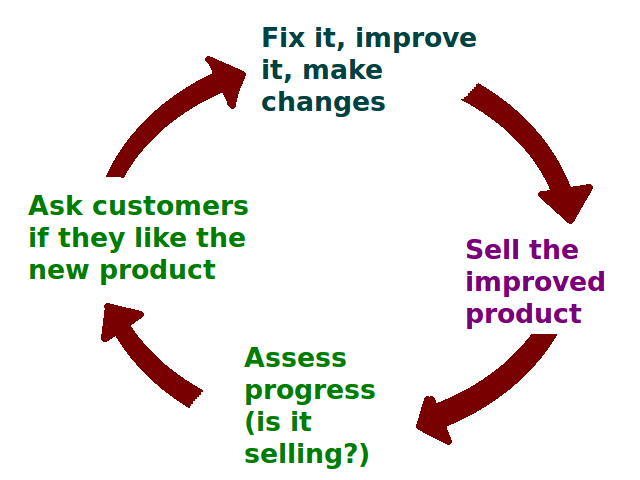
|
Agile Leadership
Rooted in agile software development and initially referred to leading self-organizing development teams (Appelo, 2011;), the concept of agile leadership is now used to more generally denote an approach to people and team leadership that is focused on boosting adaptiveness in highly dynamic and complex business environments (Hayward, 2018;Hayward, S. (2018). The agile leader: How to create an agile business in the digital age. London: Kogan Page. Koning, 2020; Solga, 2021Solga, M. (2021). The 'align - empower' model of agile leadership ('practice' whitepaper #03, cidpartners Gmb/ref>). History There are many perspectives on the origins of agile leadership, some of which align with the advent of the Agile Software Development manifesto. With the rise of Agile software development organizations discovered the need for a new leadership approach. The relentless advancements of technology have introduced an evergrowing amount of VUCA (Volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agile Software Development
Agile software development is an umbrella term for approaches to software development, developing software that reflect the values and principles agreed upon by ''The Agile Alliance'', a group of 17 software practitioners, in 2001. As documented in their ''Manifesto for Agile Software Development'' the practitioners value: * Individuals and interactions over processes and tools * Working software over comprehensive documentation * Customer collaboration over contract negotiation * Responding to change over following a plan The practitioners cite inspiration from new practices at the time including extreme programming, Scrum (software development), scrum, dynamic systems development method, adaptive software development and being sympathetic to the need for an alternative to documentation driven, heavyweight software development processes. Many software development practices emerged from the agile mindset. These agile-based practices, sometimes called ''Agile'' (with a capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity And Ambiguity
VUCA is an acronym based on the leadership theories of Warren Bennis and Burt Nanus, to describe or to reflect on the volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity of general conditions and situations. The U.S. Army War College introduced the concept of VUCA in 1987, to describe a more complex multilateral world perceived as resulting from the end of the Cold War. More frequent use and discussion of the term began from 2002. It has subsequently spread to strategic leadership in organizations, from for-profit corporations to education. Meaning The VUCA framework provides a lens through which organizations can interpret their challenges and opportunities. It emphasizes strategic foresight, insight, and the behavior of entities within organizations. Furthermore, it highlights both systemic and behavioral failures often associated with organizational missteps. V = ''Volatility'': Characterizes the rapid and unpredictable nature of change. U = ''Uncertainty'': Denotes the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership is a leadership style in which a leader's behaviors influence their followers, inspiring them to perform beyond their perceived capabilities. This style of leadership encourages individuals to achieve unexpected or remarkable results by prioritizing their collective vision over their immediate self-interests. Transformational leaders collaborate with their followers or teams to identify changes and create a vision that guides these changes through influence and inspiration. The transformation process is carried out with the active involvement of committed group members, who align their efforts with both organizational goals and their personal interests. As a result, followers' ideals, maturity, and commitment to achievement increase. This theory is a central component of the Full Range Leadership Model, which emphasizes empowering followers by granting autonomy and authority to make decisions after they are trained. The approach fosters positive changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workers' Self-management
Workers' self-management, also referred to as labor management and organizational self-management, is a form of organizational management based on self-directed work processes on the part of an organization's workforce. Self-managed economy, Self-management is a defining characteristic of socialism, with proposals for self-management having appeared many times throughout the history of the socialist movement, advocated variously by Democratic socialism, democratic, Libertarian socialism, libertarian and Market socialism, market socialists as well as anarchists and communists. There are many variations of self-management. In some variants, all the worker-members manage the enterprise directly through assemblies while in other forms workers exercise management functions indirectly through the election of specialist managers. Self-management may include worker supervision and oversight of an organization by elected bodies, the election of specialized managers, or self-directed ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer-centricity
Customer satisfaction is a term frequently used in marketing to evaluate customer experience. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified satisfaction goals".. Enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering customer loyalty are pivotal for businesses, given the significant importance of improving the balance between customer attitudes before and after the consumption process. Expectancy disconfirmation theory is the most widely accepted theoretical framework for explaining customer satisfaction. However, other frameworks, such as equity theory, attribution theory, contrast theory, assimilation theory, and various others, are also used to gain insights into customer satisfaction. However, traditionally applied satisfaction survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer-readable) format.Collins Dictionary. (n.d.). Definition of 'digitize'. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/digitize The result is the representation of an object, image, sound, document, or signal (usually an analog signal) obtained by generating a series of numbers that describe a discrete set of points or samples. The result is called ''digital representation'' or, more specifically, a ''digital image'', for the object, and ''digital form'', for the signal. In modern practice, the digitized data is in the form of binary numbers, which facilitates processing by digital computers and other operations, but digitizing simply means "the conversion of analog source material into a numerical format"; the decimal or any other number system can be used instead. Digitization is of crucial importance to data processing, storage, and transmission, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agility
Agility or nimbleness is an ability to change the body's position quickly and requires the integration of isolated movement skills using a combination of balance, coordination, speed, reflexes, strength, and endurance. More specifically, it is dependent on these six skills: * Balance – The ability to maintain equilibrium when stationary or moving (i.e., not to fall over) through the coordinated actions of our sensory functions (eyes, ears and the proprioceptive organs in our joints); * Static balance – The ability to retain the center of mass above the base of support in a stationary position; * Dynamic balance – The ability to maintain balance with body movement; an equal distribution of weight; * Speed – The ability to move all or part of the body quickly; * Strength – The ability of a muscle or muscle group to overcome a resistance; and lastly, * Coordination – The ability to control the movement of the body in co-operation with the body's sensory functions (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VUCA
VUCA is an acronym based on the leadership theories of Warren Bennis and Burt Nanus, to describe or to reflect on the volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity of general conditions and situations. The U.S. Army War College introduced the concept of VUCA in 1987, to describe a more complex multilateral world perceived as resulting from the end of the Cold War. More frequent use and discussion of the term began from 2002. It has subsequently spread to strategic leadership in organizations, from for-profit corporations to education. Meaning The VUCA framework provides a lens through which organizations can interpret their challenges and opportunities. It emphasizes strategic foresight, insight, and the behavior of entities within organizations. Furthermore, it highlights both systemic and behavioral failures often associated with organizational missteps. V = ''Volatility'': Characterizes the rapid and unpredictable nature of change. U = ''Uncertainty'': Denotes the unp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer-readable) format.Collins Dictionary. (n.d.). Definition of 'digitize'. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/digitize The result is the representation of an object, image, sound, document, or signal (usually an analog signal) obtained by generating a series of numbers that describe a discrete set of points or samples. The result is called ''digital representation'' or, more specifically, a ''digital image'', for the object, and ''digital form'', for the signal. In modern practice, the digitized data is in the form of binary numbers, which facilitates processing by digital computers and other operations, but digitizing simply means "the conversion of analog source material into a numerical format"; the decimal or any other number system can be used instead. Digitization is of crucial importance to data processing, storage, and transmission, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadership
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations. "Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the concept, sometimes contrasting Eastern world, Eastern and Western world, Western approaches to leadership, and also (within the West) North American versus European approaches. Some U.S. academic environments define leadership as "a process of social influence in which a person can enlist the aid and Peer support, support of others in the accomplishment of a common and Ethics, ethical task (project management), task". In other words, leadership is an influential Power (social and political), power-relationship in which the power of one party (the "leader") promotes movement/change in others (the "followers"). Some have challenged the more traditional managerial views of leadership (which portray leadership as something possessed or owned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior or organisational behaviour (see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is the "study of human behavior in organizational settings, the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organization itself".Moorhead, G., & Griffin, R. W. (1995). ''Organizational behavior: Managing people and organizations'' (5th edition). Boston. Houghton Mifflin, (p.4) Organizational behavioral research can be categorized in at least three ways: * individuals in organizations (micro-level) * work groups (meso-level) * how organizations behave (macro-level) Chester Barnard recognized that individuals behave differently when acting in their organizational role than when acting separately from the organization. Organizational behavior researchers study the behavior of individuals primarily in their organizational roles. One of the main goals of organizational behavior research is "to revitalize organizational theory and devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |