|
Afghan–Maratha War
The Afghan–Maratha War was fought between the Afghan Empire under Ahmad Shah Durrani and the Maratha Confederacy and the Sikh Confederacy between 1758 and 1761. It took place in north-west India, primarily the region around Delhi and Punjab. Background In 1757, the Afghans invaded Hindustan and captured the Mughal capital of Delhi, forcing the Mughal emperor to cede territories up till the Sutlej to the Afghan Empire. Delhi was placed under the occupation of an Afghan vassal, the Kingdom of Rohilkhand. The Afghan emperor, Ahmad Shah Durrani installed his son Timur Shah Durrani in Multan and returned to Afghanistan. Battle of Delhi (1757) The Mughal emperor and the imperial grand vizier alarmed by this foreign occupation, secretly sent for his vassal, the Peshwa. The Maratha Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao sent his brother Raghunath Rao along with Shamsher Bahadur, Ramsingha, Gangadhar Tatya, Sakharam Bapu Bokil, Naroshankar Rajebahadur, Sidhojiraje Gharge-Desai-Deshmukh, Manko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of Panipat
The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761 between the Maratha Empire and the invading army of the Durrani Empire. The battle took place in and around the city of Panipat, approximately north of Delhi. The Afghan (ethnonym), Afghans were supported by three key allies in Indian subcontinent, India: Najib ad-Dawlah, Najib ud-Daula who persuaded the support of the Rohilla chiefs, elements of the declining Mughal Empire, and most prized the Oudh State under Shuja-ud-Daula. Several high ranking nobles of the Mughal Empire were able to persuade Chand kingdom, Maharaja Deep Chand of the Kingdom of Kumaon, an old Himalayas, Himalayan ally of the Mughal Empire, to support the Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan side in the battle. The Maratha army was led by Sadashivrao Bhau, who was third-highest authority of the Maratha Confederacy after the Chhatrapati and the Peshwa. The bulk of the Maratha army was stationed in the Deccan Plateau with the Peshwa. Militarily, the battle pitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim Khan Gardi
Ibrahim Khan Gardi (died 14 January 1761) was a South Indian Muslim general of the Maratha Confederacy. An expert in artillery, he initially served the Nizam of Hyderabad, before working for the Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy. As a Maratha general, he commanded a force of 10,000 men, infantry and artillery. He was captured and killed by the Durrani soldiers during the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761. Military career Ibrahim Gardi was a South Indian Muslim soldier of fortune. He was of low origin. He was an expert in artillery and was in service of Nizam of Hyderabad. He served Nizam Ali Khan, Asaf Jah II and was highly attached to him and had participated in the Battle of Palkhed against the Marathas in which the Marathas won. He commanded an army of Hyderabadi Muslims. Training in French discipline He trained to the French discipline as commandant de la garde to de Bussy, a souvenir of his professional origin or title. He was originally part of Hyderabad Nizam's army. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest India (pre-1947)
Northwest India is a loosely defined region of India. In modern-day, it consists of north-western states of the Republic of India. In historical contexts, it refers to the northwestern Indian subcontinent. In contemporary definition, it generally includes the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Uttarakhand, and often Uttar Pradesh, along with the union territories of Chandigarh, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, and the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Gujarat is occasionally included as well.A Brief History of India Emiliano Unzer "In cultural and religious terms, India was home to Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism among others, and sheltered the Zoroastrians from the Persian lands to the west, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adina Beg
Adina Beg Khan (; – 15 September 1758) was a Punjabi general, administrator, and statesman who served as the Nawab of Punjab from April 1758 until his death in September of the same year. He began his career as a patwari (accountant) and later as a sepoy after joining the Mughal army, eventually drawing the attention of the Punjabi nobles. After serving through various posts, he was appointed as the Subahdar of the entirety of Punjab by Raghunath Rao on behalf of Rajaram II and later recognised as the Nawab by Emperor Alamgir II during the power vacuum in 1758. Though illiterate, Adina Beg served as the Shiqdar of Sultanpur Pargana, Faujdar of Sirhind Sarkar, Naib Nazim and then Nazim of Bist Doab Sarkar and, later, the Subahdar of the Subahs of Lahore and Multan, though his claim in Multan was disputed. He joined hands with the Sikh leader Jassa Singh Ahluwalia and the Marathas in defeating the Afghans. Despite being short, Adina Beg's reign has often been compared wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ala Singh
Ala Singh (1691–1765) was the founder and first ruler of Patiala State, Patiala. Singh was born into the Sikhs, Sikh Phulkian dynasty, rising to power through key battles in his early life, Singh expanded his territory in Punjab, India, Punjab. As an adult, Singh was constantly engaged in battles and war. Through warfare and diplomacy, Singh began to acquire territory that would form the foundations of Patiala State. In 1763, he established the city of Patiala and founded Patiala State. Singh, at various times, had both adversarial and allied relations the Afghans, Afghan Durrani Empire. Ahmad Shah Durrani, Ahmed Shah Durrani, the List of heads of state of Afghanistan, King of the Durrani Empire, granted Singh the title of Raja and other royal powers. After being granted the title of Raja, Singh became the first Sikhs, Sikh monarch in history. Singh was praised and criticised, both by his contemporaries and historians, for his shrewd and cunning policies and strategies. Many in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charat Singh
Sardar Charat Singh (1721–1770 or 1733–1774), also romanised as Charhat Singh, was the founder of Sukerchakia Misl, father of Mahan Singh, and the grandfather of Ranjit Singh, the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire. He distinguished himself at an early age in campaigns against Ahmad Shah Abdali and along with 150 horsemen split from the Singhpuria Misl to establish the Sukerchakia Misl, a separate grouping with its distinct guerilla militia. Early life Charat Singh was born to Chaudhary Naudh Singh (died 1752) and Lali Kaur in a Sandhawalia Jat Sikh family. His grandfather was Budh Singh (1670 – 1718), a disciple of Guru Gobind Singh. In 1756 he married Desan Kaur Waraich, a daughter of Sikh ruler Amir Singh Waraich. The couple had four children, two sons, Maha Singh and Suhej Singh followed by two daughters, Bibi Raj Kaur (not to be confused with the wife of Mahan Singh) and Saher Kaur. Matrimonial alliances "Charat Singh strengthened his position by matrimo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jassa Singh Ahluwalia
Jassa Singh Ahluwalia (3 May 1718 – 23 October 1783) was a Sikh leader during the period of the Sikh Confederacy, being the supreme leader of the Dal Khalsa (Sikh Army), Dal Khalsa. He was also Misldar of the Ahluwalia (misl), Ahluwalia Misl. This period was an interlude, lasting roughly from the time of the death of Banda Bahadur in 1716 to the founding of the Sikh Empire in 1801. He founded the Kapurthala State in 1772. Early life Jassa Singh was born on 3 May 1718 CE in a Kalal Sikh family in the Ahlu village near Lahore, Punjab. Originally known as Jassa Singh Kalal, he styled himself as Ahluwalia after his ancestral village. Jassa Singh is described as a member of the Kalwar (caste), Kalal or wine distiller caste. During the period of Kharak Singh of Kapurthala, Kharak Singh (r. 1870-1877) a Bhati, Bhatti Rajput origin story was also created. According to this tradition, one of the Bhatti Rajputs Rana Har Rai had to leave the throne of Jaisalmer for refusing to mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukoji Rao Holkar
Tukoji Rao Holkar (26 June 1723 – 15 August 1797), belonging to the Holkar clan of the Maratha Empire was the feudatory ruler of Indore (r. 1795–1797). Tukoji Holkar was the adopted son of Malhar Rao Holkar, he was the second son of Shrimant Tanuji Holkar, a nephew of Malhar Rao Holkar. Thus he was also the grand-nephew of Malhar Rao Holkar. He married two wives. He had four sons Kashi Rao, Malhar Rao Holkar II, Yashwant Rao, and Vithoji Rao. Life and career After the demise of Ahilyabai Holkar, Tukoji Rao was the only suitable person who could preserve the splendour of Holkar kingdom intact. He became the fourth ruler of the kingdom for a short period from 1795 to 1797 and protected the province as a courageous soldier. It was a time of crisis when Tukoji Rao received the responsibility of the Holkar Kingdom. Khanderao, husband of Ahilyabai had already lost his life in Kumbher war of 1754. Tukoji Rao Holkar was the most trustworthy commander-in-chief of Shreemant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
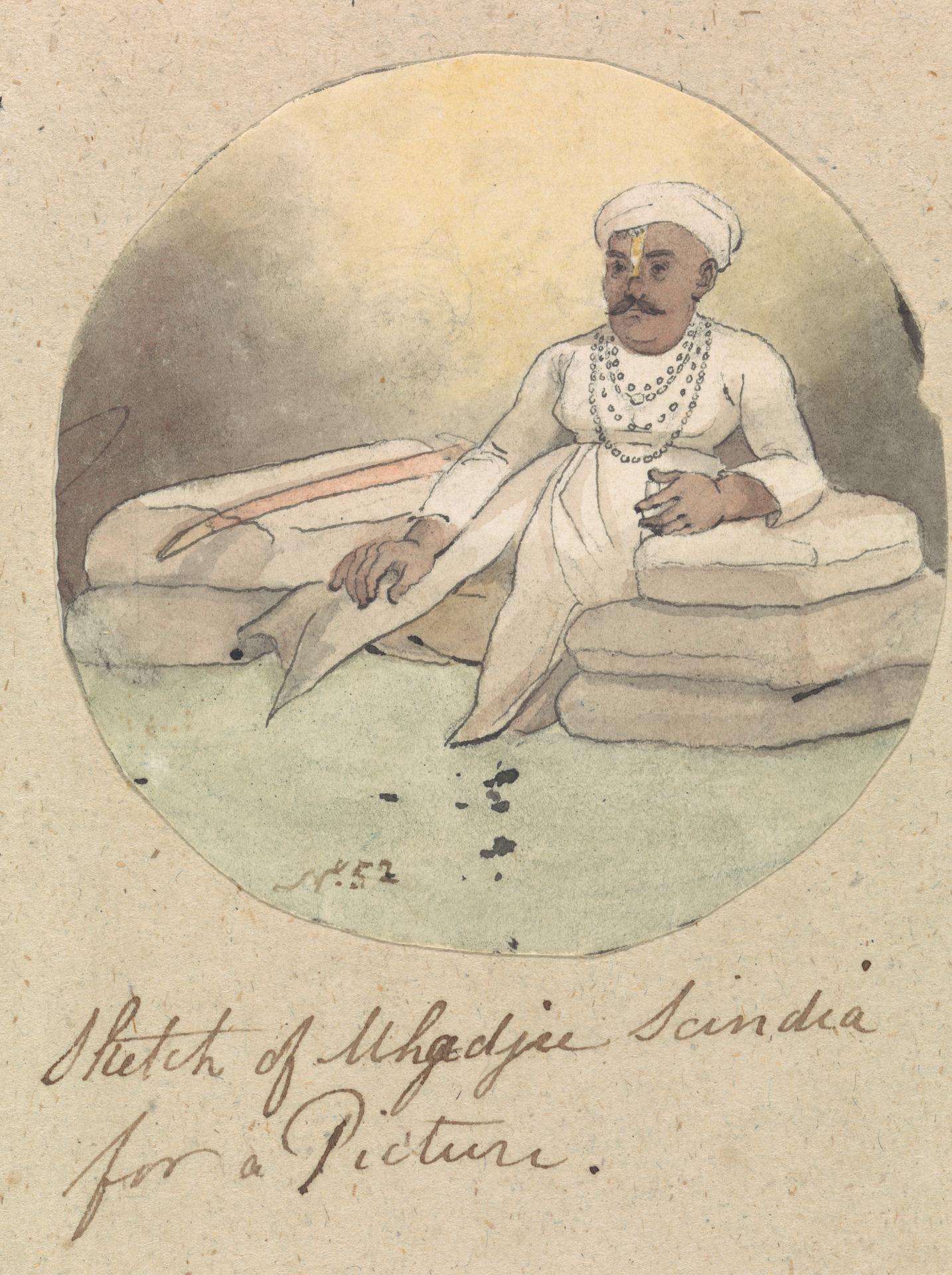
Dattaji Scindia
Dattaji Rao Shinde, also known as Dattaji Rao Scindia, (c. 1723 – 10 January 1760) was the second son of Ranoji Rao Shinde and Maina Bai, alias Nimba Bai. His elder brother was Jayappaji Rao Shinde and his younger brother was Jyotiba. Early life Dattajirao was the elder half-brother of Mahadaji Shinde, who later became the confederacy head of Gwalior princely state, famous fabricator of the Great Maratha Resurrection of 1771, and also the regent for his nephew Jankoji Rao Shinde, from 1755 until Jankoji's death in 1761. Battle with Afghans and death Balaji Baji Rao, also called Nanasaheb Peshwa, gave Dattaji Rao command of the subjugated Lahore and Multan provinces, with an army of 18,000 cavalry to stop the Afghan invasion led by Ahmed Shah Durrani, also called Ahmad Shah Abdali. The Marathas had captured the forts of Attock and Peshawar in 1757–1758, and wanted to expand their rule up to Kabul, Kandahar and the Afghanistan-Iran border. After many centuries since 1020 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malhar Rao Holkar
Malhar Rao Holkar (16 March 1693 – 20 May 1766) was a noble subedar of the Maratha Empire, in present-day India. He was one of the early officers along with Ranoji Scindia, appointed by Peshwa Bajirao I to help spread the Maratha rule to northern states and was given the estate of Indore to rule by the King chief, during the reign of the Maratha emperor Shahu I. He was founder of the Holkar dynasty that ruled Malwa. Early life Malharrao Holkar was born on 16 March 1693 to Khandu Ji Holkar in a Dhanagar khutekar-Dhangar family in Hol village near Jejuri in Pune district of Maharashtra. His father died in 1696, when he was only three years of age. Malhar Rao grew up in Taloda (Nandurbar District, Maharashtra) in the castle of his maternal uncle, Sardar Bhojrajrao Bargal. His maternal uncle held a cavalry under Maratha noble Sardar Kadam Bande. Bargal asked Malhar Rao to join his cavalry and soon after that he was placed in-charge of cavalry detachment. He married Gautama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahadji Scindia
Mahadaji Shinde (23 December 1730 – 13 February 1794), later known as Mahadji Scindia or Madhava Rao Scindia, was a Maratha statesman and general who served as the Maharaja of Gwalior from 1768 to 1794. He was the fifth and the youngest son of Ranoji Rao Scindia, the founder of the Scindia dynasty. He is reputed for having restored the Maratha rule over North India and for modernizing his army. Mahadji was instrumental in resurrecting Maratha power in North India after the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761, and he rose to become a trusted lieutenant of the Peshwa, leader of the Maratha Confederacy. Along with Madhavrao I and Nana Fadnavis, he was one of the three pillars of Maratha Resurrection. He modernized his army under adventurers like Benoît de Boigne, which allowed Maratha dominance of North India. During his reign, Gwalior became the leading state in the Maratha Confederacy and one of the foremost military powers in India. After accompanying Shah Alam II to Delhi i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakharam Bapu Bokil
Sakharam Bapu Bokil (also known as ''Sakharam Bapu'', ''Sakharam Hari Bokil'' or ''Sakharam Bhau''), born Sakharam Bhagwant Bokil, was an influential minister, diplomat and statesman of the Maratha Empire during the Peshwa administration in Pune, India. Before joining the Peshwa administration at Pune, Sakharam was the Kulkarni of Hivare. In Maharashtra and Hyderabad, there were known to be three and a half great men - or wise diplomats. The three and a half wise men were popularly known as Devā, Sakhyā, Vitthe and Nānā. Devā stood for Devāśipant, Sakhyā for Sakhārām Băpu Bokil, Vitthal for Vithal Sundar at the Court of the Nizām and Nānā for the famous Nana Phadnis. Vitthal Sundar was with the Nizam and died in the famous battle of Rakshasbhuvan on 10 August 1763. Devajipant Chorghade of Narkhed and the other two and half wise men were in Poona and Nagpur. Sakharam Bapu Bokil was one full wise man while Nana Phadnis was a half wise man. He was the hereditary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |