|
Adenovirus Genome
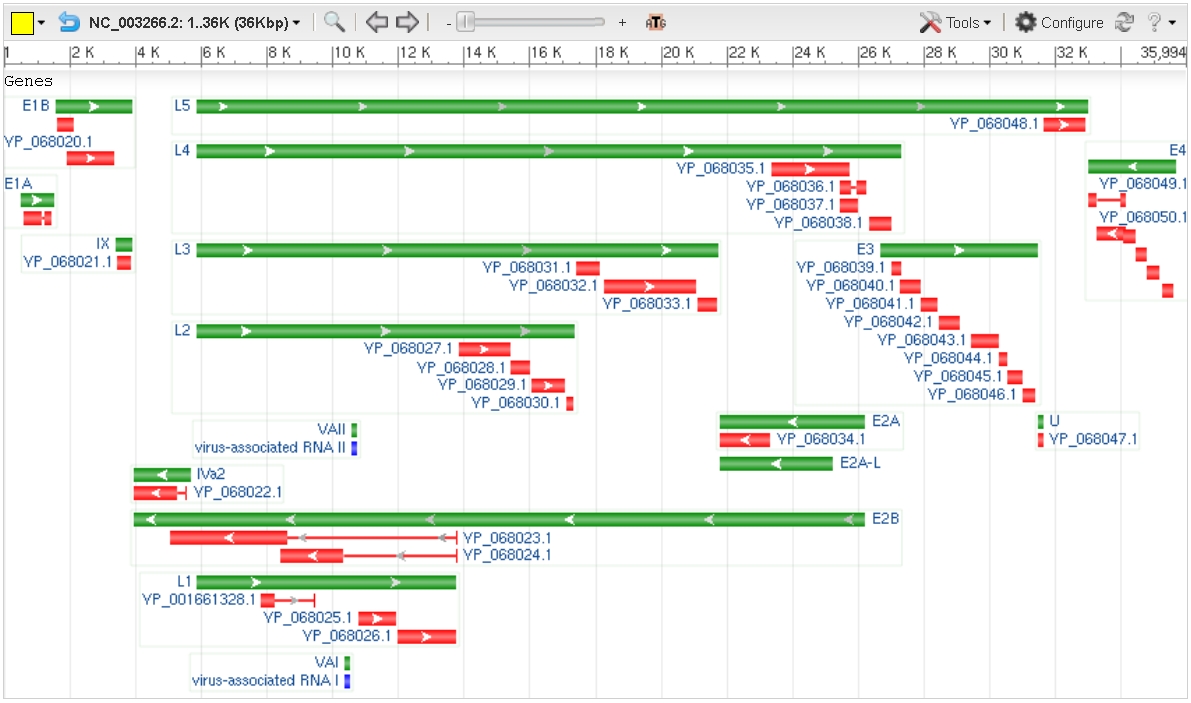
Adenoviridae, Adenovirus genomes are linear, non-segmented double-stranded (ds) DNA molecules that are typically 26-46 Kbp long, containing 23-46 protein biosynthesis, protein-coding genes. The example used for the following description is Human adenovirus E, a mastadenovirus with a 36 Kbp genome containing 38 protein-coding genes. While the precise number and identity of genes varies among adenoviruses, the basic principles of genome organization and the functions of most of the genes described in this article are shared among all adenoviruses. Transcription units The 38 genes in the Human adenovirus E genome are organized in 17 transcription (genetics), transcription units, each containing 1-8 coding sequences. Alternative splicing during processing of the pre-mRNAs produced by each transcription unit enable multiple different mRNAs to be produced from one transcription unit. The E1A, E1B, E2A, E2B, E3, and E4 transcription units are successively transcribed early in the virus# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoviridae
Adenoviruses (members of the family (biology), family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nanometer, nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of Adenovirus infection, illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a Immunodeficiency, weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genus, genera: * ''Aviadenovirus'' * ''Barthadenovirus'' * ''Ichtadenovirus'' * ''Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * ''Siadenovirus'' * ''Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexon Protein
In molecular biology, the hexon protein is a major coat protein found in adenoviruses. Hexon coat proteins are synthesised during late infection and form homo-trimers. The 240 copies of the hexon trimer that are produced are organised so that 12 lie on each of the 20 facets. The central 9 hexons in a facet are cemented together by 12 copies of polypeptide IX. The penton complex, formed by the peripentonal hexons and penton base (holding in place a fibre), lie at each of the 12 vertices. The hexon coat protein is a duplication consisting of two domains with a similar fold packed together like the nucleoplasmin subunits. Within a hexon trimer, the domains are arranged around a pseudo 6-fold axis. The domains have a beta-sandwich structure A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encapsidation
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor MRNA
Precursor or Precursors may refer to: *Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor ** The Precursor, John the Baptist Science and technology * Precursor (bird), hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of unrelated animals * Precursor (chemistry), compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound * Precursor (physics), phenomenon of wave patterns caused by the dispersion of an impulse's frequency components as it propagates through a medium * Precursor in the Course (medicine), course of a disease, the state preceding a particular stage in that course * Precursor cell (biology), a unipotent stem cell * Earthquake precursor, phenomenon that occurs before an earthquake and allegedly -though, so far, not demonstrably- can predict the earthquake * Gehrlein Precursor, a glider * LNWR Precursor Class (other), classes of passenger locomotives developed for the London and North Western Railway Fiction *Elder rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Overview For transcription to take place, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA, known as RNA polymerase, must attach to the DNA near a gene. Promoters contain specific DNA sequences such as response elements that provide a secure initial binding site for RNA polymerase and for proteins called transcription factors that recruit RNA polymerase. These transcription factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a nucleic acid double helix, double helix of two Complementary DNA, complementary DNA strand, strands. DNA is often called double helix. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and the ribosome creates the protein utilizing amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * '' Aviadenovirus'' * '' Barthadenovirus'' * '' Ichtadenovirus'' * ''Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * '' Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |