|
Agencies Of British India
An agency of British India was an internally autonomous or semi-autonomous unit of British India whose external affairs were governed by an agent designated by the Viceroy of India. Description The agencies varied in character from fully autonomous self-governing dependencies such as princely states, where the agent functioned mainly as a representative of the Viceroy, to tribal tracts which were integral parts of the British Empire and where the agent was completely in charge of law and order. The agent of a protected tract or princely state usually lived outside the territory in his charge, as opposed to a Resident who usually lived within his confines and was frequently the District Collector of the adjoining British district. Civil and criminal justice in agencies were usually administered through locally made laws, and the Indian Penal Code was not applicable by default in these agencies. List of agencies Political agencies were created, merged or abolished at dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency (country Subdivision)
Agencies are a type of administrative division Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...: * Agencies of British India, which grouped the autonomous princely states.https://archive.today/20140717212144/http://princelystates.com/CurrentIssue/fa-04-01d.shtml * Agencies of Pakistan, the main subdivisions of the Federally Administered Tribal Areas. References Types of administrative division {{geo-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bikaner Agency
Bikaner State was the Princely State in the north-western most part of the Rajputana province of imperial British India from 1818 to 1947. The founder of the state Rao Bika was a younger son of Rao Jodha ruler of and founder of the city of Jodhpur in Marwar. Rao Bika chose to establish his own kingdom instead of inheriting his father's. Bika defeated the Jat clans of Jangladesh which today refers to the north and north-western Rajasthan along with his uncle Rao Kandhal and his adviser Vikramji Rajpurohit and founded his own kingdom. Its capital was the city of Bikaner. The state was noted for the Bikaner style of Miniature Painting. Covering a vast area of Bikaner State was the second largest state under the Rajputana Agency after Jodhpur State with a revenue of Rs.26,00,000 in the year 1901. Heeding the 1947 call of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel to integrate the princely states into the new independent India, Bikaner's last ruler, Maharaja Sadul Singh, advised by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa Agency
Malwa Agency was an administrative section of British India's Central India Agency. The headquarters of the political agent was at Neemuch (Nimach). The other chief towns of the region were : Ratlam and Jaora. History The Malwa Agency was formed in 1895 out of princely states in the Northern Malwa region formerly under the authority of the British agent for Indore and the abolition of the Western Malwa Agency which had been a sub-agency of the Central India Agency since 1854.Sir William Wilson Hunter. ''The Imperial Gazetteer of India''. London: Trübner & co., 1885. The Dewas States ( Dewas Senior & Dewas Junior) were added to Malwa Agency in 1907. In 1925 Malwa Agency was amalgamated with Bhopawar Agency to form the Malwa and Bhopawar Agency, renamed the Malwa and Southern States Agency in 1927. The Dewas States were transferred to Bhopal Agency in 1931, and in 1934 the agency was once again renamed Malwa Agency. After Indian independence in 1947, the rulers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahi Kantha Agency
Mahi Kantha was a political agency or collection of princely states in British India, within the Gujarat Division of Bombay Presidency. In 1933, the states of the Mahi Kantha Agency, except for Danta State, Danta, were included in the Western India States Agency. The total area of the agency was ; the population in 1901 was 361,545. History The states came within the British sphere of influence after the Second Anglo-Maratha War of 1803–1805. In 1811, when the Maratha power was declining, the British Government stipulated to collect and pay over to the ruler of Baroda the yearly tribute of the Mahi Kantha states. In 1820 they finally took over the management of the whole territory, agreeing to collect and pay over the tribute free of expense to Baroda, while Baroda was pledged not to send troops into the country, or in any way to interfere with the administration. After a few disturbances in the 1830s, in 1857-58 and 1867, peace remained unbroken in the region until 1881, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras States Agency
The Madras States Agency was a colonial agency for the indirect rule of princely states associated with British India. Founded in 1923, it consisted of these five princely states (by precedence) : * Travancore, ruled by a Maharaja with a hereditary salute of 19-guns; * Cochin, ruled by a Maharaja with a hereditary salute of 17-guns; * Pudukkottai, ruled by a Raja with a hereditary salute of 11-guns; * Banganapalle, ruled by a Nawab with a hereditary salute of 9-guns; * Sandur, a non-salute state ruled by a Raja. History Prior to 1923, the five states have been subject to the government of the Madras Presidency which was represented in each state by a resident usually the District Collector of a neighbouring Madras district.Great Britain India Office. '' The Imperial Gazetteer of India,'' Oxford, Clarendon Press 1908 When in 1923, all the states were brought under the direct control of the Government of India, the individual residencies were abolished and replaced with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolaba Agency
The Deccan States Agency, also known as the Deccan States Agency and Kolhapur Residency, was a political agency of India, managing the relations of the Government of India with a collection of princely states and jagirs (feudal 'vassal' estates) in western India. History The agency was created 1933 with the merger of the Kolhapur Agency (Kolhapur Residency), Poona Agency, Bijapur Agency, Dharwar Agency and Kolaba Agency. It was composed of a number of princely states and jagirs in Western India, located in the present-day Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka, six of which were Salute states. The princely states included in the agency were under the suzerainty, but not the control, of the British authorities of the Bombay Presidency. After Indian Independence in 1947, the states all acceded to the Dominion of India, and were integrated into the Indian state of Bombay. In 1956 the Kannada language speaking southern portion of Bombay state, which included the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
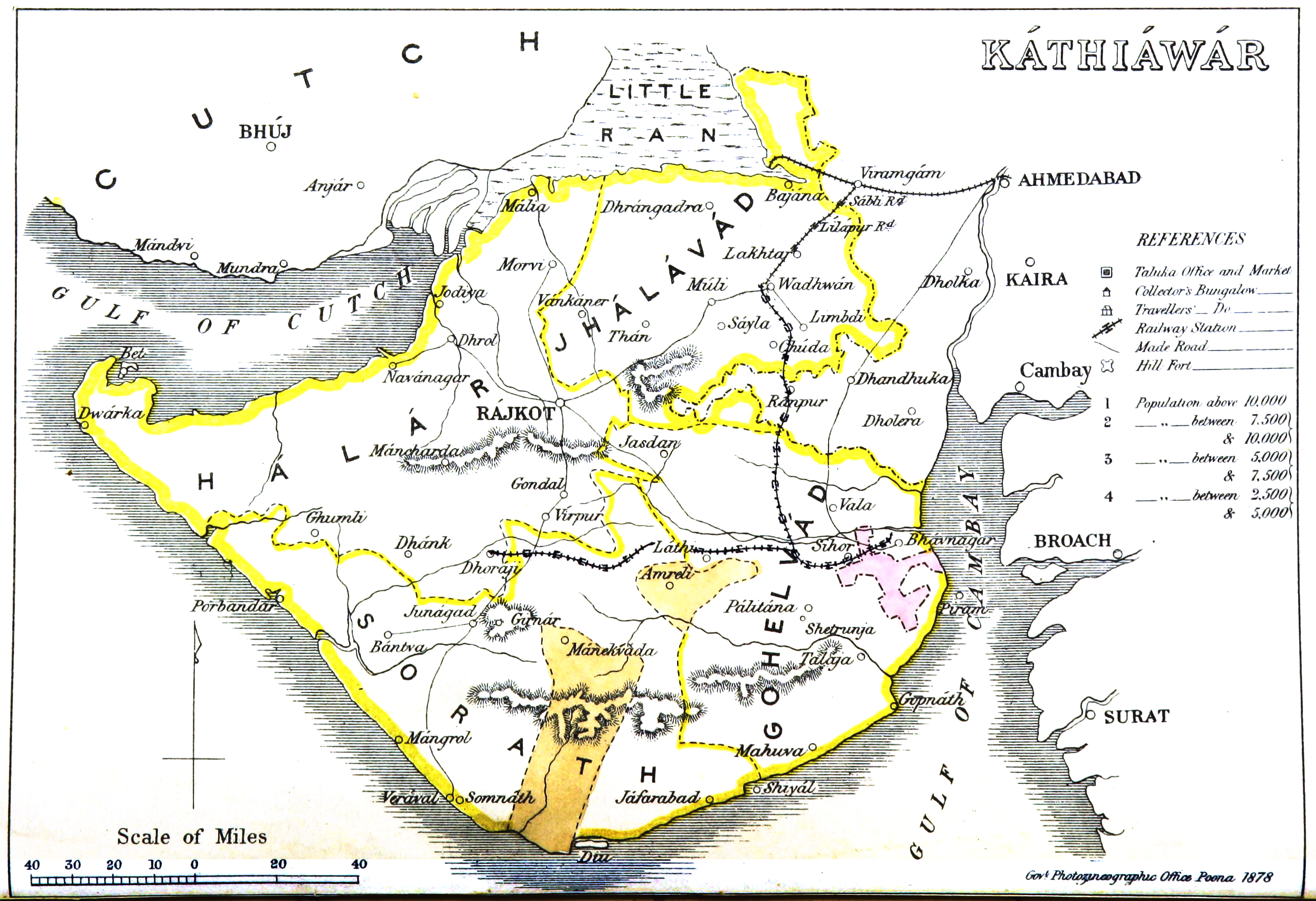
Kathiawar Agency
The Kathiawar Agency, on the Kathiawar peninsula in the western part of the Indian subcontinent, was a political unit of some 200 small princely states under the suzerainty of the Bombay Presidency of British Raj. The agency's headquarters were at Rajkot, the town where the Political Agent used to reside. He reported to the Political Department office at Bombay, Bombay Presidency. History The agency was formed in 1822, after the princely states in the area became British protectorates. The region was severely affected by the famine of 1899–1900. Between 1891 and 1901, the population of the states covered by the Agency decreased by 15 per cent, largely due to the results of the famine. On 10 October 1924, the agency was abolished and merged into the Western India States Agency, which had three subdivisions:The Indian Year Book, Volume 11 by Bennett, Coleman & Company, 1924,pp:151–152 * Eastern Kathiawar Agency (from 1926 onwards) * Western Kathiawar Agency (from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaira Agency
Khambhat state or Cambay state was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The city of Khambhat in present-day Gujarat was its capital. The state was bounded in the north by the Kaira district ( Kheda) and in the south by the Gulf of Khambhat. Cambay was the only state in the Kaira Agency of the Gujarat division of the Bombay Presidency, which merged into the Baroda and Gujarat States Agency in 1937. History Maharaja of Parmar Rajputs had established the State of Cambay. Cambay was invaded in 1730 by the penultimate Mughal governor of Gujarat, Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I, the last of the Mughal governors of Gujarat, at the time of the dismemberment of Mughal rule in India. In 1742 Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I defeated his brother-in-law Nizam Khan, governor of Khambhat, and established himself in his place. Hub of mercantile activity The traders and the merchants reached here from across the world. Cambay was known for its cotton and silk cloths. Camba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilgit Agency
The Gilgit Agency () was an agency within the British Indian Empire. It encompassed Hunza, Nagar and the governorships of Yasin, Koh Ghizer, Ishkoman, Punial and the tribal areas of Gor, Darel, Tangir, the district of Chilas and the Gilgit tehsil of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir.The primary objective of establishing the Gilgit Agency was to bolster and fortify these regions, particularly in the context of concerns about Russian encroachment in the area. The agency headquarters was based in the town of Gilgit, within the Gilgit tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir. Gilgit Agency was bounded in the west by the Chitral State, in the northwest by Afghanistan's Wakhan corridor, in the east by Chinese Turkestan, in the south by the Kashmir province, and in the southeast by the Ladakh ''wazarat'' of Jammu and Kashmir (which included Baltistan). An Officer on Special Duty was established in 1877 in the town of Gilgit till 1882 to monitor the Baroghil and Ishkoman passes. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganjam Hill Tracts Agency
Ganjam Hill Tracts Agency was an agency in the Ganjam district of the erstwhile Madras Presidency, British India. It was created by the Act XXIV of 1839 from the ' Maliahs' or Highlands, the tribal lands inhabited by the Khonds and the Soras. The territory consists of the western part of Ganjam district. It was about five-twelfths of the district and had a total area of 3,500 square miles. When the province of Orissa was created on 1 April 1936, the Ganjam Hill Tracts Agency was partitioned into two, leaving the southern part of the Paralakhemundi State in Madras and the rest of the agency in Orissa Province. Most of the erstwhile Ganjam Hill Tracts Agency lie in the Srikakulam district of Andhra Pradesh and the Gajapati and Ganjam districts of Odisha. See also *Agencies of British India An agency of British India was an internally autonomous or semi-autonomous unit of British India whose external affairs were governed by an agent designated by the Viceroy of India. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
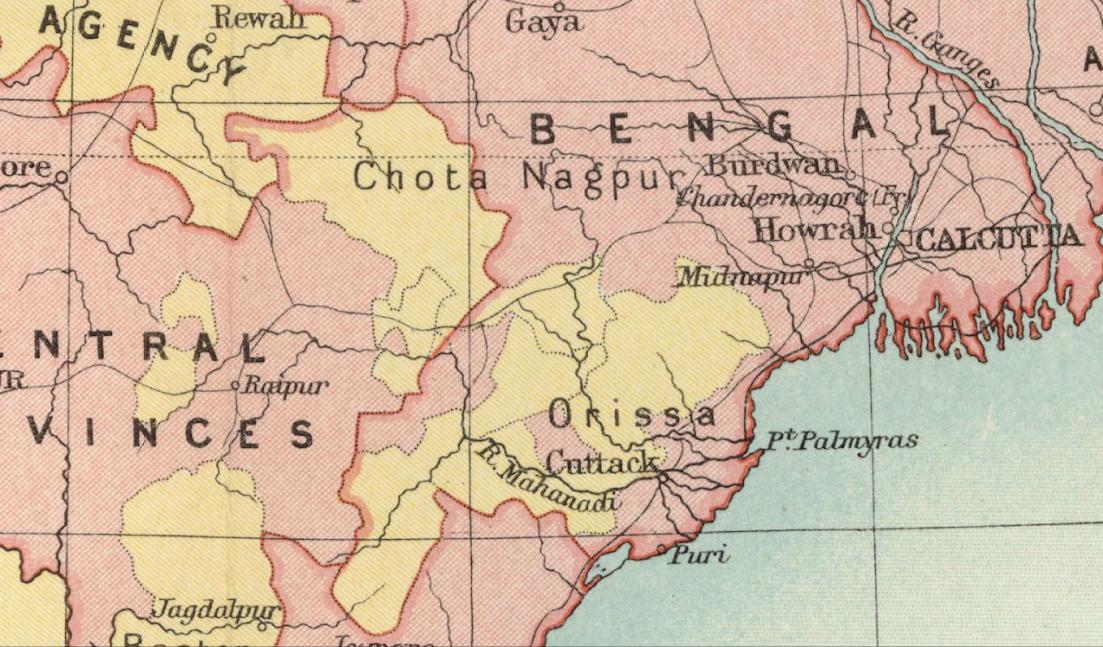
Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the British Raj. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added. History Since the 19th century the princely states and the tributary states of Orissa and Chhota Nagpur were not part of Bengal, but British relations with them were managed by its government through the Bengal Presidency. The Eastern States Agency was created on 1 April 1933. This agency dealt with 42 princely states in eastern India, located in the present-day Indian states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal and Tripura. Before the creation of the Eastern States Agency in 1933, 23 native states of the former Orissa Tributary States and Chhota Nagpur States were under the suzerainty of the British provinces of Bihar and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan States Agency
The Deccan States Agency, also known as the Deccan States Agency and Kolhapur Residency, was a political agency of India, managing the relations of the Government of India with a collection of princely states and jagirs (feudal 'vassal' estates) in western India. History The agency was created 1933 with the merger of the Kolhapur Agency (Kolhapur Residency), Poona Agency, Bijapur Agency, Dharwar Agency and Kolaba Agency. It was composed of a number of princely states and jagirs in Western India, located in the present-day Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka, six of which were Salute states. The princely states included in the agency were under the suzerainty, but not the control, of the British authorities of the Bombay Presidency. After Indian Independence in 1947, the states all acceded to the Dominion of India, and were integrated into the Indian state of Bombay. In 1956 the Kannada language speaking southern portion of Bombay state, which included the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |