|
Adiabatic Accessibility
In thermodynamics, adiabatic accessibility determines if one equilibrium state of a system can transition to another solely through an adiabatic process, meaning no heat is exchanged with the environment. The concept was coined by Constantin Carathéodory in 1909 ("adiabatische Erreichbarkeit") and taken up 90 years later by Elliott Lieb and J. Yngvason in their axiomatic approach to the foundations of thermodynamics. It was also used by R. Giles in his 1964 monograph.Robin Giles: "Mathematical Foundations of Thermodynamics", Pergamon, Oxford 1964 Adiabatic accessibility plays a crucial role in defining fundamental concepts such as entropy and understanding the limitations on state transformations in thermodynamic systems. Description A system in a state ''Y'' is said to be adiabatically accessible from a state ''X'' if ''X'' can be transformed into ''Y'' without the system suffering transfer of energy as heat or transfer of matter. ''X'' may, however, be transformed to ''Y'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics, which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantity, physical quantities but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to various topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering, and mechanical engineering, as well as other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the thermodynamic efficiency, efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
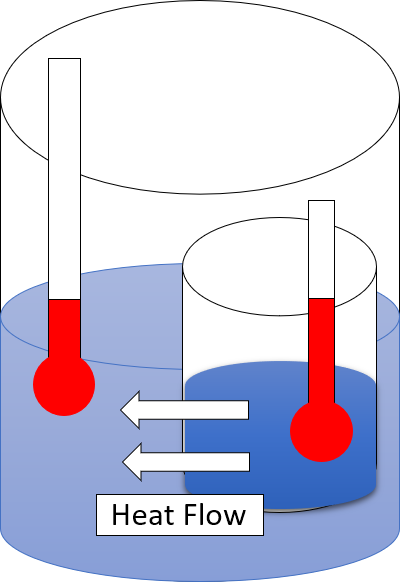
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium is a notion of thermodynamics with axiomatic status referring to an internal state of a single thermodynamic system, or a relation between several thermodynamic systems connected by more or less permeable or impermeable walls. In thermodynamic equilibrium, there are no net macroscopic flows of mass nor of energy within a system or between systems. In a system that is in its own state of internal thermodynamic equilibrium, not only is there an absence of macroscopic change, but there is an “absence of any ''tendency'' toward change on a macroscopic scale.” Systems in mutual thermodynamic equilibrium are simultaneously in mutual thermal, mechanical, chemical, and radiative equilibria. Systems can be in one kind of mutual equilibrium, while not in others. In thermodynamic equilibrium, all kinds of equilibrium hold at once and indefinitely, unless disturbed by a thermodynamic operation. In a macroscopic equilibrium, perfectly or almost perfectly ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic System
A thermodynamic system is a body of matter and/or radiation separate from its surroundings that can be studied using the laws of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic systems can be passive and active according to internal processes. According to internal processes, passive systems and active systems are distinguished: passive, in which there is a redistribution of available energy, active, in which one type of energy is converted into another. Depending on its interaction with the environment, a thermodynamic system may be an isolated system, a Closed system#In thermodynamics, closed system, or an Open system (systems theory), open system. An isolated system does not exchange matter or energy with its surroundings. A closed system may exchange heat, experience forces, and exert forces, but does not exchange matter. An open system can interact with its surroundings by exchanging both matter and energy. The physical condition of a thermodynamic system at a given time is described by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Process
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings only as Work (thermodynamics), work and/or mass flow.. A translation may be founhere. Also a mostly reliabltranslation is to be foundin As a key concept in thermodynamics, the adiabatic process supports the theory that explains the first law of thermodynamics. The opposite term to "adiabatic" is ''diabatic''. Some chemical and physical processes occur too rapidly for energy to enter or leave the system as heat, allowing a convenient "adiabatic approximation".Bailyn, M. (1994), pp. 52–53. For example, the adiabatic flame temperature uses this approximation to calculate the upper limit of fire, flame temperature by assuming combustion loses no heat to its surroundings. In meteorology, adiabatic expansion an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantin Carathéodory
Constantin Carathéodory (; 13 September 1873 – 2 February 1950) was a Greeks, Greek mathematician who spent most of his professional career in Germany. He made significant contributions to real and complex analysis, the calculus of variations, and measure theory. He also created an axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics. Carathéodory is considered one of the greatest mathematicians of his era and the most renowned Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician since Ancient history, antiquity. Origins Constantin Carathéodory was born in 1873 in Berlin to Greeks, Greek parents and grew up in Brussels. His father , a lawyer, served as the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman ambassador to Belgium, St. Petersburg and Berlin. His mother, Despina, née Petrokokkinos, was from the island of Chios. The Carathéodory family, originally from Bosna, Edirne, Bosna, was well established and respected in Istanbul, Constantinople, and its members held many important governmental positions. His grandfather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematische Annalen
''Mathematische Annalen'' (abbreviated as ''Math. Ann.'' or, formerly, ''Math. Annal.'') is a German mathematical research journal founded in 1868 by Alfred Clebsch and Carl Neumann. Subsequent managing editors were Felix Klein, David Hilbert, Otto Blumenthal, Erich Hecke, Heinrich Behnke, Hans Grauert, Heinz Bauer, Herbert Amann, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, Wolfgang Lück, Nigel Hitchin, and Thomas Schick. Currently, the managing editor of Mathematische Annalen is Yoshikazu Giga (University of Tokyo). Volumes 1–80 (1869–1919) were published by Teubner. Since 1920 (vol. 81), the journal has been published by Springer. In the late 1920s, under the editorship of Hilbert, the journal became embroiled in controversy over the participation of L. E. J. Brouwer on its editorial board, a spillover from the foundational Brouwer–Hilbert controversy. Between 1945 and 1947, the journal briefly ceased publication. References External links''Mathematische Annalen''homepage a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakob Yngvason
Jakob Yngvason (born 23 November 1945) is an Icelandic/Austrian physicist and emeritus professor of mathematical physics at the University of Vienna. He has made important contributions to local quantum field theory, thermodynamics, and the quantum theory of many-body systems, in particular cold atomic gases and Bose–Einstein condensation. He is co-author, together with Elliott H. Lieb, Jan Philip Solovej and Robert Seiringer, of a monograph on Bose gases. Career After graduating from high school in 1964 in Reykjavík, Yngvason studied physics at Göttingen University, obtaining his Diploma in physics in 1969, and a doctorate (''dr.rer.nat'') in 1973. His thesis advisor was Hans-Jürgen Borchers. Yngvason was assistant professor at the University of Göttingen, 1973–1978, 1978–1985 research scientist at the Science Institute of the University of Iceland, and during 1985–1996 professor of theoretical physics at the University of Iceland. In 1996, he became professor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. Entropy is central to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an isolated system left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease with time. As a result, isolated systems evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest. A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics is that certain processes are irreversible. The thermodynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasistatic Processes
In thermodynamics, a quasi-static process, also known as a quasi-equilibrium process (from Latin ''quasi'', meaning ‘as if’), is a thermodynamic process that happens slowly enough for the system to remain in internal physical (but not necessarily chemical) thermodynamic equilibrium. An example of this is quasi-static expansion of a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen gas, where the volume of the system changes so slowly that the pressure remains uniform throughout the system at each instant of time during the process. Such an idealized process is a succession of physical equilibrium states, characterized by infinite slowness.Rajput, R.K. (2010). ''A Textbook of Engineering Thermodynamics'', 4th edition, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd, New Delhi, pages 21, 45, 58. Only in a quasi-static thermodynamic process can we exactly define intensive quantities (such as pressure, temperature, specific volume, specific entropy) of the system at any instant during the whole process; otherwise, sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder regions of matter (or 'downhill' in terms of the temperature gradient). Another statement is: "Not all heat can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. For example, the first law allows the process of a cup falling off a table and breaking on the floor, as well as allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrium Chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is concerned with systems in '' chemical equilibrium''. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid–base, host–guest, metal–complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria. Thermodynamic equilibrium A chemical system is said to be in equilibrium when the quantities of the chemical entities involved do not and ''cannot'' change in time without the application of an external influence. In this sense a system in chemical equilibrium is in a stable state. The system at chemical equilibrium will be at a constant temperature, pressure or volume and a composition. It will be insulated from exchange of heat with the surroundings, that is, it is a closed system. A change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |