 |
Aether Drag Hypothesis
In the 19th century, the theory of the luminiferous aether as the hypothetical Transmission medium, medium for the propagation of light waves was widely discussed. The aether hypothesis arose because physicists of that era could not conceive of light waves propagating without a physical medium in which to do so. When experiments failed to detect the hypothesized luminiferous aether, physicists conceived explanations for the experiments' failure which preserved the hypothetical aether's existence. The aether drag hypothesis proposed that the luminiferous aether is dragged by or entrained within moving matter. According to one version of this hypothesis, no relative motion exists between Earth and aether. According to another version, the Earth does move relative to the aether and the measured speed of light should depend on the speed of this motion ("aether wind"), which should be measurable by instruments at rest on Earth's surface. In 1818, Augustin-Jean Fresnel proposed that the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
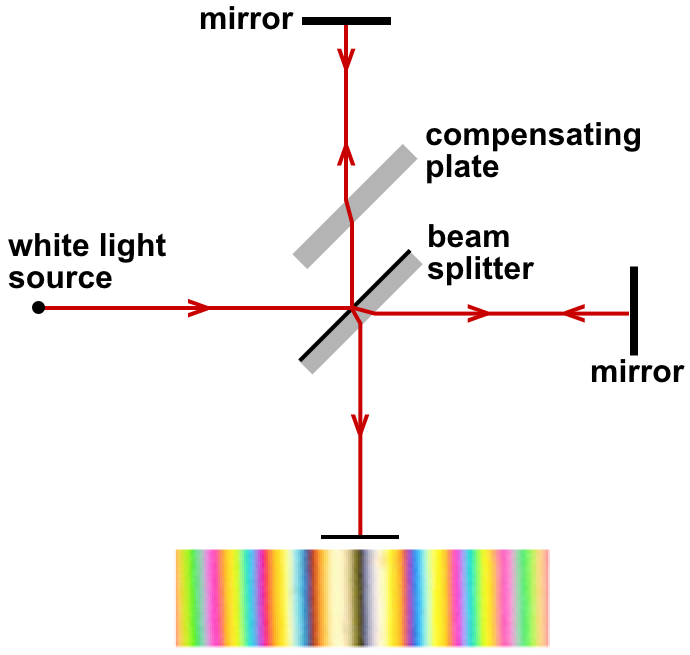 |
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether (''luminiferous'' meaning 'light-bearing') was the postulated Transmission medium, medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum (space completely filled with matter) of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 19th century, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Sir Oliver Lodge's Ether Machine
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as part of "", with the equivalent "My Lord" in English. Traditionally, as governed by law and custom, Sir is used for men who are knights and belong to certain orders of chivalry, as well as later applied to baronets and other offices. As the female equivalent for knighthood is damehood, the ''suo jure'' female equivalent term is typically Dame. The wife of a knight or baronet tends to be addressed as Lady, although a few exceptions and interchanges of these uses exist. Additionally, since the late modern period, Sir has been used as a respectful way to address a man of superior social status or military rank. Equivalent terms of address for women are Madam (shortened to Ma'am), in addition to social honorifics such as Mrs, Ms, or Miss. Etym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Galilean Transformation
In physics, a Galilean transformation is used to transform between the coordinates of two reference frames which differ only by constant relative motion within the constructs of Newtonian physics. These transformations together with spatial rotations and translations in space and time form the inhomogeneous Galilean group (assumed throughout below). Without the translations in space and time the group is the homogeneous Galilean group. The Galilean group is the group of motions of Galilean relativity acting on the four dimensions of space and time, forming the Galilean geometry. This is the passive transformation point of view. In special relativity the homogeneous and inhomogeneous Galilean transformations are, respectively, replaced by the Lorentz transformations and Poincaré transformations; conversely, the group contraction in the classical limit of Poincaré transformations yields Galilean transformations. The equations below are only physically valid in a Newtonian fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Principle Of Relativity
In physics, the principle of relativity is the requirement that the equations describing the laws of physics have the same form in all admissible frames of reference. For example, in the framework of special relativity, the Maxwell equations have the same form in all inertial frames of reference. In the framework of general relativity, the Maxwell equations or the Einstein field equations have the same form in arbitrary frames of reference. Several principles of relativity have been successfully applied throughout science, whether implicitly (as in Newtonian mechanics) or explicitly (as in Albert Einstein's special relativity and general relativity). Basic concepts Certain principles of relativity have been widely assumed in most scientific disciplines. One of the most widespread is the belief that any law of nature should be the same at all times; and scientific investigations generally assume that laws of nature are the same regardless of the person measuring them. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. Biography Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born in 1857 in Hamburg, then a sovereign state of the German Confederation, into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic family. His father was Gustav Ferdinand Hertz. His mother was Anna Elisabeth Pfefferkorn. While studying at the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums in Hamburg, Hertz showed an aptitude for sciences as well as languages, learning Arabic. He studied sciences and engineering in the German cities of Dresden, Munich and Berlin, where he studied under Gustav R. Kirchhoff and Hermann von Helmholtz. In 1880, Hertz obtained his PhD from the University of Berlin, and for the next three years remained for post-doctoral study under Helmholtz, serving as his assistant. In 1883, Hertz took a post as a lecturer in theore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Common-path Interferometer
A common-path interferometer is a class of interferometers in which the reference beam and sample beams travel along the same path. Examples include the Sagnac interferometer, Zernike phase-contrast interferometer, and the point diffraction interferometer. A common-path interferometer is generally more robust to environmental vibrations than a "double-path interferometer" such as the Michelson interferometer or the Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Although travelling along the same path, the reference and sample beams may travel along opposite directions, or they may travel along the same direction but with the same or different polarization. Double-path interferometers are highly sensitive to phase shifts or length changes between the reference and sample arms. Because of this, double-path interferometers have found wide use in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive-index changes, surface irregularities and the like. There are applications, however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Gustaf Wilhelm Hammar
Gustaf Wilhelm Hammar (Gustav Vilhelm Hammar) (June 22, 1893 – August 19, 1954) was a Swedish-born American experimental physicist. He was the eldest of six children of Anders Vilhelm Hammar and Elin Christina Hammar (née Olsson). He emigrated to the United States in 1913, attended Bethel University in St. Paul, Minnesota, and by 1920 was married and living with his wife, Louise (with whom he was ultimately to have four children), in King County, Washington. He obtained his M.S. degree at the University of Idaho in 1924 and a Ph.D. from the California Institute of Technology in 1927. His Ph.D. dissertation topic was titled "Magnetic Susceptibilities of Some Common Gases." He returned to the University of Idaho in 1926 to teach, and became the head of the physics department in 1930, a position that he held for sixteen years. He led a productive materials science laboratory and was mindful of practical applications of his research—for example, as an extension of his re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hammar Experiment
The Hammar experiment was an experiment designed and conducted by Gustaf Wilhelm Hammar (1935) to test the aether drag hypothesis. Its negative result refuted some specific aether drag models, and confirmed special relativity. Overview Experiments such as the Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887 (and later other experiments such as the Trouton–Noble experiment in 1903 or the Trouton–Rankine experiment in 1908), presented evidence against the theory of a medium for light propagation known as the luminiferous aether; a theory that had been an established part of science for nearly one hundred years at the time. These results cast doubts on what was then a very central assumption of modern science, and later led to the development of special relativity. In an attempt to explain the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment in the context of the assumed medium, aether, many new hypotheses were examined. One of the proposals was that instead of passing through a static and un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Trouton–Noble Experiment
The Trouton–Noble experiment was an attempt to detect motion of the Earth through the luminiferous aether, and was conducted in 1901–1903 by Frederick Thomas Trouton and H. R. Noble. It was based on a suggestion by George FitzGerald that a charged parallel-plate capacitor moving through the aether should orient itself perpendicular to the motion. Like the earlier Michelson–Morley experiment, Trouton and Noble obtained a null result: no motion relative to the aether could be detected.F. T. Trouton and H. R. Noble, "The mechanical forces acting on a charged electric condenser moving through space," ''Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. A'' 202, 165–181 (1903). This null result was reproduced, with increasing sensitivity, by Rudolf Tomaschek (1925, 1926), Chase (1926, 1927) and Hayden in 1994. Such experimental results are now seen, consistent with special relativity, to reflect the validity of the principle of relativity and the absence of any absolute rest frame (or aether). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Stellar Aberration
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon where celestial objects exhibit an apparent motion about their true positions based on the velocity of the observer: It causes objects to appear to be displaced towards the observer's direction of motion. The change in angle is of the order of where is the speed of light and the velocity of the observer. In the case of "stellar" or "annual" aberration, the apparent position of a star to an observer on Earth varies periodically over the course of a year as the Earth's velocity changes as it revolves around the Sun, by a maximum angle of approximately 20 arcseconds in right ascension or declination. The term ''aberration'' has historically been used to refer to a number of related phenomena concerning the propagation of light in moving bodies. Aberration is distinct from parallax, which is a change in the apparent position of a relatively ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether (''luminiferous'' meaning 'light-bearing') was the postulated Transmission medium, medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum (space completely filled with matter) of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 19th century, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |