction of the male Saxe-Wittenberg line of the House of Ascania in 1422, the duchy and the electorate passed to the House of Wettin. The electoral privilege was tied only to the Electoral Circle, specifically the territory of the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg. In the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin noble house w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Kingdom of Croatia, the Republic of Venice, the Austrian Empire, and presently the Croatia, Republic of Croatia. Dalmatia is a narrow belt stretching from the island of Rab (island), Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar, Šibenik, and Dubrovnik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf I, Duke Of Saxe-Wittenberg
Rudolf I ( – 12 March 1356), a member of the House of Ascania, was Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg from 1298 until his death. By the Golden Bull of 1356 he was acknowledged as Elector of Saxony. Life Rudolf was the eldest son of the Saxon duke Albert II (c. 1250 – 1298), who initially ruled jointly with his brother John I but gradually concentrated on the Ascanian Saxe-Wittenberg territory. Rudolf's father consolidated his position by marrying the Habsburg princess Agnes (1257–1322), a daughter of King Rudolf I of Germany, whom he had elected King of the Romans in 1273. Upon the death of Margrave Henry III of Meissen in 1288, Duke Albert II applied at his father-in-law King Rudolf for the enfeoffment of his son and heir with the Saxon County palatine on the Unstrut river, which ensued a long lasting dispute with the eager clan of the Wettin dynasty. Albert's attempts to secure the succession in the lands of the extinct Saxon counts of Brehna were more successful: when thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascanian
The House of Ascania () was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt. The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schloss Askanien'' in German, which was located near and named after Aschersleben. The castle was the seat of the County of Ascania, a title that was later subsumed into the titles of the princes of Anhalt. History File:Schloss Ballenstedt, Hofseite.JPG, Ballenstedt Castle File:Arms of the house of Ascania (ancient).svg, First coat of arms of the family Map of Anhalt (1747-1793).svg, Map of Anhalt (1747–1793) The earliest known member of the house, Esiko, Count of Ballenstedt, first appears in a document of 1036. Genealogists assume him to have been a grandson (through his mother) of Odo I, Margrave of the Saxon Ostmark (). From Odo, the Ascanians inherited large properties in the Saxon Eastern March. Esiko's grandson Otto, Count of Ballenstedt, die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belzig
Bad Belzig (), until 2010 Belzig, is a historic town in Brandenburg, Germany located about southwest of Berlin. It is the capital of the Potsdam-Mittelmark district. Geography Bad Belzig is located within the Fläming hill range and in the centre of the High Fläming Nature Park. The plains north of the town are home to one of the few great bustard populations in Germany. Since 2003, when 14 surrounding villages were incorporated into Bad Belzig, some of them voluntarily, others by Brandenburg Landtag (state parliament) legislation, Bad Belzig has an area of 234.83 km². These villages became districts (''Ortsteile'') of Belzig: The forest of Verlorenwasser near Werbig encompassed the geographical centre of East Germany. History A Slavic peoples, Slavic fort of ''Belizi'' was first mentioned in a 997 deed issued by Otto III, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Otto III in favour of the Archbishopric of Magdeburg. Whether this denotation refers to Bad Belzig or the neighbouring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amt Neuhaus
Amt Neuhaus is a municipality in the District of Lüneburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. ''Amt'' means "municipal office" in German. The original "municipal office of ''Neuhaus''" existed since at least the 17th century until 1885, consecutively as part of Saxe-Lauenburg (which ceased to exist in 1689), Electorate of Hanover (1689-1810), Kingdom of Hanover (1814-1866), and the Prussian Province of Hanover (1866-1885). In 1885, Prussia dissolved the municipality of Neuhaus, while the area remained part of the Province of Hanover. However, in 1945 the area of the former municipality was annexed to Mecklenburg and thus became a part of the Soviet Occupation Zone due to lying on the right bank of the Elbe River, and thus along with the former County of Blankenburg and the municipality of Calvörde became one of a few small areas of the Province of Hanover (since 1946 Lower Saxony) that were part of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. After German reunification in 1990, the municipalitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg () was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until their duchy was finally elevated to the Electorate of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. History Ascanian struggle for Saxony The Eastphalian count Otto of Ballenstedt (d. 1123), ancestor of the House of Ascania, had married Eilika, a daughter of Duke Magnus of Saxony from the House of Billung. As the Billung male line became extinct upon Magnus's death in 1106, Otto hoped to succeed him, however King Henry V of Germany enfeoffed Count Lothair of Supplinburg. During the following long-term dispute between Henry and Lothair, Otto was able to gain the title of a Saxon (anti-)duke, though only for a short time in 1122. Lothair was elected King of the Romans in 1125 and in 1134 he vested Otto's son Albert the Bear with the Saxon No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herzogtum Lauenburg and originally its eponymous capital was Lauenburg upon Elbe, though the capital moved to Ratzeburg in 1619. Former territories not part of today's district of Lauenburg In addition to the core territories in the modern district of Lauenburg, other territories, mostly south of the river Elbe, occasionally belonged to the duchy: * The tract of land along the southern Elbe bank (), reaching from Marschacht to the ''Amt Neuhaus'', territorially connecting the core of the duchy with these more southeastern Lauenburgian areas. This land was ceded to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814. It is now part of the Lower Saxon Harburg (district). * The Amt Neuhaus proper, then including areas on both sides of the Elbe, which was cede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-elector
The prince-electors ( pl. , , ) were the members of the Electoral College of the Holy Roman Empire, which elected the Holy Roman Emperor. Usually, half of the electors were archbishops. From the 13th century onwards, a small group of prince-electors gained the privilege of electing the King of the Romans. The king would then later be crowned Emperor by the pope. Charles V (elected in 1519) was the last emperor to be crowned (1530); his successors assumed the title "Elected Emperor of the Romans" (; ) upon their coronation as kings. The dignity of elector carried great prestige and was considered to be behind only the emperor, kings, and the highest dukes. The electors held exclusive privileges that were not shared with other princes of the Empire, and they continued to hold their original titles alongside that of elector. The heir apparent to a secular prince-elector was known as an electoral prince (). Rights and privileges Electors were rulers of ( Imperial Estates) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf, King Of The Romans
Adolf (c. 1255 – 2 July 1298) was the count of Nassau from about 1276 and the elected king of Germany from 1292 until his deposition by the prince-electors in 1298. He was never crowned by the pope, which would have secured him the Holy Roman Emperor, imperial title. He was the first physically and mentally healthy ruler of the Holy Roman Empire ever to be deposed without a papal excommunication. Adolf died shortly afterwards in the Battle of Göllheim fighting against his successor Albert I of Germany, Albert of Habsburg. He was the second in the succession of so-called count-kings of several rivalling comital houses striving after the Roman-German royal dignity. Family Adolf was the reigning count of a small German state. He was born about 1255 and was the son of Walram II, Count of Nassau and his wife, Adelheid of County of Katzenelnbogen, Katzenelnbogen. Adolf’s brother was Diether of Nassau, who was appointed Archbishopric of Trier, Archbishop of Trier in 1300. Adolf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenceslaus II Of Bohemia
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid (; ; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1305), and King of Poland (1296–1305). He was the only son of King Ottokar II of Bohemia and Ottokar's second wife Kunigunda. He was born in 1271, ten years after the marriage of his parents. Kunigunda was the daughter of Rostislav Mikhailovich, lord of Slavonia, son of a Grand Prince of Kiev, and Anna of Hungary, daughter of Béla IV of Hungary. His great-grandfather was the German king Philip of Swabia. Wenceslaus II was the grandfather of the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV. He was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty. Early years In 1276 Rudolf I, King of the Romans, placed Ottokar under the ban of the empire and besieged Vienna. This compelled Ottokar in November 1276 to sign a new treaty by which he gave up all claims to Austria and the neighbouring duchies, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |