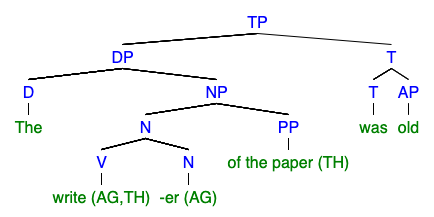
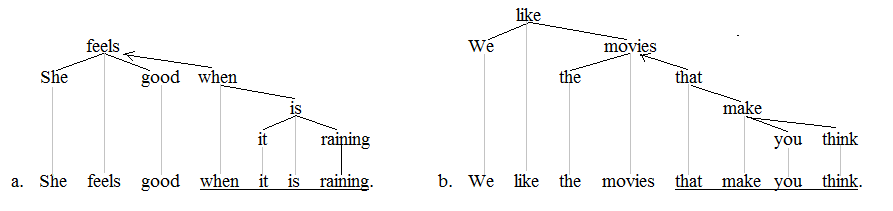
|
Adi Language (Galo)
The Galo language is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language of the Tani languages, Tani group, spoken by the Galo people. Its precise position within Tani is not yet certain, primarily because of its central location in the Tani area and the strong effects of intra-Tani contacts on the development of Tani languages. It is an endangered language according to the general definitions, but prospects for its survival are better than many similarly-placed languages in the world. Dialects The major Galo dialects are Pugo, spoken around the district capital Along, Arunachal Pradesh, Aalo; Lare, spoken to the south of Aalo; and a dialect that can be called Kargu kardi, pertaining to the dialect spoken in the northwest near the Tagin people, Tagin area. There may be additional Galo dialects further north, which remains largely unresearched. There are numerous subdialects that often correspond to regional or clan groupings. Neighbouring languages include Assamese language, Assames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and largest town. It borders the Indian states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares Borders of India, international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region in the north at the McMahon Line. Arunachal Pradesh is claimed in its entirety by China as South Tibet as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region; China Sino-Indian War, occupied some regions of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962 but later withdrew its forces. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,383,727 and an area of . With only 17 inhabitants per square kilometre, it is the least densely populated state of India. It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishi Language
Nyishi (also known as Nishi, Nisi, Nishang, Nissi, Nyising, Leil, Aya, Akang, Bangni-Bangru, Solung) is a Sino-Tibetan language of the Tani branch spoken in Papum Pare, Lower Subansiri, Kurung Kumey, Kra Daadi, East Kameng, Pakke Kesang, Kamle districts of Arunachal Pradesh and Darrang District of Assam in India. According to the 2011 census of India, the population of the Nishi speakers is approximately 280,000. Though there are plenty of variations across regions, the dialects of Nishi, such as Akang, Aya, Nyishi (raga), Tagin are easily mutually intelligible, with the exception of the rather small in population Bangni-Bangru and Solung Dialects being very different from the former. 'Nisi' is sometimes used as a cover term for western Tani languages. Nishi is a subject–object–verb language. Origin The main origin of this language has been pointed out by George Abraham Grierson as ‘Dafla’. He included different varieties under a common name which is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect (linguistics)
In linguistics, aspect is a grammatical category that expresses how a verbal action, event, or state, extends over time. For instance, perfective aspect is used in referring to an event conceived as bounded and unitary, without reference to any flow of time during the event ("I helped him"). Imperfective aspect is used for situations conceived as existing continuously or habitually as time flows ("I was helping him"; "I used to help people"). Further distinctions can be made, for example, to distinguish states and ongoing actions ( continuous and progressive aspects) from repetitive actions ( habitual aspect). Certain aspectual distinctions express a relation between the time of the event and the time of reference. This is the case with the perfect aspect, which indicates that an event occurred prior to but has continuing relevance at the time of reference: "I have eaten"; "I had eaten"; "I will have eaten". Different languages make different grammatical aspectual disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier (linguistics)
A classifier (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a word or affix that accompanies nouns and can be considered to "classify" a noun depending on some characteristics (e.g. humanness, animacy, sex, shape, social status) of its referent. Classifiers in this sense are specifically called noun classifiers because some languages in Papuan languages, Papua as well as the Indigenous languages of the Americas, Americas have verbal classifiers which categorize the referent of its Argument (linguistics), argument. In languages that have classifiers, they are often used when the noun is being counted, that is, when it appears with a numeral (linguistics), numeral. In such languages, a phrase such as "three people" is often required to be expressed as "three ''X'' (of) people", where ''X'' is a classifier appropriate to the noun for "people"; compare to "three blades of grass". Classifiers that appear next to a Numeral (linguistics), numeral or a Quantifier (linguistics), qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relator Noun
Relational nouns, or relator nouns, are a word class in many languages. They are characterized as functioning syntactically as nouns although they convey the meaning for which other languages use adpositions (prepositions and postpositions). In Mesoamerican languages, the use of relational nouns constitutes an areal feature of the Mesoamerican linguistic area, including the Mayan languages, Mixe–Zoquean languages, and Oto-Manguean languages. Relational nouns are also widespread in Southeast Asia (e.g. Vietnamese, Thai), East Asia (e.g. Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, Lhasa Tibetan), Central Asia (e.g. the Turkic languages), Armenian, the Munda languages of South Asia (e.g. Sora), and in the Micronesian languages. A relational noun is grammatically speaking a simple noun, but because its meaning describes a spatial or temporal relation, rather than a "thing", it describes location, movement, and other relations, just like prepositions in the languages that have them. When used, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complement) and postpositions (which follow their complement). An adposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in, under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as "in England", "under the table", "of Jane" – although there are a few exceptions including ''ago'' and ''notwithstanding'', as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead (like Turkic languages) or have both types (like Finnish). The phrase formed by an adposition together with its complement is called an adpositional phrase (or prepositional phr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation, also known as nouning, is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head (linguistics), head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivation (linguistics), derivational affix (e.g., the noun "legalization" from the verb "legalize"), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion (word formation), conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation. English language, English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural language, natural part of language, but some insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause Chaining
In language, a clause is a constituent or phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any objects and other modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated ( ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. Some dependent clauses are non-finite, i.e. they do not contain any element/verb marking a specific tense. Matrix Clauses A clause that contains one or more dependent or su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Verb
A finite verb is a verb that contextually complements a subject, which can be either explicit (like in the English indicative) or implicit (like in null subject languages or the English imperative). A finite transitive verb or a finite intransitive verb can function as the root of an independent clause. Finite verbs are distinguished from non-finite verbs such as infinitives, participles, gerunds etc. History The term ''finite'' is derived from (past participle of "to put an end to, bound, limit") as the form "to which number and person appertain". Verbs were originally said to be ''finite'' if their form limited the possible person and number of the subject. More recently, finite verbs have been construed as any verb that independently functions as a predicate verb or one that marks a verb phrase in a predicate. Under the first of those constructions, finite verbs often denote grammatical characteristics such as gender, person, number, tense, aspect, mood, modali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Tone
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with ''phoneme''. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas, and the Pacific. Tonal languages are different from pitch-accent languages in that tonal languages can have each syllable with an independent tone whilst pitch-accent languages may have one syllable in a word or morpheme that is more prominent than the others. Mechanics Most languages use pitch as intonation to convey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutinating
An agglutinative language is a type of language that primarily forms words by stringing together morphemes (word parts)—each typically representing a single grammatical meaning—without significant modification to their forms ( agglutinations). In such languages, affixes ( prefixes, suffixes, infixes, or circumfixes) are added to a root word in a linear and systematic way, creating complex words that encode detailed grammatical information. This structure allows for a high degree of transparency, as the boundaries between morphemes are usually clear and their meanings consistent. Agglutinative languages are a subset of synthetic languages. Within this category, they are distinguished from fusional languages, where morphemes often blend or change form to express multiple grammatical functions, and from polysynthetic languages, which can combine numerous morphemes into single words with complex meanings. Examples of agglutinative languages include Turkish, Finnish, Japanese, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Language
A synthetic language is a language that is characterized by denoting syntactic relationships between words via inflection or agglutination. Synthetic languages are statistically characterized by a higher morpheme-to-word ratio relative to analytic languages. Fusional languages favor inflection and agglutinative languages favor agglutination. Further divisions include polysynthetic languages (most belonging to an agglutinative-polysynthetic subtype, although Navajo and other Athabaskan languages are often classified as belonging to a fusional subtype) and oligosynthetic languages (only found in constructed languages). In contrast, rule-wise, the analytic languages rely more on auxiliary verbs and word order to denote syntactic relationship between words. Adding morphemes to a root word is used in inflection to convey a grammatical property of the word, such as denoting a subject or an object. Combining two or more morphemes into one word is used in agglutinating l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |